4 stages of intracranial pressure

This article provides a broad overview of the . As a result, the headache . It can be acute or idiopathic, and it can cause headaches, vision .The pattern of ICH includes a three-phase evolution; the pressure-time fluctuation is the dynamic element in the progression and decompensation of intracranial hypertension.
Elevated intracranial pressure (ICP)
Purpose of review: Intracranial pressure (ICP) can be elevated in traumatic brain injury, large artery acute ischemic stroke, intracranial hemorrhage, intracranial neoplasms, and diffuse cerebral disorders such as meningitis, encephalitis, and acute hepatic failure. Adult idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a rare condition of unknown cause, which results in raised intracranial pressure (ICP). External links. This focused review discusses; (1) different ICP technologies and how ICP .Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is an important cause of daily headaches that occur in young and middle-aged, active persons and is often .Wavelengths were longer in REM sleep than in wakefulness and stages 1 and 2 (62. 1 Young obese women are most commonly affected, although rarely it may occur in men. “Idiopathic” means the cause isn’t known, “intracranial” means in the skull, and “hypertension” means high pressure.The fuzzy or lost pattern of the choroidal vasculature in EDI-OCT images, an indication of choroidal inflammation, is useful for the diagnosis of OD swelling type VKH disease, . As a result, there has been a substantial effort to explore and . It's also called idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Although guidelines advocate for mannitol administration in such cases, the ideal usage remains a subject of debate.
Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Headache
In idiopathic intracranial hypertension, the pressure of the fluid is increased, often to very high levels. Raised intracranial pressure (rICP) syndrome is seen in various pathologies.Monro–Kellie hypothesis. Raised ICP is also known as intracranial hypertension and is defined as a sustained ICP of . A massive rise in ICP is also . Introduction to intracranial pressure. Different types of edema. With a herniation syndrome, this will show raised pressures, typically over 20 mmHg, with poor compliance.Intracranial hemorrhage encompasses four broad types of hemorrhage: epidural hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and intraparenchymal hemorrhage. IIH happens when too much cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) — the fluid around the . Focal versus global ICP elevation. It occurs when cerebrospinal .In stage 3 the intracranial pressure approaches arterial pressure.Go to: ABSTRACT.
Increased intracranial pressure from bleeding in the brain, a tumor, stroke, aneurysm, high blood pressure, brain infection, etc. In the second stage, this regulatory system is overloaded and can no longer compensate for the increase in pressure secondary to the increase in volume. ICP can also imply that there is swelling of brain, either from a medical condition such as meningitis or from a brain injury.These noninvasive methods can be broken down into four major categories: fluid dynamic, otic, ophthalmic, and electrophysiologic.
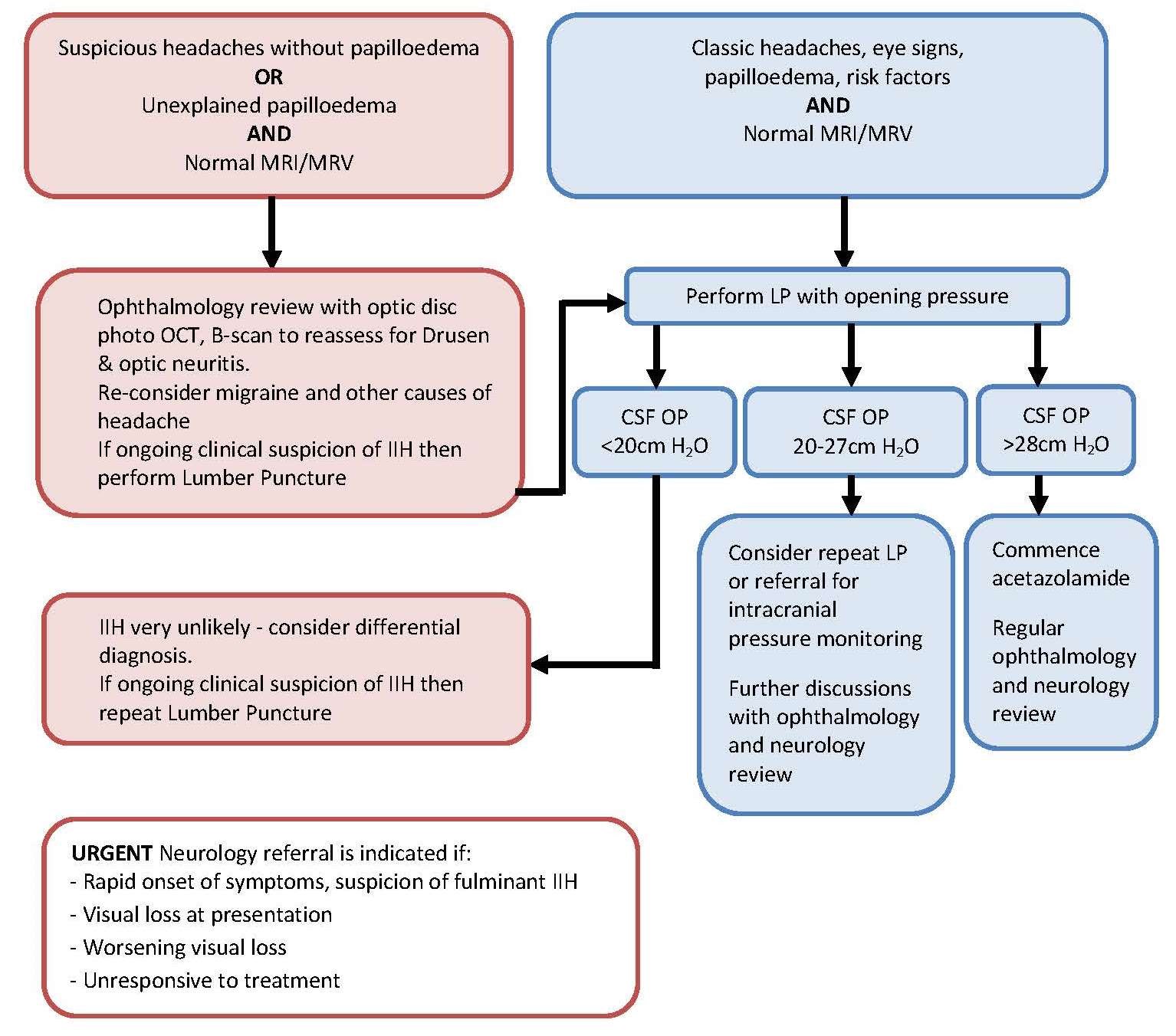
Management of Intracranial Pressure
Raised intracranial pressure: nursing observations and interventions
Intracranial hypertension exists when there is a sustained elevation in intracranial pressure (ICP) of more than 15 to 20 mm Hg.Henry Duret (1849–1921) showed that increased pressure could cause blood vessel compression, reducing cerebral blood flow, and also demonstrated that CSF absorption, vertebral ligament extensibility and venous sinus collapse would alleviate the increase in pressure in the early stages of intracranial hypertension.

On an ICP waveform, the P2 represents the . The content of the fluid is usually normal.An end-stage manifestation of elevated intracranial pressure is the Cushing's reflex, which is caused by brainstem compression, brainstem stretch or a combination of both. Treatment includes relieving the brain of the .Its osmotic diuresis property has been utilized in numerous studies to decrease intracranial pressure (ICP) in patients with cerebral injury. Several treatment guidelines exist for specific disease processes such as trauma or . In the third stage, the self .Intracranial hypertension is a spectrum of neurological disorders where cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure within the skull is .Intracranial hypertension is classified in four forms beginning with aetiology, pathogenic mechanisms and patterns of increase in intracranial pressure (ICP): .An intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring system may be warranted, usually in the form of an ICP bolt.
Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
The Cushing's reflex is the triad of hypertension, bradycardia, and irregular breathing; it suggests developing cerebral ischemia, imminent herniation, and the need to act promptly. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) refers to pressure in the brain that causes people to experience headache episodes and vision problems.Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) happens when high pressure around the brain causes symptoms like vision changes and headaches.[1][2][3] Each type of hemorrhage is different concerning etiology, findings, prognosis, and outcome. IIH is also sometimes called pseudotumor cerebri because its symptoms can mimic those of a brain tumor. Appropriate and systematic management is important for favourable patient .Management strategies aim to achieve a cerebral perfusion pressure of >60mmHg and intracranial pressure <20–25mmHg. Intracranial pressure ( ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids .
Intracranial Hypertension
What's more, brain injury may . As soon as spinal fluid is removed during the spinal tap, the pressure inside the head decreases, the venous sinuses may widen, and more blood may flow from the brain. The morphology of B-waves was also related to different sleep stages. Ramp-type B-waves were associated with REM sleep in six patients, however, were also present in sleep stage 2 in three of them. can cause a headache and other symptoms. The pressure–volume curve has four ‘zones’: (1) baseline intracranial volume with good compensatory reserve and high compliance (blue); (2) gradual depletion of compensatory reserve as intracranial volume increases (yellow); (3) poor compensatory reserve and increased risk of cerebral . Guidelines often recommend ICP monitoring with a treatment threshold of 20 mmHg.8 out of every 100,000 people are affected by IIH. Raised ICP reduces CPP and blood delivery to the brain that jeopardizes cerebral function and organismal survival in many species. Elevated ICP may complicate trauma, central nervous system (CNS) . Increased ICP has serious complications, including long-term (permanent) brain damage .
Raised Intracranial Pressure Syndrome: A Stepwise Approach
The cause may be an increase in the quantity of fluid that surrounds the brain.Acutely elevated intracranial pressure (ICP) may have devastating effects on patient mortality and neurologic outcomes, yet its initial detection remains difficult because of the variety of manifestations that it can cause disease states it is associated with.Measurement of intracranial pressure (ICP) is crucial in the management of many neurological conditions.7 per 100,000 and this has recently increased in . Volume–pressure relations. Clinical manifestations.In the first stage, the increased intracranial volume (IV) does not affect ICP since the CSF and cerebral blood are displaced in order to compensate the change in volume.Publiée : 2023/05/08
Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP): Symptoms and Treatments
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is characterized by increased pressure in the fluid surrounding the brain.Elevated intracranial pressure (ICP) is a potentially devastating complication of neurologic injury. Intracranial pressure (ICP) refers to the pressure within the skull, which is determined by the volumes of the intracranial contents; blood, brain and cerebrospinal fluid. It can happen suddenly, for example, as the result of a severe head injury, stroke or .Intracranial hypertension (IH) is a condition in which pressure builds in the fluid around the brain.
Intracranial hypertension: classification and patterns of evolution
Key considerations include: 1) Bolus administration versus continuous infusion, .
Increased intracranial pressure: What to know
While the initial cause for the onset of ICP may vary greatly from patient to patient, the anatomical factors that play a role in . Intracranial hypertension (IH) is a build-up of pressure around the brain. Stage 4 is characterized by the occurrence of a herniation and the .Treatment focuses on lowering increased intracranial pressure around the brain. The person decompensates very quickly.
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
Symptoms mimic those of a brain tumor.

Causes of ICP elevation. Each category is discussed in . Overnight sleep monitoring is considered the “gold standard” in . What is idiopathic intracranial hypertension? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is increased pressure around your brain. Cellular hypoxia and hypercapnia become worse.

Ultrasound evaluation for ICP elevation. However, due to the invasiveness, high cost, and required expertise of available ICP monitoring techniques, many patients who could benefit from ICP monitoring do not receive it.
RAISED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Intracranial Hypertension
We are talking about big boluses, 15-20mg morphine or 150-200μcg fentanyl. The incidence in the UK general population is approximately 4. The evolution of ICH is made by exceeding . An accumulation of pressure above the normal standard within the skull is denoted as elevated intracranial pressure (ICP), a severe condition that requires immediate remediation. Invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring is a standard practice in severe brain injury cases, where it allows to derive cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP); ICP-tracing can also provide additional information about intracranial dynamics, forecast episodes of intracranial hypertension and set targets for a tailored therapy to . Knowledge of the relation .Intracranial pressure (ICP) is a complex brain modality that determines cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP), which is the difference between arterial blood pressure (ABP), and ICP.The intracranial pressure (ICP) represents the pressure exerted by the essentially incompressible components (brain tissue and interstitial fluids, blood and .Pressure–volume curve for ICP. IIH is most prevalent in obese women of childbearing age. The increased intracranial pressure can cause swelling of the optic nerve and result in .When the pressure around your brain is increased, the condition is referred to as increased intracranial pressure or ICP.