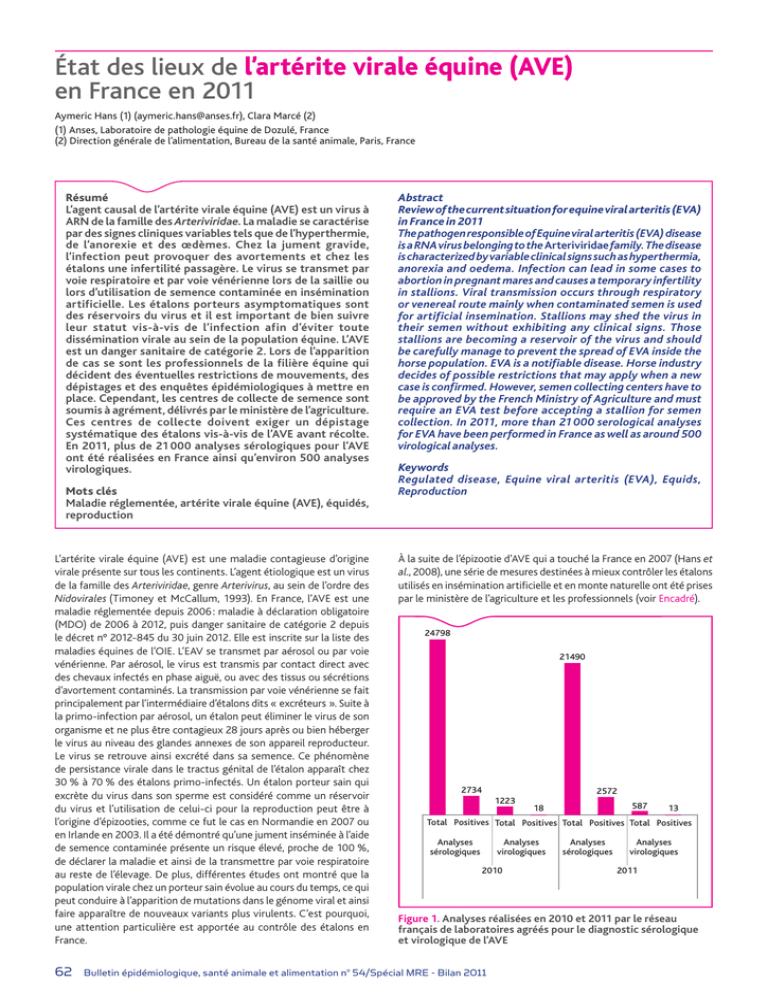
Adaptation vs habituation

Explore the difference between sensory adaptation and habituation with examples. habituation features.Hey guys, I’m having a little trouble distinguishing between habituation and sensory adaptation.As I understand it, adaptation refers to a decreased response of sensory receptors to a given stimulus intensity, and this is mostly a peripheral process.Habituation relates to how you repond to a stimulus, and how over time you will stop responding to a stimulus because you're used to it not being a threat or requiring a response. Traditionally, habituation has been distinguished from sensory adaptation and motor fatigue by the process of dishabituation; however this distinction can also be made .Our sensory system adjusts its function driven by both shorter-term (e.Habituation is very similar to sensory adaptation. Habituation in Relationships. How Habituation Affects Your Life. Basically, sensory adaptation involves physiological adaptation, while habituation involves psychological adaptation. Adaptation occurs as one adjusts to changes in their environment, new information, or experiences. When first exposed to a stimulus, such as a sound, the stimulus will get our attention and evoke a response (a ‘conditioned stimulus‘). Essentially, it’s a process of getting used to stimuli that are harmless and unchanging without the need for cognitive effort.Non associative learning. I came up with an example, but I’m not sure if it’s correct. Habituation happens when one’s emotional reaction or response to a certain stimulus is reduced due to frequent or repeated exposure.Sight and hearing adaptation experiments can rely simply on light and tones, while chemical substances cannot as easily be directed to the olfactory epithelium.Habituation, die Gewöhnung an Bedingungen, speziell die Gewöhnung an wiederkehrende sensorische Reize im Unterschied zu einer Akkomodation (z.
Non associative learning (video)
In psychology, the process of becoming accustomed to an internal or external stimulus, such as a noxious smell or loud noise. There are two forms of adult neuroplasticity associated with the vestibular system: vestibular adaptation and vestibular compensation. 3, 10 This change is thought to be due to long-term changes within the nervous system, and there is clinical evidence indicating that the . Barry, Seema Bhatnagar, David F.,, To maximize the effect of these exercises, optokinetic and postural training are often performed simultaneously over the treatment course. The terms neural adaptation and habituation are often confused for one another. Lack of habituation and neural plasticity can lead to sensory overload and fatigue.Both habituation and neural plasticity play a role in sensory adaptation and fatigue, as they affect the brain’s sensitivity to stimuli. Die Habituation ist kurzfristig und sie kann durch interferierende Reize und Prozesse .Vestibular rehabilitation exercise are divided into three categories: adaptation, habituation, and substitution.
With desensitization, what I am understanding is that it is .
Adaptation sensorielle vs habitude : r/Mcat
The therapist must .Definition of Habituation. Motor fatigue tends to be a more pressing problem than sensory adaptation in most habituation experiments.
As nouns the difference between adaptation and habituation is that adaptation is (label) the quality of being adapted; adaption; adjustment . During habituation, one has some conscious control over whether one notices . The latter gives an evolutionary advantage as . Habituation is a behavioral phenomenon while neural adaptation is a physiological phenomenon, although the two are not entirely separate. Various senses—including hearing, touch, smell, proprioception, and sight—can adapt in response to .
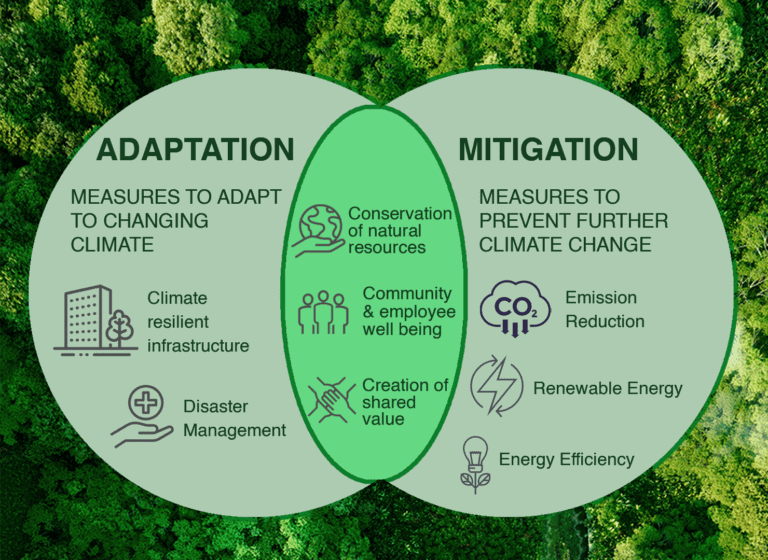
Habituation implies a higher more central change in the stimulus-response circuitry that is more like what we think of as learning.Experimentally, habituation can be distinguished from sensory adaptation or motor fatigue by the demonstration of dishabituation or by demonstrating stimulus specificity . Transcranial magnetic stimulation. During habituation, we have some conscious control over whether we notice something to which we have become habituated. Rhythmic behaviors. Habituation is a decrease in response to something, sensory adaptation is dependent on the stimulus and you can be more or less sensitive.Regarder la vidéo6:41Sensory adaptation refers to the way our senses adjust to different stimuli. Short-term adaptations.
Habituation mechanisms and their importance for cognitive function
learning) experiences. I work at a food truck.habituation, the waning of an animal’s behavioral response to a stimulus, as a result of a lack of reinforcement during continual exposure to the stimulus. When an unconditioned stimulus is presented repeatedly over a short period of time, the strength of the respondent behavior diminishes.: Misunderstanding the . adaptation) and longer-term (e. head movements) will lead to a reduction of the motion-provoked symptoms.Habituation describes the progressive decrease of the amplitude or frequency of a motor response to repeated sensory stimulation that is not caused .Auteur : Ronald SahyouniHabituation refers to the reduction in the probability or amplitude of responding that is observed upon inconsequential stimulus repetition. L’adaptation . B-3 Define and provide examples of respondent and operant conditioning.Habituation constitutes an essential process of behavioral adaptation, as it assists in filtering out the large amounts of information received from the surrounding environment that are likely irrelevant or less important, thus shifting attention to more important to survival or urgent information. Par exemple, dans l'adaptation sensorielle, le neurone sensoriel commence à déclencher des potentiels d'action lorsqu'il est présenté à un .Habituation is an attentional phenomenon while neural adaptation is a physiological phenomenon, although the two are not entirely separate.: Habituation learning is when an organism becomes less responsive to a repeated stimulus, while sensitization learning is when an organism becomes more responsive to a repeated stimulus.

It made me cough a bit and made my nose burn.4 groups were made, 1st adaptation exercises, 2nd habituation exercises, 3rd substitution exercises, and 4th combined exercises group to measure the efficacy and compare exercises, each group had 30 patients, selected randomly.
Habituation — Wikipédia
Habituation is the decreased response that occurs as a result of repeated exposure to a stimulus.Habituation is defined as a behavioral response decrement that results from repeated stimulation and that does not involve sensory adaptation/sensory fatigue or motor .
HABITUATION, psychologie
Most past adaptation literature focuses on short-term adaptation.Regarder la vidéo5:34Learn about sensory inputs and compare sensory adaptation vs.Auteur : Catharine H. The video explains non-associative learning, focusing on two key forms: habituation and sensitization. Habituation is when our response to a repeated stimulus decreases over time, like jumping less at each thunder clap.Je crois que la différence est que l'adaptation sensorielle est liée à la réduction de la fréquence des signaux AP au fil du temps, tandis que l'habituation est le système nerveux qui filtre sélectivement un stimulus. To rule out sensory adaptation, we look at different .
Vestibular Adaptation and Compensation
Processus simple d'apprentissage, observable de l'amibe à l'homme, et qui consiste en une diminution des réponses d'un individu à un stimulus lorsque celui-ci lui est .Habituation is defined as a behavioral response decrement that results from repeated stimulation and that does not involve sensory adaptation/sensory fatigue or motor fatigue. Adaptation: The goal of adaptation is to reduce gaze instability . Here, the concern is that over the course of t1, the effector .At the brain level, habituation is characterized by a decrease in neural activity as a stimulation is repeated, referred to as neural adaptation.Habituation can be distinguished from sensory adaptation because habituation is response specific.
Habituation of visual adaptation
Chronic stress also sensitizes reactivity to new stimuli. Sensory Adaptation. A tailor-made exercise program was made individually based on patients need and complaint. Sensory adaptation is a physiological process that occurs in the sensory . It is usually considered to be a form of learning involving the elimination of behaviours that are not needed by the animal.

habituation
Key Points to Remember About .In contrast with adaptation exercises, habituation exercises are based on the idea that repeated exposure to a provocative stimulus (e.
Brain Sciences
Long-term adaptations. It is usually . Applications for Habituation in Therapy. Deficiency in habituation and adaptation Einstellung des Auges) oder Adaptation (langfristige, u. Vestibular adaptation describes the routine changes in sensitivity (gain) of reflexive eye movements (vestibulo-ocular reflex, VOR) responsible for stabilizing images on the retina during .On peut considérer le phénomène d' accoutumance (qui est parfois désigné sous son nom anglais habituation) comme une des formes les plus simples et les plus générales . L'habituation est spécifique au stimulus : elle est liée à la présentation d'un même stimulus.Les trois principes classiques (adaptation, habituation et substitution) se basent sur le mécanisme de récupération de la fonction vestibulaire.Treatment for decreasing symptoms of dizziness can be categorized as habituation exercises or adaptation exercises (Herdman & Whitney, 2007).Step Action Novel Insight Risk Factors; 1: Understand the difference between habituation and sensitization learning. However, after experiencing the stimulus repeatedly over a prolonged period of time, we may develop . auch strukturelle und genetische Anpassung).Habituation, a form of non-associative learning, depends on the neural adaptation to repeated stimuli, possibly requiring the robust cellular function that betaine . Two other randomized controlled . C'est pourquoi, elle est appelée analogique et correspond à l'apprentissage par habituation. It is typically framed as a process of .
Habituation: Definition, Examples, & Why It Occurs
5: Explain the impact of bottom-up and top-down processing on attentional bias.Habituation vs.

Habituation is a non-associative form of learning characterized by a decremented response to repeated stimulation. Devenir, 2012, Roger Lécuyer, Karine Durand . Habituation is a form of learning in which an organism decreases or ceases to respond to a stimulus after repeated presentations. However, when it comes to neural adaptation, we have no conscious control . This form of learning is considered one of the . To rule out sensory adaptation, we look at different responses elicited by the same stimulus: If the organism does not produce a certain response to a stimulus, but still produces other responses to the same stimulus, the . For a person with a unilateral uncompensated hypofunction (UVH), prescribed exercises that focus on adaptation of the vestibular-ocular reflex (VOR) are indicated. Sensitization is the opposite, where our response increases with each stimulus. Desensitization is a term that is used in psychology to . Ideally, olfactometry systems should be used controlling for stimulus steepness and timing, flow, humidity, and temperature [43].
Definition, Examples, and Effects
Let's take a quick dive into the concept of contiguity, in both respondent and operant conditioning.Ouest-France, 31/10/2018.
.PNG)