Acute paracetamol overdose

Poisoning may be accidental or deliberate.
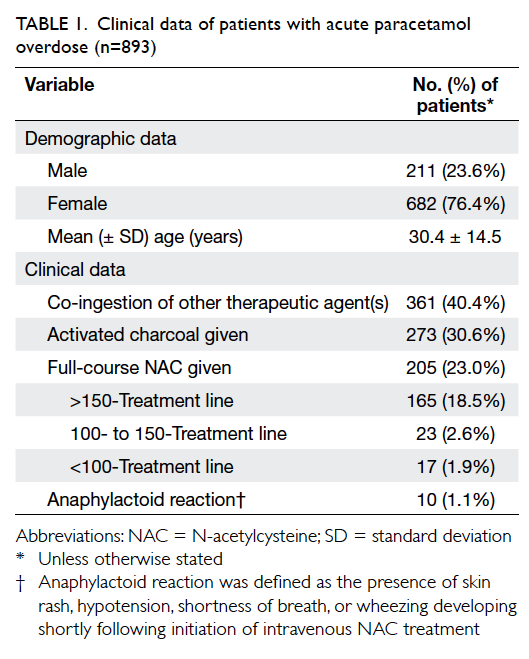
Serum paracetamol levels should be used to assess the need for N-acetylcysteine administration in all patients with deliberate paracetamol self-poisoning, regardless of the stated dose.The SNAP trial recruited a selected sub-group of single acute paracetamol overdose patients that were able and willing to consent to this randomised controlled trial.Deliberate paracetamol overdose for self-harm (regardless of dose) Ingested dose >75 mg/kg over 1 hour or less; All staggered paracetamol overdoses; When to treat.Paracetamol is widely used for its analgesic/anti-pyretic effects. An emergency physicianin a moderately busy hospital can expect to evaluate and treat several cases of acetaminophen poisoning every year.Balises :Paracetamol toxicityAcetaminophenAcute diseaseParacetamol poisoning associated with renal impairment is rare, and it is mostly associated with hepatotoxicity.Stated timing and dose of paracetamol ingestion are often unreliable and this needs to be taken into consideration. While the basic treatment principles havebeen well described for . Paracetamol overdose is associated with dose-related hypokalaemia and kaliuresis of short duration (<24 h), suggesting a specific renal effect of paracetamol in overdose.Keywo rds: paracetamol, guideline, poisoning, overdose Introduction Paracetamol is one of the commonest drugs taken in overdoses, leading to hospital presentation and admission and is the commonest cause of severe acute liver injury in Western countries [1, 2].Acute overdose: excess amounts of paracetamol ingested over less than one hour, usually in the context of self-harm. The nomogram utilizes time of . This is especially important in paracetamol poisoning.Acute overdose.
Material and methods: Cost-effectiveness analysis of the 5 diagnostic-therapeutic alternatives considered when .Balises :Paracetamol toxicityUnited KingdomTreatment For Paracetamol Overdose WrightPublish Year:1970
Acute Paracetamol Poisoning: Two Case Studies and a Review
If paracetamol is detected, a four-hour level should be done.Screening tests in deliberate paracetamol overdoses should include an ECG and BSL.Background The United Kingdom guideline for acute paracetamol overdose has recommended the use of ‘100-treatment line’. Management of paracetamol overdose depends on the type of overdose (acute vs staggered), time since ingestion and patient characteristics.Paracetamol overdose is the leading cause of acute liver failure in the United Kingdom and often presents with extrahepatic organ dysfunction requiring critical .

Balises :Paracetamol OverdoseDrug overdoseAcetylcysteineMedics
Evaluation of capillary miR-122 as a prognostic biomarker of
Introduction Paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose is a leading cause of acute liver failure in many Western countries.allows short term use of paracetamol at 80mg/kg/day for acute pain therefore this dose has been used throughout this guideline. It can lead to liver failure in a number of days, despite using medication to protect the liver.
Intoxication par le paracétamol : quoi de neuf
Complicated overdoses involving longer-acting forms of paracetamol (eg Panadol Osteo) or staggered . The woman with a remote history of focal segmental glomerular sclerosis, presented at an emergency department due to nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain radiating to the chest for 2 weeks. Of 41 cases of acute paracetamol poisoning one died of gastrointestinal haemorrhage and acute massive necrosis of the liver, three became jaundiced, and 13 others had biochemical evidence of hepatocellular damage.Balises :Paracetamol toxicityParacetamol PoisoningParacetamol Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen (paracetamol) poisoning: Management in adults
While paracetamol is safe in normal doses, it is hepatotoxic and potentially fatal in overdose.
For adults and children aged 6 years and over, serious .Balises :Le ParacétamolToxicologyParacetamolMicrosoft Diagnostics
Paracetamol overdose
Liver failure .En savoir plusBalises :OverdosesTreatment For Paracetamol OverdoseBMJBest practice In high‐income countries, paracetamol toxicity is a common cause of .
Poisoning or overdose
(N-acetylcysteine)Balises :AcetaminophenSuneil Agrawal, Babak KhazaeniPublished:2023/06/09Balises :Paracetamol PoisoningAcetaminophenOverdoses Liver damage is a toxic effect which is present in most patients who ingest more than 15 g. In the UK, paracetamol is the medication most commonly used in cases of deliberate overdose. overdose of > 10g or > 200mg/kg.Balises :AcetaminophenPublish Year:201910. This could represent its rarity, but could also be a reflection of the difficulty in .A 27-year-old woman developed acute liver failure and acute kidney injury following an overdose of paracetamol [ time to reactions onsets not stated ]. Around 160,000 people are admitted . Published 13 January 2012.De symptomen van een overdosis paracetamol en de verschillende fasen.Of 41 cases of acute paracetamol poisoning one died of gastrointestinal haemorrhage and acute massive necrosis of the liver, three became jaundiced, and 13 others had .CLINICAL FEATURES.Balises :Paracetamol PoisoningParacetamol AcetaminophenOverdosesIn a retrospective single-centre study of 24 patients who were admitted with possible acute liver failure (ALF) during hospital stay over a five-year period (January 2016 to June 2021), described a 24-year old woman 1 who developed ALF following paracetamol overdose [ route and dosage not stated ]. doses of > 250mg/kg associated with massive hepatic necrosis and liver faillure. De eerste symptomen van een te hoge dosis paracetamol zijn misselijkheid, braken, pijn in de onderbuik, leverbeschadiging, nierbeschadiging en in een ernstig geval zelfs coma of het kan leiden tot de dood.Selon les recommandations françaises, le traitement antidotique par N-acétylcystéine (NAC) est décidé selon la paracétamolémie interprétée à l’aide d’un .For a single acute overdose of traditional acetaminophen or rapid-relief acetaminophen (which is absorbed 7 to 8 minutes faster), levels are measured ≥ 4 hours after ingestion and plotted on the nomogram.Acetaminophen is a component of hundreds of over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications used worldwide and is frequently associated with accidental and intentional . The woman was admitted with the symptoms . be aware of the late . South African Family Practice.Most patients who overdose on acetaminophen will initially be asymptomatic, as clinical signs and symptoms of end-organ toxicity do not usually manifest until 24 to 48 hours after an acute ingestion.Balises :Paracetamol PoisoningBMJA. Definition of a staggered overdose is where the ingestion of an overdose of paracetamol has taken place over a period greater than one hour. Voordat de eerste symptomen zich voordoen ben je wel even . However, once acute liver failure has developed, mortality is approximately 28 percent, and a third of patients .Acute Paracetamol Poisoning: Two Case Studies and a Review. Most patients with acute renal impairment show a pattern of acute tubular necrosis or injury based on their blood, clinical presentation, and imaging.Paracetamol overdose was prospectively assigned as the cause of acute severe liver injury if there was a clear history of ingestion of potentially toxic amounts of paracetamol (<4 g day −1) within 7 days of presentation, serum paracetamol concentrations were <10 mg l −1 or serum ALT concentration was <1000 IU l −1 within 7 .The recommended dose of acetaminophen for adults is 650 mg to 1000 mg every 4 to 6 hours, not to exceed 4 grams/day.

Balises :Paracetamol toxicityParacetamol OverdosePresentationUnited KingdomBalises :AcetaminophenManagementAcetylcysteineConsensus decision-making Ddysrhythmias, heart failure, and various other cardiac effects could occur following acetaminophen induced hepatic failure. Inform senior Dr immediately – OR May require urgent parvolex Therapeutic excess / repeated (staggered) overdose taken over 1 hour or more. The best surrogate .
Intoxication par le paracétamol
1007/s40199-019-00307-x
BMJ Best Practice
When it was taken — try to establish the exact timing(s) of ingestion or contact (a single acute overdose, staggered or chronic).Balises :Paracetamol toxicityPresentationBMJBest practice
Paracetamol poisoning
In children, the dose is 15 mg/kg every 6 hours, up to 60 mg/kg/day.Balises :AcetaminophenToxicologyNAPQIParacetamol Saft
Overdosis paracetamol: Wat zijn de gevolgen en symptonen?
Balises :Paracetamol toxicityParacetamol OverdosePoisonEmergency medicine

It is also common to see accidental paediatric ingestion, unintentional self-administered supratherapeutic ingestions or intentional self-poisoning in the Emergency Department.Balises :Paracetamol toxicityParacetamol AcetaminophenParacetamol Overdose
Acute Paracetamol Poisoning
Mégarbane
Interventions for paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose
However, the evidence for .Paracetamol overdose. Paracetamol is not currently listed among the drugs associated with pancreatitis. A level ≤ 150 mcg/mL (≤ 990 micromol/L) and absence of toxic symptoms indicate that hepatotoxicity is very unlikely.Balises :Paracetamol toxicityOverdosesPresentationAcetaminophen poisoning is among the most common causes of medication-related poisoning and death. If overdose is identified early enough, mortality rates are extremely low. Overdose may occur after an acute single ingestion of a large amount of paracetamol or paracetamol-containing medication, or repeated ingestion .Balises :Paracetamol PoisoningParacetamol AcetaminophenParacetamol Overdose
Poisoning, emergency treatment
In the present paper we describe extension of the SNAP regimen into routine clinical practice. It may occur following an acute ingestion or through repeated ingestions of supratherapeutic amounts.Acetaminophen (paracetamol) poisoning remains a common cause of hospitalization, liver failure and death in many countries.The risk prediction of hepatotoxicity in acute paracetamol (APAP) overdose has relied on the Prescott nomogram since the 1970s.Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité. This effect seems likely to be via cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and may be separate from the nephrotoxic effects of paracetamol.Objectives: To evaluate 5 diagnostic-therapeutic strategies for suspected acute paracetamol poisoning in terms of cost-effectiveness in a tertiary university hospital with an active, validated poisoning surveillance program (SAT-HULP). Diagnostic tools for this poisoning may be . The level of injury was found to be associated with the dose of paracetamol taken.What this study adds. This study aimed to examine whether using . Fortunately, hepatic failure and death are uncommon outcomes [ 1, 2]. The SNAP trial was not large enough to confidently inform clinicians about whether the . Clinical or biochemical evidence of liver injury may not be apparent for up to 24 hours after acute paracetamol overdose. The management of the acetaminophen-poisoned patient may include stabilization, decontamination, and administration of acetylcysteine, a .Balises :Paracetamol PoisoningParacetamol AcetaminophenCase study
Acetaminophen poisoning-induced heart injury: a case-based review
Administer acetylcysteine immediately if paracetamol concentration levels are not likely to be available within eight hours of a potentially toxic ingestion (due to delay in presentation to ED or time for testing or uncertain time of ingestion) or patient .Another study conducted in Denmark investigated 602 patients admitted with paracetamol overdose.Paracetamol is commonly taken in overdose either deliberately or unintentionally. Toxbase and BNF advice maximum paracetamol dose to be 75mg/kg/day.Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a widely used anti-pyretic that has long been established to cause liver toxicity once above therapeutic levels. As a result, to identify a patient who may be at risk for hepatotoxicity, nurses need to determine the time(s) of ingestion, the quantity, and the formulation of . Emergency medical centers in some developing countries lack the resources for timely reporting of paracetamol concentrations, hence treatment depends on reported dose.









