Accusative vs dative case

In sentences that have just the subject and a single object, the nouns take the Accusative Case, unless the Prepositions or the verb requires the use of Nominative, Dative or Genitive.
Dative & Accusative Objects
Dative Case: Explanation and Examples
German Dative Case (Complete Guide for Beginners A1
In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories.In any language, a case is a way to show how a word integrates into a sentence. Mann), their article (der, die das, etc.
German Prepositions: Accusative, Genitive, Dative
We’ll demystify the four cases with German preposition charts and other essential tools.German Adjective Endings: Nominative, Accusative, and Dative Cases. dative or genitive objects). Here’s a list of frequently used German verbs that always take the dative case:-. Modified 1 month .Let’s understand the nominative and accusative case with these examples: –.Accusative Case: Unraveling the Basics. Contrary to the dative case, the accusative case indicates the direct object. (I’m going by car. What is being had? A table. This terminology is correct as far as it goes, but in the case of the dative it may suggest an incomplete definition of the roles the dative object . The accusative case, which deals with the direct object.
Manquant :
dative case
The accusative case can also be used to indicate motion towards something. The recipient of the direct object is the .These include bis, durch, für, gegen, ohne, um, after which the accusative case is always used, and an, auf, hinter, in, neben, über, unter, vor, zwischen which can govern either . Note:If the ships were staying in the harbor, the phrase in the harbor would be in the dative case (see below). There are four German cases: nominative, accusative, dative and genitive. Finish: 15 cases. It answers the question “whom” or “what. „Er singt ein Liebeslied.by Morgan Smitherman in Grammar on June 23, 2023. Michelle Baumgartner Updated October 23, 2023 18 min read.German has only 4 cases: Nominative (Nominativ) Accusative (Akkusativ) Dative (Dativ) Genitive (Genitiv) Other languages have a way more! Hungarian: 18 cases.the accusative case. So take it positive and appreciate that you only have to learn four cases. The Dative Case (Der Dativ) The dative case describes the indirect object of a sentence in German and English and answers the question, “wem?” (whom), or “was?” (what).This dative object is usually the only object in the sentence. Next, auf is a preposition of locality - These normally rule the accusative, if a motion is involved, and the dative, if a static location is denoted to. accusatival (əˌkjuːzəˈtaɪvəl ) adjective. By correctly identifying the case required in each context, you can communicate effectively and precisely. the dative case. German dative prepositions are . to resemble / to look like. There is a simple German sentencing-building principle to keep in mind: after you’ve named your subject (nominative case) and paired a verb with it, the next ‘slot’ to fill in defaults to being in the accusative case. The plural, feminine ( die) and neuter ( das) genders don't change in the accusative.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
German Preposition Charts: Understanding German Cases
The chart below outlines a complete list of each type.Accusative Case (ऍक्युझेटीव्ह केस) किंवा Dative Case (डेटिव्ह केस) म्हणजे .So, your first action would be: Look up the preposition in the dictionary and check which case(s) it might rule.
German cases guide: Nominative, accusative, dative & genitive
The Accusative Case Is the Objective Case In English, we use the term objective case for the accusative case and the dative case.The photographer is taking pictures. H&S Produktion / Getty Images. Nominative Case. We will explain what German cases are, give examples of each, and provide guidance to help you to identify which German case to use and when.There are 4 cases in German: nominative, accusative, dative and genitive.
German Two-Way Prepositions
auf, as in your example, you will find: Präposition mit Dativ und Akkusativ.Dative vs accusative.

New learners often confuse the accusative and dative cases in German.
Accusative or dative exercises
Literally: I am driving with the car.), adjectives (e. Exercise 2 PREMIUM.Here, we will briefly introduce the German cases: the nominative case, the accusative case, the dative case, and the genitive case. Further making these prepositions easier to learn by rote: only the masculine gender ( der) changes in the accusative case. to turn someone down. The nominative case is the case used for subjects completing an action.
The German case system
Master the German Accusative Case
Find the verb = gave Step 2.
German/Grammar/Prepositions with accusative and dative
The accusative case is used to mark accusative objects (vs. „Ich habe ein Eis.English language evolution has led to a shift from distinct accusative and dative cases to a combined oblique or objective case. Misusing them frequently can cause serious confusion, and it sounds poor. Because we don’t really distinguish in English between the direct and indirect object, knowing when to choose the accusative and when the dative can be . Dative vs Accusative. Example: Ich fahre mit dem Auto.
Accusative and dative in German explained
In simpler terms, accusative is . To find the direct object in the accusative case, ask “What?” after the verb.Indirect object in the dative case: you; Accusative Case vs.Two-way prepositions require nouns either in the accusative case or in the dative case. In order to be able to write accurately in German, it’s important to recognise and understand the four different cases: nominative, accusative, dative and . by Brita Corzilius. This change streamlines usage, as the objective case now encompasses both direct and indirect objects and is used with prepositions. Other parts of speech, including secondary or predicate direct objects, will also influence a sentence’s construction. schön) and the noun substitutes (pronouns) are adjusted to the case. Accusative and .Meaning of nominative, genitive, dative and accusativegerman. The accusative case is used for nouns that are the recipients of the action the subject completes. Stay tuned to learn about: The nominative case, which focuses on the subject of a sentence. The noun or pronoun which is either the direct or indirect object of a verb or the object of a preposition is called the objective or accusative or dative case.Accusative or dative.
Accusative or dative
The most important thing and the key to handling the Dative case - just like the Accusative - is: The Dative is used. This overview shows how most nouns are declined in German. an accusative .The nominative case is used for subjects, while the accusative case is employed for direct objects and objects of prepositions.A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and numerals) that corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. Click on one of the links below to learn more noun declension in German grammar. In the sentence Ich sehe den Hund (I see the dog), ' den . How do you know which German prepositions go with what case? How are you supposed to know which to . The genitive case, which shows possession .
German Prepositions That Take the Accusative Case
Asked 5 years ago. I will take care of this issue. Harry ate ice cream. The Viking ships came into the harbor. In traditional terminology the two objects are known as indirect and direct, respectively. As a result, the case system in modern English is simpler and more . The group of words ‘ ate ice cream’ is the Predicate.German nouns must be declined to reflect the case that they are in; nominative, accusative, dative or genitive. There are exercises at the end of each lesson so you can practise what you .
70 Basic Dative Verbs and Accusative Verbs in German
Collins English Dictionary.Accusative Case ( Akkusativ ): The accusative case shows who or what is the direct object of the action.Master the nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive cases in German. The correct form of articles and pronouns must match the case used in the sentence.The adjective endings - en, - e, and - es correspond to the articles den , die, and das respectively (masc.
ACCUSATIVE definition and meaning
: of, relating to, or being a grammatical case (see case entry 1 sense 3a) that marks the direct object of a verb or the object of some prepositions. For instance, in English, one . (grammar) Applied to the case (as the fourth case of Latin, Lithuanian and Greek nouns) which expresses the immediate object on which the action or influence of a transitive verb has its limited influence. “Dative case” will be used for the indirect object. Most German sentences include at least one case, but .
The German Cases Explained In 5 Steps
• for the direct object of a sentence: who or what is being ? Ich habe einen Tisch. Ask For whom? (i. If you are learning German, one of the important early lessons is .German cases are four: the nominative case (subject of the sentence); the accusative case (the direct object); the dative case (the indirect object), and the genitive case . In sentence 1, The noun Harry is the Subject of the verb ‘ ate’. IF both dative AND accusative pronouns are being used, however, the standard slot order changes to nominative + accusative + dative. Once you notice the parallel and the agreement of the letters n , e , s with den , die , das, it makes the process a little clearer. It’s kind of like looking at a schematic of a building and figuring out how the floors, stairs, rooms and hallways fit together.Here are the 2 key points to remember regarding the dative case & word order in German: The German case ‘slots’ are in this standard order: nominative + dative + accusative.

The horse kicked the boy. to cancel on somebody /. Ask What? = a letter Step 3.Dative and Accusative Together. Examples of “dative case”: He gave the .Certain prepositions can require different cases depending on their meaning in the sentence, and the subgroup we're dealing with now are those which require either . There are 10 two-way prepositions: an, auf, hinter, in, neben, entlang, über, unter, vor, zwischen. The auditor is auditing the files. The Dative and Instrumental . In German, determining whether to use the accusative or dative case depends on the function of a noun in a sentence. In the instance where a person is the goal . Published on December 31, 2020 / Updated on November 7, 2022. Cases are not something strange to English, pronouns for example use a certain kind of cases, for example we say “ he speaks”, and “give him ” and not “give he”, ., Who is the recipient?) = the postman Therefore, the direct object is a letter. On the other hand, the dative case is utilized for indirect objects and objects of prepositions.Accusative is the proper word to use when referring to the direct object of a sentence, whereas dative is used to indicate the indirect object. Luckily, you'll need only to commit five accusative prepositions to memory. Copyright © HarperCollins Publishers. It is the answer to the question, “Who ate ice cream?”. Declension of nouns, article, adjectives . Examples: I have met Alice. More commonly, the English dative appears in combination with an accusative object.Here are the 2 key points to remember regarding the dative case & word order in German: The German case ‘slots’ are in this standard order: nominative + dative + . The Viking ships are moving towards the harbor, so into the harbor is in the accusative case. The dative case, which highlights the indirect object. either the accusative or dative case (also called two-way prepositions) the genitive case.
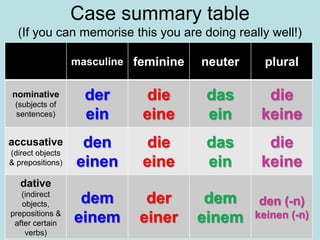
Accusative is used for direct objects, while dative is used for indirect objects.