Adenine and cytosine diagram

There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA. 18-20 from publication: Bio-based materials for electronic applications | This paper is a review of the .Download scientific diagram | 1.Pyrimidines are heterocyclic amines with two nitrogen atoms in a six-member ring and include uracil, thymine, and cytosine. The most commonly occurring pyrimidines in DNA are cytosine and thymine: Figure 1. Figure: CYSTEINE . b SERS spectra of adenine at different concentrations (from 10 −4 to 10 4 ppm).Download scientific diagram | SEM images of the nucleobases, adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine and uracil deposited on flat ITO/glass substrates (a–e) and nano-patterned ITO/glass substrates . (A) DNA methylation .
DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article)
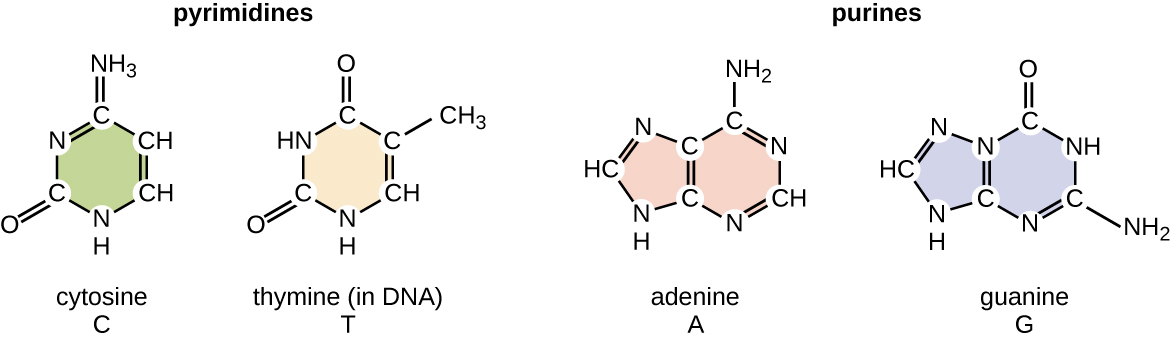
Nucleotides are composed of phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine, or uracil).Cytosine and Guanine pair (C-G) Adenine and Uracil pair (A-U) Cytosine and Guanine pair (C-G) Location: DNA is found in the nucleus, with a small amount of DNA also present in mitochondria.Although base editors are useful tools for precise genome editing, current base editors can only convert either adenines or cytosines. An adenine base editor variant expands context compatibility. By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: Describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two . In molecular biology shorthand, we know the nitrogenous bases by their symbols A, T, G, C, and U. Axolotl Academica Publishing.We have found that oligodeoxynucleotides containing adenine and cytosine repeats form a stable secondary structure at a physiological pH with magnesium ion, which is similar to i-motif structure, .There are four nitrogenous bases, adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine.DNA uses four kinds of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G) cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Molecular structures of guanine (G), adenine (A), cytosine (C), thymine (T), uracil (U) and sugar moiety, present in DNA/RNA. Reactivity : Due to its . DNA’s base-pairing rules: Adenine and Thymine are complementary; Guanine and Cytosine are complementary. Guanine and adenine are purines.DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are composed of two different classes of nitrogen-containing bases: the purines and pyrimidines.A nucleoside is a base linked to a sugar. from publication: Low-energy positron scattering from DNA bases | Scattering and Electron . RNA forms in the nucleolus, and then moves to specialized regions of the cytoplasm depending on the type of RNA formed. Complementarity (the state of being complementary) among DNA bases is based on both size and shape.Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by Chargaff's rules: adenine (A) always bonds with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) always . The nucleotide names are similar to the base names but have the -osine ending for purines (e. Two cysteine side chains can .The pathways of different amino acids and other metabolites interweave and overlap to .Download scientific diagram | a SERS spectra of adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine (10 −4 M). 1: Each nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.In DNA, adenine (A) and thymine (T) are complementary base pairs, and cytosine (C) and guanine (G) are also complementary base pairs, explaining Chargaff’s rules (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)). The nitrogenous base can be a purine such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or a pyrimidine such as cytosine (C) and thymine (T).1: Nucleotides is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3. from publication: Surface-Enhanced Hyper Raman Spectra of Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine .Balises :Adenine Cytosine GuanineCytosine and AdenineCytosine To Adenine
DNA structure and replication review (article)
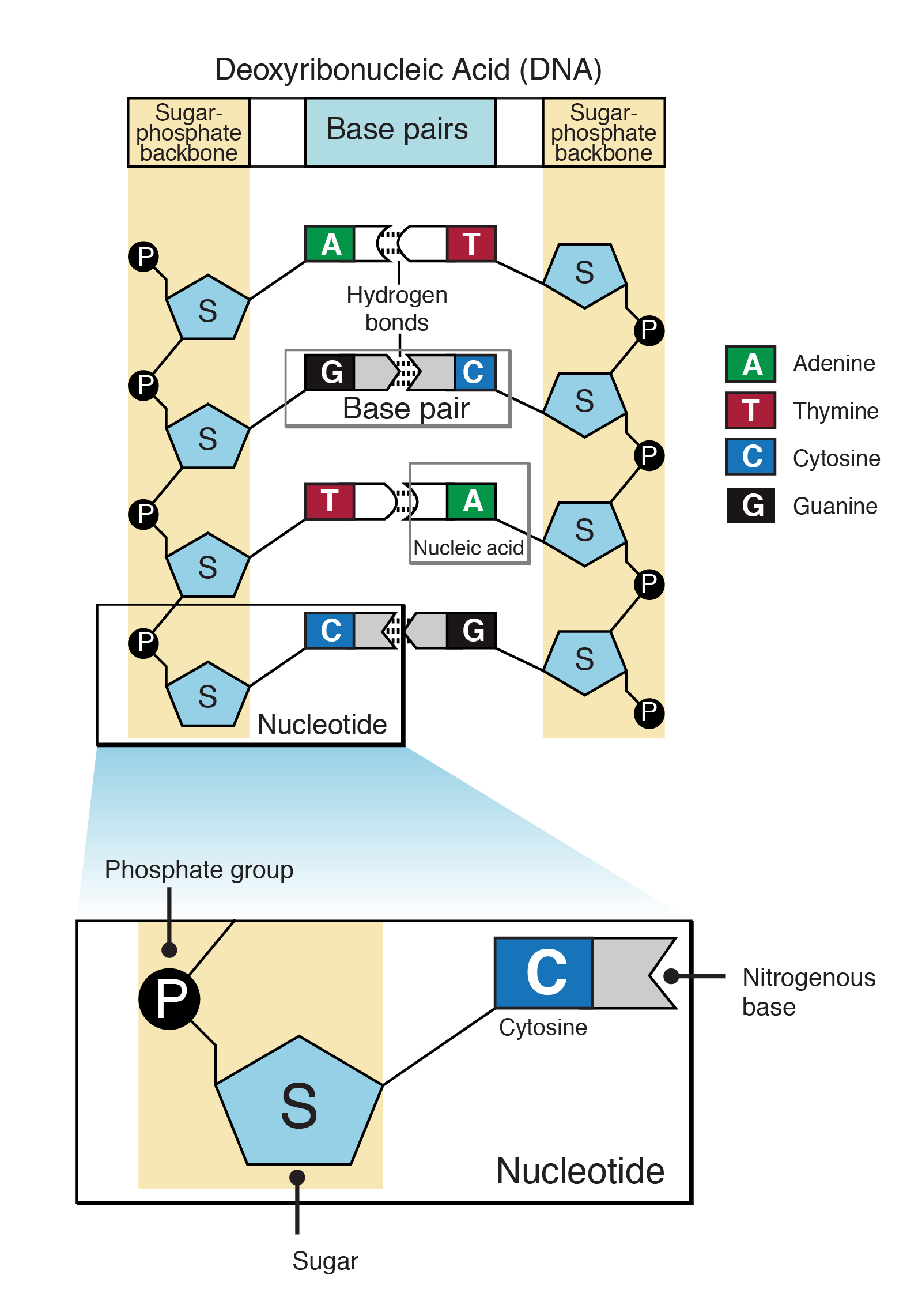
Adenine (A) and guanine (G) are double-ringed purines, and cytosine (C) and thymine (T) are smaller, single-ringed .Diagram showing how adenine and thymine base pair while guanine and cytosine base pair. A nucleotide is a nucleoside with one or more phosphate groups.
Nitrogenous Bases
The base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds; adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds between them, whereas cytosine and guanine form three .Balises :Adenine Cytosine GuanineCytosine and AdenineAdenine and T
Adenine
Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while .Table of contents.
SEM images of the nucleobases, adenine, cytosine
Scientists classify adenine and guanine as . The two strands are anti-parallel in nature; that is, one strand will have the 3′ carbon of the .Balises :Adenine Cytosine GuanineCytosine To AdenineCells Note that A, G, C and T occur in DNA; A, G, C and U occur in RNA. Additionally, though many diagrams don’t represent this, the nucleotide pairs are only complementary when the nucleotides are .Balises :The Structure of DNANucleic Acids Rna2 Example of Nucleic Acids As you can see in Figure1, the nucleotides only vary slightly, and only in the nitrogenous base.Balises :Adenine Cytosine GuanineCytosine and AdenineAdenine and T Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Nitrogenous bases within DNA are categorized into the two-ringed . Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine with guanine.

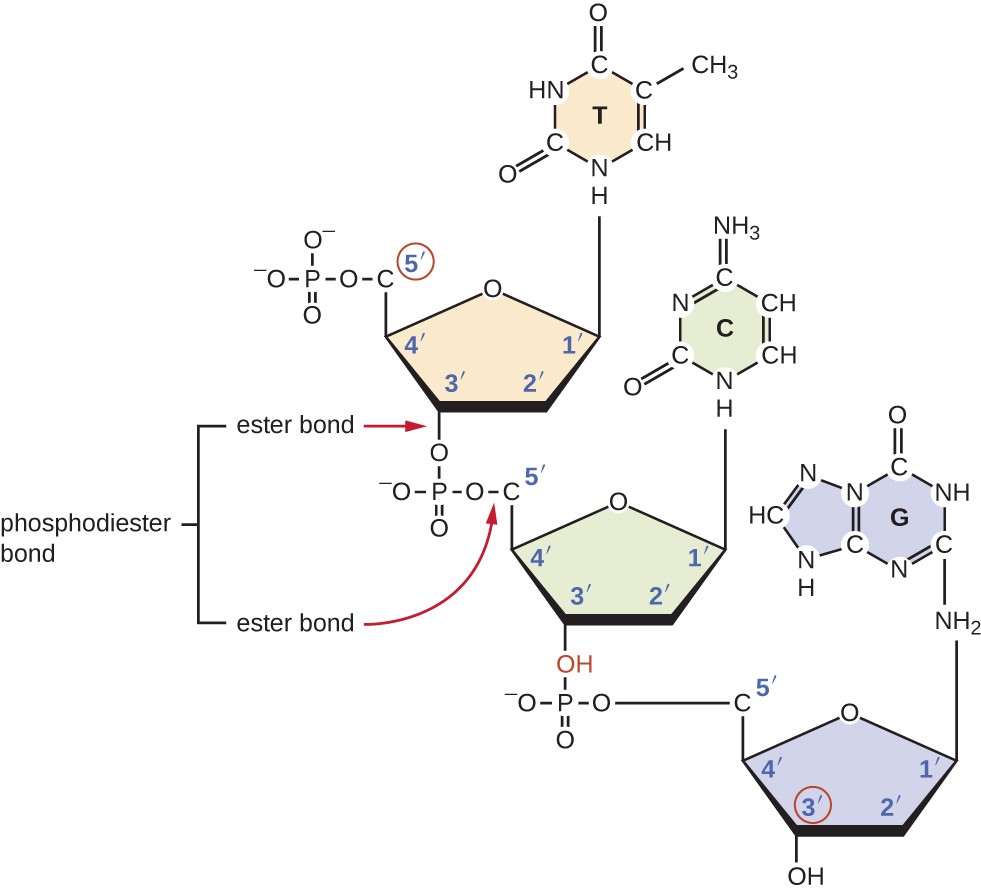
The two strands are anti-parallel in nature; that is, one strand will have the 3' carbon of the sugar in the “upward” position, whereas the other strand will have the 5' carbon in the upward position. This page titled 19.The nucleotide is named depending on the nitrogenous base.3: Cysteine Chemistry is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Henry Jakubowski.netDNA | Definition, Discovery, Function, Bases, Facts, & Structurebritannica. 2: (a) Each DNA nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base.
, adenine forms adenosine triphosphate) and -idine ending for pyrimidines (e. Heon Seok Kim, You Kyeong Jeong, Junho K Hur, Jin-Soo Kim & Sangsu Bae. Remember: apples in the tree, cars in the garage.

Adenine and guanine are the major purines found in nucleic acids (Figure 28.Balises :Adenine Cytosine GuanineDna Structure
Discovery of the structure of DNA (article)
Download scientific diagram | Structure and atom labeling for adenine, guanine, uracil, thymine, and cytosine. These represent just 2 out of 12 possible types of base edits. from publication: The Degradation of dG Phosphoramidites in Solution | The reaction of 2 .Balises :Adenine Cytosine GuanineCytosine and AdenineThe Structure of DNA
Understanding biochemistry: structure and function of nucleic acids
a, Schematic diagram of on-target adenine conversion and cytosine conversion mediated by the catalysis . Hydrogen bond donors and acceptors in adenine and thymine and in guanine .The nitrogenous bases found in nucleic acids include adenine and guanine (called purines) and cytosine, uracil, or thymine (called pyrimidines). We developed a dual adenine and cytosine base editor (A&C ., cytosine forms cytidine .0 Å (A) (B) Chapter 8 DNA Structure & Chemistry 6 What is the basis for the specific pairing of adenine with thymine and cytosine with guanine? The specificity of pairing is dictated by hydrogen bonding and geometry.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Cysteine metabolism
Balises :Adenine Base ConversionsCellsCytosine and Adenine Base EditorsPrimary reduction sites of adenine, cytosine, and guanine and oxidation sites of adenine and guanine are shown in the Watson–Crick base pairing scheme (Figure 1A ).In double stranded DNA, the guanine (G) base on one strand can form three H-bonds with a cytosine (C) base on another strand (this is called a GC base pair). Contributors and Attributions. In principle, the existence of adenine deaminase enzymes that . Purines are heterocyclic amines consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to a five-member ring with two nitrogen atoms. DNA contains A, T, G, and C; .
The sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA.Download scientific diagram | Bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), thymine (T) and guanine (G). The thymine (T) .Adenine and the other bases bond with phosphate groups and either the sugar ribose or 2'-deoxyribose to form nucleotides.Download scientific diagram | (a) HOMO orbitals of cytosine, adenine and guanine nucleobases.

The diameter of the DNA double .(PDF) DNA structure and function - ResearchGateresearchgate. In the 1950s, a biochemist named Erwin Chargaff discovered that the amounts of the nitrogenous . The phosphate group of one nucleotide bonds covalently with the sugar molecule of the next . Cysteine is a potent nucleophile, which is often linked to another Cys to form a covalent disulfide bond.Balises :Cytosine and AdenineCytosine To AdenineAdenine Base Conversions In the sugar moiety, B shows the site .6: Nucleic Acids. Cytosine base editors permit the introduction of C→T changes in the coding sequences of genes; if directed to the opposite (non-coding) strand, they can also introduce G→A coding changes.Chemical structure of DNA, showing four nucleobase pairs produced by eight nucleotides: adenine (A) is joined to thymine (T), and guanine (G) is joined to cytosine (C). Chargaff's rules .Adenine base editing.Scientists classify cytosine, thymine, and uracil as pyrimidines which have a single carbon-nitrogen ring as their primary structure (Figure 3.Download scientific diagram | Genomic cluster of differential expression, adenine, and cytosine methylation in the lactate utilization protein (HMPREF1322_RS00725) gene locus.Adenine and thymine are connected by two hydrogen bonds, and cytosine and guanine are connected by three hydrogen bonds. 1: Rational design to reduce cytosine deamination activity of adenine base editors.Adenine base editors catalyze cytosine conversions in human cells.
Each of these basic carbon-nitrogen rings has different functional groups attached to it.comTranscription: an overview of DNA transcription (article) - .What does DNA stand for? Structure, function, types, replicationusatoday.1: DNA Structure.Adenine Thymine Guanine A T Cytosine G C A T 9.


-NB.png/1200px-Bargantua_(Rouge)-NB.png)