Addition polymerization vs condensation

Typically, PIP includes addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Naturally occurring and . The now-empty bonding positions on the two monomers .comPolycondensation et polyaddition pour les matériaux .comPolycondensation et polyaddition - Techniques de l'Ingénieurtechniques-ingenieur.Addition polymerization involves the addition of monomers without the loss of any side products.comAddition and Condensation Polymerisation (inc.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis The elements of the first three of these have been . Condensation polymerization is a reaction that joins two functional groups such as an alcohol and a carboxylic acid and forms a second small molecule such as water.
Water is also .
Fiche explicative de la leçon: Polymérisation
The main difference between addition and condensation polymerization is that in former the polymers are formed by the addition of monomers with no by-products while in the . Nylon and Polyester are some of the most common examples of products of this type of polymerization. Addition polymerization typically occurs at high temperatures and pressures. Know the properties and uses of common synthetic condensation polymers.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 3 minAddition polymerization typically requires high pressure and temperature conditions and is a faster process, suitable for industrial-scale production.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Difference Between Addition And Condensation Polymerization
The most common and thermodynamically favored chemical transformations of alkenes are addition . The terminal functional groups on a . Condensation polymerization is crucial in producing synthetic fibers, fabrics, and plastics with specific .Synthesis of Addition Polymers is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4. Biodegradable Polymers. In the figure given above, there is a reaction between adipic acid monomer and hexamethylene diamine monomer which gives the final product as polyamide and a by-product which is a water molecule. This process occurs through the breaking of double or triple bonds in the monomers, .Condensation polymerization (also known as step-growth) requires that the monomers possess two or more kinds of functional groups that are able to react with each other in such a way that parts of these groups combine to form a small molecule (often H 2 O) which is eliminated from the two pieces. JoVE publishes peer-reviewed scientific video protocols to accelerate biological, medical, chemical and physical research. Based on the nature of the chemical reaction involved in the formation of a polymer, there are two . Adipic acid is a carboxylic acid with two carboxyl groups on either end of the molecule. In addition polymerization, the . A large number of important and useful polymeric materials .
The addition reaction may occur by way of radical, cationic, or anionic intermediates.
10 Differences Between addition and condensation polymerization
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Chapter 20. The reaction is shown in the graphic on the left. The monomers have two functional groups present, one on each end.Difference Between Addition and Condensation .This video discusses polymers that are formed through condensation polymerization reactions. Functional groups on monomers react with each other to form linkages such as ester or amide linkages and are . Monomers are the building blocks of polymers. Although polymers of this kind might be considered to be .

In the case of condensation polymerization, D = [M 0 (1 + p) / (1 - p)]/[M 0 / (1 - p)] D = 1 + p. Relatively low cost compared to alternatives; Most are thermoplastics; Strong and light weight; Non-biodegradable (environmental implications) Differences.Polymerization - Addition Polymers.
![[Polymers #2] Addition & Condensation Polymers (With Mechanism of ...](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/xXjJG52iNNk/maxresdefault.jpg)
techniques-ingenieur. a small molecule, such as water or methanol, is produced as a byproduct).
Fiche explicative de la leçon: Polymérisation
This is a key difference between condensation polymers and addition polymers: Addition polymerisation forms the polymer molecule only. This is because the backbone of those molecules contains weaker bonds.Différence entre la polymérisation par addition et la . They are huge chains or sometimes even 3D structures of repeating units known as monomers.Addition Polymerization vs. This review summarized . Once the growth of a chain is initiated by formation of an active center, chain propagation is usually rapid by addition of a sequence of monomers. In addition polymerization (sometimes called chain-growth polymerization), a chain reaction adds new monomer units to the growing polymer molecule one at a time through double or triple bonds in the monomer.Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization are two different methods of polymerization used to create polymers.Natural proteins as well as some common . The functional groups at the ends of one monomer . The polymerization reactions typically happen in crystal, which promotes the topochemical process. Condensation Polymerisation or Step Growth Polymerisation. Alkanes, alkenes, alcohols and carboxylic acids are different homologous series of organic compounds. Addition polymerization involves the repeated addition of monomers to form a polymer chain without the production of any byproducts. The formation of condensation polymers occurs by the repeated condensation reaction between two different tri-functional or bi-functional .Examples of Condensation Polymerization. Polymers of Commercial Importance.
Polymers
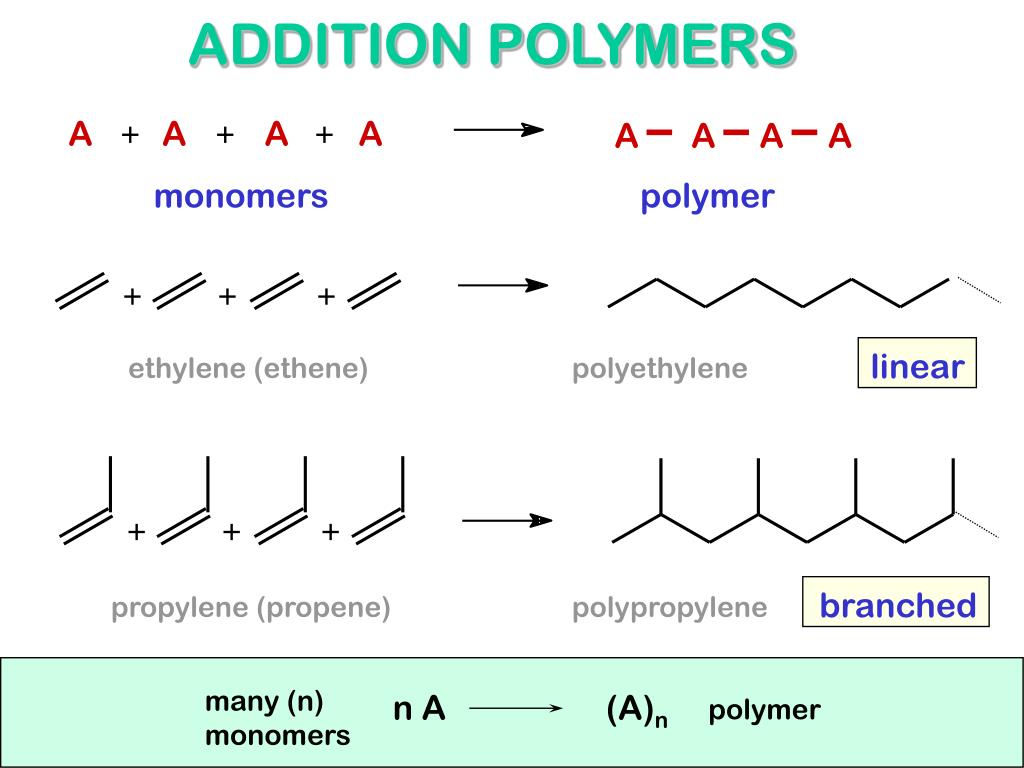
1 Addition polymerization. Addition Polymerizations •Step-growth mechanism •Often afford a condensate by-product (monomer and repeat unit not equivalent) •High degrees of . This text is adapted from Openstax, .Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization are two modes of polymerization reactions in the formation of polymers.Under pressure of 1–100 GPa, unsaturated organic molecules tend to form covalent bond to each other for a negative enthalpy change, which often produces polymeric materials with extended carbon skeleton. Condensation Polymerization What's the Difference? Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization are two different methods of .Condensation polymerizations are typical of monomers containing two or more reactive atomic groupings; for example, a compound that is both an alcohol and an acid can . Because p is always a fraction, the result is that the dispersity of a condensation polymerization is statistically expected to be less than 2. Examples include polyamides such as kevlar and nylon 6.Condensation polymerization is a slower reaction compared to addition polymerization and, in many cases, requires the presence of heat.There are two general types of polymerization reactions: addition polymerization and condensation polymerization.Condensation polymers form more slowly than addition polymers, often requiring heat, and they are generally lower in molecular weight. Polypropylene: The reaction to make polypropylene (H 2 . Polymerisation is the process of joining a large number of small molecules to make very large molecules.Une réaction de polymérisation par addition ou condensation conduira toujours à une substance ayant une masse moléculaire supérieure à celle des monomères. PVC (polyvinyl chloride), which is found in plastic wrap, simulated leather, water pipes, and garden hoses, is formed from vinyl chloride (H 2 C=CHCl). Basic terms like polymer, monomer and their properties have been explained.The most important type of addition polymerization is that of alkenes (usually called vinyl monomers) such as ethene, propene, ethenylbenzene, and so on.Condensation polymerization. The polymerization process takes place in three distinct steps: 1.Condensation polymerization, also known as step-growth polymerization, requires a catalyst, such as an acid or an enzyme, and the monomers must have at least two reactive functional groups, such as amines or carboxylic acids. Polymers are very different from the other kinds of organic molecules that you have seen so far.Other Addition Polymers. Condensation polymerization can occur under milder conditions but often requires catalysts and can be slower due to the step-growth nature of the reaction. Chain growth is used to polmerize a wide array of compounds that contain carbob-carbon double bonds (alkenes or olefins) as well as a .Addition polymerization is the successive addition of alkene monomers to one another. In polymer chemistry, condensation polymers are any kind of polymers whose process of polymerization involves a condensation reaction (i.You might also be interested to know that addition polymers include strong C-C bonds.Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a common condensation polymer.More organic chemistry - AQA Condensation polymerisation - Higher.By now you are familiar with the concept of polymers. One pair of monomers that can form a polyamide is that of adipic acid and hexanediamine. Condensation polymerization involves the formation of a small molecule, such as water or alcohol, as a byproduct of the reaction.Unlike addition polymerization, condensation polymerization typically involves monomers with two different functional groups. The reaction occurs by eliminating small molecules, such as water, alcohol, or ammonia, as the polymer chain grows.Addition Polymers vs Condensation Polymers. The former mainly appears in the unsaturated molecules.In chain-growth (or chain) polymerization, the only chain-extension reaction step is the addition of a monomer to a growing chain with an active center such as a free radical, cation, or anion.This is a key difference between condensation polymers and addition polymers: Addition polymerisation forms the polymer molecule only; Condensation polymerisation forms . Addition Polymerization. Whereas other compounds are of relatively . In general, we recognize four basic kinds of mechanisms for polymerization of vinyl monomers - radical, cationic, anionic, and coordination.
Condensation polymerization

On the other hand, condensation polymers tend to be more biodegradable. Both types of polymers are produced from organic monomers which consist of carbon atoms as the backbone.1: Hydrocarbons. Given 99% conversion of monomers with average molecular weight 120 g/mol, calculate M . Because of this reason, these polymers are non-biodegradable and very difficult to recycle. When these molecules react with each other, a molecule of water is .A key reason is that step growth is mostly limited to condensation polymerization of carboxyloid compounds such as polyamides and polyesters, as well as a few related materials such as polyurethanes.Condensation polymerization reaction.Main Difference – Addition Polymerisation vs Condensation Polymerisation.What is the main difference between addition and condensation polymerization? The main difference lies in the formation of by-products during the . In addition polymerization, the monomers add to one .Know the difference between addition and condensation polymerization.