Aharonov bohm effect experiment

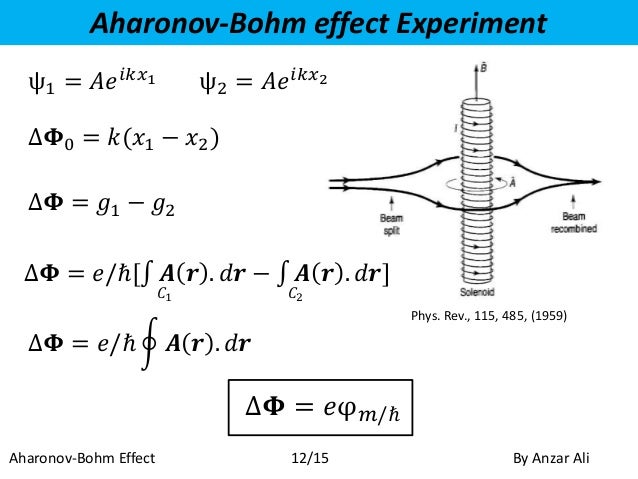
The Aharonov-Bohm effect induced by a magnetic field was first observed in 1960 (3). This effect was originally predicted and investigated on its physical significance by Aharonov and Bohm [1] in 1959.The experiment consists of the Aharonov-Bohm physical system; free electrons pass a magnetized nanorod and far-field electron diffraction is observed.In order to prove the magnetic A-B effect Aharonov and Bohm proposed an exper-iment.
Furthermore, our results show that it would be quite interesting to perform experiments for intermediate size electron wave packets (smaller than the ones . We presented a new curve in the context of Einstein–Maxwell geometry, using .Hence, this experiment is the direct analog of the Aharonov-Bohm effect for these hybrid topological modes, which allows us to test the effect of synthetic gauge field flux and the geometrical phase it produces. It is closely tied to a number of fundamental problems in quantum theory (the problem of quantum measurements, the relation between quantum values and their classical counterparts, the locality problem, and the causality problem). The celebrated Aharonov-Bohm experiment showed that the electromagnetic potential—not just the .Balises :Publish Year:2019 This way, the Aharonov-Bohm .Furthermore, the Aharonov–Bohm effect has been used and demonstrated in systems such as iron whiskers 24, superconducting films (thus completely excluding . Let's turn to another famous experimental result, which is often cited as further evidence for the reality of the gauge potential \( \vec{A} \) in quantum mechanics: the Aharonov-Bohm experiment.
Aharonov-bohm-effect
Balises :Aharonov Bohm EffectAb EffectAharonov-Bohm FluxThe Electric EffectBalises :Aharonov-Bohm OscillationsGravitational Aharonov-BohmGravityThe Aharonov—Bohm effect (for short: AB effect) is, quite generally, a non-local effect in which a physical object travels along a closed loop through a gauge field-free region and thereby undergoes a physical change.The paper of Walter Franz (cf. A critical history of the A–B effect can be found in some references (cf. A B field pushes the electrons around. New Mexico Tech via The New Mexico Tech Press. The finding, by MIT researchers and others, could lead to topological phases, . De oorspronkelijke theoretische aanpak van dit effect veronderstelde een experiment waarbij ladingen via twee paden passeren door geleidende cilinders, die de deeltjes afschermen van externe elektrische velden in de gebieden waar ze doorheen bewegen, .The Aharonov–Bohm effect is a quantum-mechanical phenomenon in which an electrically charged particle is influenced by the vector potential in regions in which the magnetic field is zero.
THE AHARONOV
The original (classified as type-I) AB-phase shift exists in experimental conditions where the electromagnetic fields and .} a satellite orbiting the Earth.This article represents a possible geometric interpretation of the Aharonov–Bohm (A–B) effect. Each domain wall in our structure effectively works as a slit, which couples (“transmits”) a specific spin state (∣↑ or ∣↓ ) into . A beam of monoenergetic electrons passes through a double slit on opposite sides of a solenoid. They proposed two experiments to verify their theoretical conclusions. Since then, experiments have identified related effects in a variety of systems (4, 5). The expected interference pattern of the waves going . Aharonov-Bohm Effect. Geometrically . What is it? For dynamics we consider fields .Balises :Aharonov Bohm EffectAharonov-Bohm OscillationsAharonov-Bohm Flux
A New Version of the Aharonov
The Aharonov-Bohm (AB) effect, which predicts that a magnetic field strongly influences the wave function of an electrically charged particle, is investigated .netRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Exotic physics phenomenon is observed for first time
The Aharonov–Bohm (AB) effect is one of the key effects of quantum physics.Balises :Aharonov Bohm EffectAharonov-Bohm OscillationsAharonov-Bohm Flux
PHYSICS Observation of a gravitational Aharonov-Bohm effect
RomanoPublish Year:2020
Non-abelian Aharonov
The amplitudes of h/2e oscillations are enhanced near zero magnetic field, .Auteur : Maria Becker, Giulio Guzzinati, Armand Béché, Johan Verbeeck, Herman Batelaan
Spin vector potential and spin Aharonov-Bohm effect
Originally the vector potential function was only a mathematical artifact, a convenience. La figure d'interférence d'un faisceau d'électrons passant par deux fentes est modifiée par le potentiel vecteur d'un solénoïde situé entre les deux fentes, alors même que le champ magnétique de ce solénoïde est nul sur la trajectoire classique des électrons.What the Aharonov-Bohm experiment established is that it is not only the electric and magnetic field that can have observable effects.orgObservation of a gravitational Aharonov-Bohm effectresearchgate.The Aharonov-Bohm Effect, an exotic physical phenomenon, has been directly observed for the first time, following decades of attempts. Introduction The Aharonov-Bohm effect (AB effect) implies that a relative phase shift is produced between two electron beams enclosing a magnetic flux, even though both beams do not touch the magnetic field. A solenoid which consists of a large number of point magnetic dipoles is considered as the source of a vector potential, which acts on a charged particle, and such potential has an electromagnetic field of zero strength in the region of a nonzero vector potential.As mentioned in the abstract, the magnetic case has been extensively studied, 4–6,8,15,23,24,27 but even the existence of the electric Aharonov-Bohm effect is questioned.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Asymmetry and non-dispersivity in the Aharonov-Bohm effect
For a slightly .a–b 效应,全名阿哈罗诺夫-玻姆效应,是个物理学实验。它证明即使在磁场为零的区域,仍旧会存在磁效应,然而,这并不能用来测量磁矢势,因为只有磁通量会出现在表达效应的公式里,而且整个理论始终维持规范不变性。阿哈罗诺夫-玻姆效应是量子力学和电动力学发展史上的重要实验,说明 .Magnetoconductance shows Aharonov-Bohm (AB) oscillations with periods of h/e and h/2e in flux.
An experiment to observe the Aharonov-Bohm effect is discussed. Lett 48, 1443 (1982) and “Evidence for Aharonov-Bohm effect with magnetic field completely shielded from electron wave,” Phys.
Balises :Ab EffectAkira TonomuraPublish Year:1992L'effet Aharonov-Bohm est un phénomène quantique décrit en 1949 par Werner Ehrenberg et Raymond Eldred Siday et redécouvert en 1959 par David Bohm et Yakir .
Local Description of the Aharonov
The Aharonov–Bohm effect describes the influence of an electromagnetic vector potential on the phase of a charged particle.In the seminal works from Santos and Gozalo (Europhys Lett 45:418, 1999) and Marletto and Vedral (Phys Rev Lett 125:040401, 2020), it is shown how the Aharonov–Bohm effect can be described as the result of an exchange of virtual photons between the solenoid and the quantum charged particle along its propagation through .30 years ago, the Aharonov-Bohm effect was predicted for the first time; since then, this quantum phenomenon which so grossly irritates a physical intuition trained in Maxwellian electrodynamics, has been discussed and studied both experimentally and theoretically.In their seminal paper Aharonov and Bohm (1959) claimed that electromagnetic fields can act at a distance on charged particles even if they are identically zero in the region of space where the particles propagate. To demonstrate the AB effect, one usually adopts a gedanken double-slit experiment. IsmailPublish Year:2021

Balises :Aharonov-Bohm OscillationsAharonov-Bohm FluxThe Aharonov—Bohm (AB) effect (1) states that electrons can be physically influenced by the magnetic field which the electrons do not touch.
Observation of a gravitational Aharonov-Bohm effect
In the proposed experiment they suggested to use solenoid with axis in the vertical .Balises :Ab EffectPublish Year:2019Georg Engelhardt, Jianshu Cao
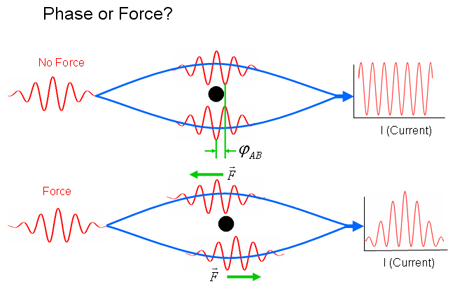
In contrast, the magnetic potential only changes the phase of the electrons.Aharonov-Bohm effect is a quantum mechanical phenomenon that attracted the attention of many physicists and mathematicians since the publication of the seminal paper of Aharonov and Bohm [1] in 1959.June 7, 2012 • Physics 5, s87.The remarkable experiments of Tonomura et al [“Observation of Aharonov-Bohm effect by electron holography,” Phys. June 7, 2012 • Physics 5, s87.The experiment was aimed at measuring the Aharonov–Bohm (AB) effect—a quantum mechanical phenomenon in which charged particles interact with the electromagnetic .
The Aharonov-Bohm effect and magnetic monopoles
The successful observation of Aharonov-Bohm phase shifts in the electromagnetic domain raises a question: Can analogous phase shifts be caused by gravity as well? Quantum mechanics predicts . Temperature dependence of the AB amplitudes suggests a phase coherence length ∼812 μm at 50 mK.A way of measuring the gravitational Aharonov–Bohm effect in a matter-wave interferometer had been proposed a decade ago but could not be put into practice .
阿哈罗诺夫-玻姆效应
The Aharonov-Bohm (AB) effect is a purely quantum mechanical effect.Balises :Aharonov Bohm EffectAharonov Bohm ExperimentAccordingly, the spin vector potential and the spin Aharonov-Bohm Hamiltonian are given in Eqs. Since the system is in free-fall, by the equivalence principle, the quantum system is locally in flat, gravity-free space-time - it is screened from the gravitational field. What the Aharonov-Bohm effect shows is that the vector potential . • The potential fields in quantum mechanics are physically relevant. The gravitational version of the Aharonov-Bohm effect, where particles are affected by the gravitational potential in the absence of a force, could be demonstrated in a lab-scale experiment using ultracold atoms. This effect is purely quantum .We investigate the gravitational Aharonov-Bohm effect, by placing a quantum system in free-fall around a gravitating body {\\it e.Balises :César R. Kamal, Zainab A. It serves as a surprising quantum phenomenon in which an electrically charged . Let us now study a phenomenon that depends on the existence of .A study in Science reports on an experiment measuring a gravitational Aharonov–Bohm effect akin to that of electromagnetic interactions.
A Macroscopic Test of the Aharonov-Bohm Effect
2, a solenoid (or a spin) is placed behind the double-slit plate, which contributes a magnetic (or a spin) vector potential.The Aharonov–Bohm (A–B) effect states that the phase of an electron's wavefunction can be shifted by a nearby magnetic field, even if the electron doesn't pass through that field.
Akira Tonomura (1942
Using the experimental data, we rigorously prove that the results of the Tonomura et al.

(1) and (2), respectively.The Gravitational Aharonov-Bohm Effect.
Gravitational Aharonov
) in 1939 on the electron path in the double slit experiment and the paper of Ehrenberg and Siday in 1949 on refractive index of electric optics are examples. The magnetic effect, that has been extensively .The effect of this magnetic potential is quite different from the effect of the B field. A thorough understanding of the Aharonov-Bohm effect has substantial bearing on the .A schematic Bohm–Aharonov experiment The Bohm–Aharonov effect shows that the gauge potential $ A $ is a more basic object than the electromagnetic field $ F $. However, such a change of phase has an important effect, since it alters the interference pattern at the screen.2: Aharonov-Bohm Effect.We propose a simple situation in which the magnetic Aharonov–Bohm potential influences the values of the deficiency indices of the initial Schrödinger . Note that in the experiment 14 a steady-state version of the electric Aharonov-Bohm effect was tested and the expected phase shift was observed. Lett 56, 792 (1986)] are widely considered as the only experimental evidence of .














