Acute tubular necrosis clinical indicators
92, severe sepsis.
Acute Kidney Injury: A Guide to Diagnosis and Management
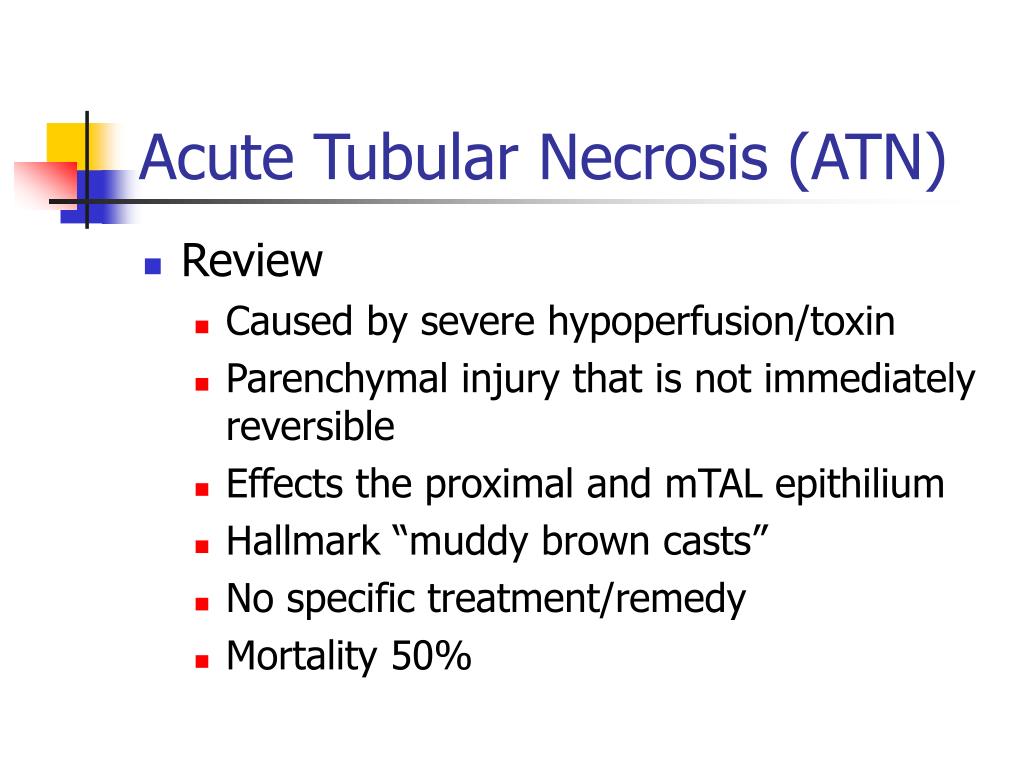
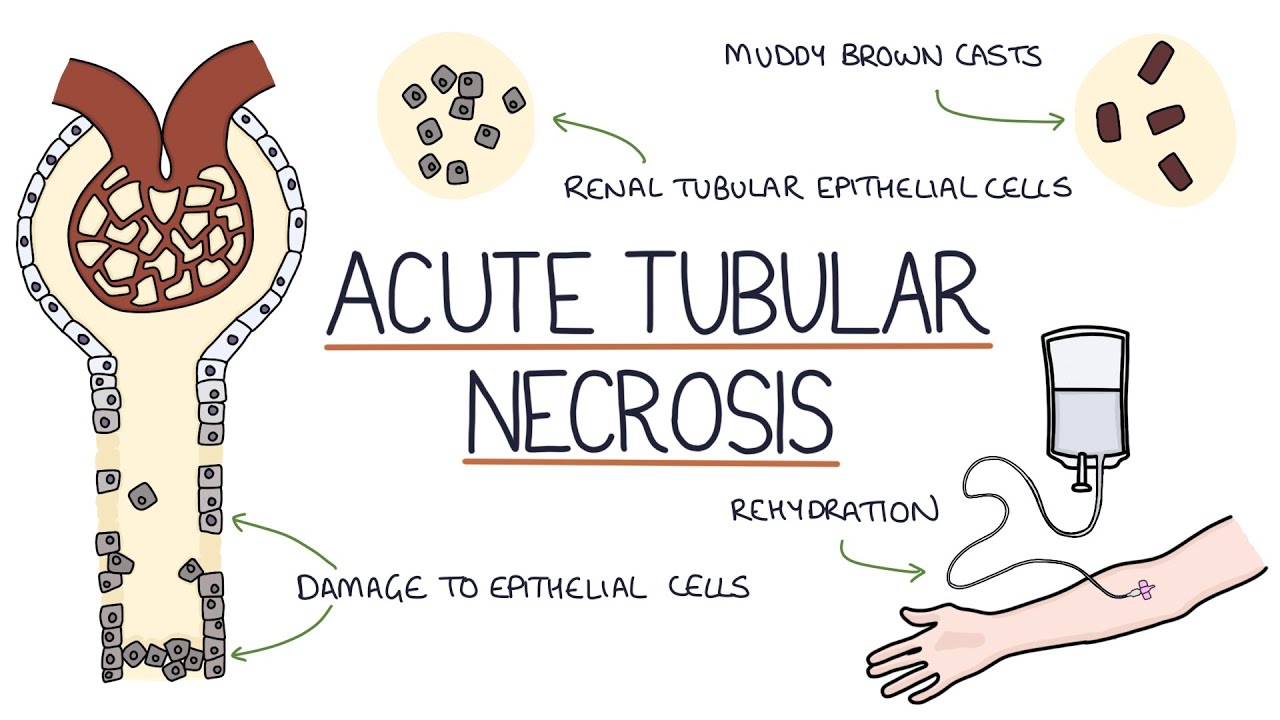
1 (Nephropathy induced by other drugs, medicaments, and biological substances) as well as T50.Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is a subset of ATI ( Kidney Int Rep 2020;5:1993 ) Clinically similar to acute interstitial nephritis (AIN); histopathology needed .Acute tubular necrosis History of receiving nephrotoxic medications (including over-the-counter, illicit, and herbal), hypotension, trauma or myalgias suggesting rhabdomyolysis, recent exposure to . The BUN-to-cre-atinine ratio can exceed 20:1 in conditions that promote reabsorption of urea, such as large volume loss, which suggests pre-renal AKI. They require close monitoring of urine output and renal function.Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is kidney injury characterized by acute tubular cell injury and dysfunction. Trouble waking up/drowsiness. Medullary ischemia results from hypoxic injury to the thick limb of the loop of Henle. Electron microscopy showed mitochondrial enlargement, depletion, and dysmorphic changes.Renal biopsy revealed toxic acute tubular necrosis, with distinctive proximal tubular eosinophilic inclusions representing giant mitochondria visible by light microscopy.
Finding novel . The history commonly reveals risk . The tubules are tiny ducts in the .0, whereas AKI with ATN associated with contrast-induced nephropathy codes to N17.A Light microscopy of the cortical renal parenchyma, periodic acid-Schiff staining shows acute tubular injury with loss of brush border and simplification of tubular cells with presence of red blood cell casts (PAS ×20; scale bar 100 μm). It is also often used to evaluate renal transplants when . Various drugs have been linked to kidney injury including phenylbutazone, ibuprofen, and mefenamic acid. Clinical follow-up after tenofovir discontinuation was available for 11 of 13 patients (mean .Read chapter 28-7 of Symptom to Diagnosis: An Evidence-Based Guide, 4e online now, exclusively on AccessMedicine.Acute tubular necrosis is very slow to recover and can take weeks to months for complete recovery of renal function. Acute kidney injury (AKI) due to ischemic acute tubular necrosis (ATN) typically lasts 7 to 21 days [ 1 ], with most patients returning to or near their previous baseline level of kidney function as the necrotic tubular cells regenerate. The absence of early indicators of renal failure is a significant contributor to this. Histopathological findings include: Ischemic Acute Tubular Necrosis.Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is common in hospitalized patients, particularly in the intensive care unit. Nuclear medicine. Subclinical AKI. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) has been shown to be a good early biomarker of ischemic ATN. They could potentially be able to differentiate between prerenal azotemia and acute tubular injury. • Complete Blood Count: Used to detect infection, chronic anemia, blood loss, or thrombotic microan-giopathy. Any and all medications need to be renally dosed .

Ischemia and exposure to nephrotoxins are the primary causes of ATN. Possible preventive and therapeutic measures for ischemic ATN will be reviewed here. Rate of creatinine rise. Ischemic damage .
Manquant :
What tests are used to .Common Clinical Indicators For Acute Tubular NecrosisAcute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
In clinical medicine, acute kidney damage (AKI) is a recurring problem. Prerenal Azotemia.ATN – Acute kidney injury with tubular necrosis is assigned to N17.8X5A (adverse effect of diagnostic agents, initial en-counter). Renal scintigraphy can help differentiate acute tubular necrosis from other causes of renal failure such as renal cortical necrosis. 19,20 Lastly, postrenal causes are associated with obstructive . inflammation has been proposed to be a . The two most common etiologies of Acute kidney injury are prerenal azotemia, caused by reversible renal hypoperfusion, and acute tubular . The condition is asymptomatic unless it causes renal failure. Early: Changes range from swelling of the cell to focal tubular .This scheme enables the diagnosis of acute tubular injury to be categorized into two potentially simple ideas: first, evidence of injured cells derived from non-invasive biomarkers, and second . Urine osmolality (in mOsm/kg or mmol/kg) < 450 (usually 500. This state can be caused by the increase in the use of drugs, chemical toxins, and microbial agents .Underlying sepsis is an independent risk factor for acute tubular necrosis, even in the absence of hemodynamic compromise.Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is kidney injury Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) characterized by acute tubular cell injury and dysfunction.Acute tubular necrosis is most common in hospitalized patients and is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Data Sources: MEDLINE search for all clinical studies of . Despite substantial therapeutic advancements, AKI-related mortality and morbidity continue to be quite high.0, urinary tract infection.Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is a kidney disorder involving damage to the tubule cells of the kidneys, which can lead to acute kidney failure. The tubules are tiny ducts in the kidneys that help filter the blood when it passes through the kidneys.AKI due to tubular damage is termed acute tubular necrosis (ATN) and accounts for approximately 85% of intrinsic AKI.
Manquant :
tubular necrosisPathology Outlines
2 micromol/L) Variable and fluctuates. It may not normalize at all sometimes.Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) results in AKI from a number of processes. In some AKI cases, kidney damage may develop, but clinical manifestations and kidney dysfunction may not be present, and it is called subclinical AKI [].
Manquant :
clinical indicatorsAcute tubular necrosis Information
The two major causes of AKI that occur in the hospital are prerenal disease and acute tubular necrosis (ATN). Acute tubular necrosis is only one ofmany causes of such acute renal failure (Table 1) and, in fact, even this entity is heterogenous in etiology and pathophysiology. Another important thing to consider for these patients is to avoid any further insult to the kidneys, such as nephrotoxic drugs. The diagnosis is suspected when azotemia develops after a hypotensive . Acute Tubular Necrosis. Common causes .are hallmark indicators of kidney injury.81, acute respiratory failure.Swelling and fluid retention.Auteur : Muhammad O.Fig 1 Acute tubular necrosis may be manifest only by regenerating flattened tubular epithelium without frank necrosis of individual tubular cells, as shown in some tubules to . Common causes are hypotension or sepsis that . This coding reflects a patient with an SOI and ROM of 4, which shows she was very sick.In acute tubular necrosis, the kidneys usually have a normal appearance on ultrasound, but may be enlarged and increased echogenicity 5. Together, they account for approximately 65 to 75 .3 mg/dl from baseline in 48 hours or less.If the clinical scenario doesn't contradict it, all patients with acute renal dysfunction should receive a fluid challenge.Acute kidney injury (AKI) describes a sudden loss of kidney function that is determined on the basis of increased serum creatinine levels (a marker of kidney . Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) refers to acute kidney injury as a result of severe tubular damage.5 mg/dL/day (26. Increased Cr >1.For instance, acute tubular necrosis, acute interstitial nephritis, glomerulonephritis, and intratubular obstruction are just a few of the disorders that are associated with intrinsic renal AKI due to the presence of renal ischemia, sepsis, or nephrotoxins.Acute tubular necrosis observed in the kidney is one such example.Common causes of acute tubular necrosis include the following: Renal hypoperfusion, most often caused by hypotension or sepsis (ischemic ATN; most common, especially in patients in an intensive care unit) Nephrotoxins.The most common intrinsic cause of acute kidney injury is acute tubular necrosis.
Major surgery (often due to multiple factors) Other causes of ATN include.B Hematoxylin and eosin staining demonstrates erythrocyte casts in tubular lumen and in Bowman’s space .<0. Nausea and vomiting. This is more common in . [22] Similarly, alcohol consumption has been studied to lead to hepatic inflammation, necrosis, and steatosis.
Acute Kidney Injury (Nursing) Article
Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN) Clinical Presentation
Despite substantial therapeutic advancements, AKI-related mortality and morbidity .
Acute Kidney Injury Fact Sheet
Over the past four decades, the mortality rate from . Test* Acute Tubular Necrosis.
Acute kidney injury
The definition of acute kidney injury (AKI), despite improvements in criteria, continues to be based on the level of serum creatinine and urinary output that do not specifically indicate tubular function or injury, or glomerular function or injury that is not significant enough to warrant acute hospitalization of the patient.Therefore, we present the case of a 62-year-old female patient with essential thrombocythemia who experienced rapid renal dysfunction after her anagrelide dosage .Various novel serum and urinary biomarkers are showing potential as useful indicators for the diagnosis, classification, and prognosis of AKI. The tubular pressure builds up, and glomerular filtration is inhibited.
Diagnosis and Tests. Hanif, Atul Bali, Kamleshun Ramphul
Clinical Indicators for Acute Kidney Injury
Feeling sluggish.Many diseases are associated with acute loss· of glomerular and tubular function resulting in abnormalities of fluid and electrolyte balance.5, acute kidney failure with lesion of tubular necrosis. Common causes are hypotension or sepsis that causes renal hypoperfusion and nephrotoxic medications.Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité. Acute tubular necrosis is most common in .Acute tubular necrosis (ATN): An acute kidney injury due to an endogenous (tumor lysis syndrome, rhabdomyolysis, severe sepsis, hemolysis) or exogenous toxin (ethylene glycol, aminoglycoside, radiology contrast, certain chemotherapy), is known to cause ATN, or renal ischemia.
Acute Tubular Necrosis: Pathophysiology and Management
Increase of Cr >0.In this Review, we describe the weaknesses of isolated SCr-based diagnoses, the clinical and molecular subtyping of acute tubular injury, and the role of . Over the past four decades, the mortality rate from ATN has remained at 50% to 80%.