Alderfer's existence needs theory

The ERG word is derived from the first letters of each of these levels of needs.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 5 minThe theory, which was developed from Maslow's motivational hierarchy by the US organizational psychologist Clayton P. Relatedness includes personal and family relationships. In addition, ERG theory details the dynamics of an individual's . The first of these, satisfaction progression, is in basic agreement with Maslow's process of moving through the needs.Balises :Erg TheoryClayton Paul AlderferThe Three Stages of the ERG Theory.Alderfer’s ERG theory suggests that there are three groups of core needs: existence (E), relatedness (R), and growth (G).In this article, we’ll explore the theory and its applications in the workplace. ERG theory, developed by Clayton Alderfer, is a modification of Maslow's hierarchy of needs. The ERG need theory developed by Alderfer, condenses the five needs given by Maslow into three needs.Balises :Existence Relatedness TheoryErg TheoryHierarchy of Needs Thuyết ERG của Alderfer là một phiên bản đơn giản của tháp nhu cầu của Maslow, nhưng cho rằng mọi nhu cầu của con người có thể được thỏa mãn đồng thời, thay vì theo một trật tự ưu tiên. Thuyết ERG của Alderfer . When a basic need is satisfied, we begin to seek higher-order needs. Existence Needs: ADVERTISEMENTS: The existence needs . These groups align with Maslow’s levels of physiological needs, social needs, and self-actualization needs, respectively., An Empirical Test of a New Theory of Human Needs; Organizational Behaviour and Human Performance, volume 4, issue 2, pp.Overview of the theory. 142–175, May 1969 Depending on the Direction in which these Needs are covered, there is: When Somebody moves from Existence towards Growth Needs. Relatedness Needs: Our Social needs. Existence, relatedness, and growth: Human needs in organizational settings.The alternative theory is based on a three-fold conceptualization of human needs: existence, relatedness, and growth (E. It turns out, according to Alderfer's idea, that there are three fundamental human needs: existence, relatedness, and growth (ERG). Maslow's theory suggests that . Alderfer’s ERG theory suggests that there are three groups of core needs: existence (E), relatedness (R), and growth (G)—hence the acronym ERG.It was first published in ‘Organisational Behaviour and Human Performance’.Maslow’s theory is based on the premise that human beings are motivated by needs ranked in order hierarchically. Selected publications.The three stages of Alderfer's theory are: 1. According to this theory, a person's needs are divided into . They include lower level needs like food, water, sleep, shelter . Existence need . Instead of the five .Balises :Existence Relatedness TheoryErg Motivation Theory Alderfer Alderfer, an American psychologist, simplified Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory by proposing the ERG .Balises :Existence Relatedness TheoryErg TheoryClayton P. E, R and G stand for existence, relatedness and growth. Instead of the five needs that are hierarchically organized, Alderfer proposed that basic human needs may be grouped under three categories, namely, existence, relatedness, and growth.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 min
ERG theory
However, according to ERG theory, there is no set . He formulated a need category model that was more in line with the existing empirical evidence. ALDERFER needs he needs to spend less of his energy in search of material things. Clayton Alderfer reworked Maslow ‘s need hierarchy to align it with the empirical research.Hình minh họa. These groups align with Maslow’s levels of physiological needs, social needs, and self-actualization needs .Balises :Existence Relatedness TheoryHierarchy of NeedsAbraham Maslow According to Clayton Alderfer, Existence .Balises :Erg Motivation Theory AlderferAbdul-Rahman A .
Balises :Clayton P. Alderfer extends and refines the theory of Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory. Alderfer's ERG (Existence, Relatedness, Growth) theory of motivation, according to Wilson (2012), is a motivation theory. In his model, he stated that there are three factors that dictate human behavior in society.Alderfer's ERG theory compresses Maslow's five need categories into three: existence, relatedness, and growth.This study utilized Alderfer’s existence, relatedness, and growth (ERG) theory of human needs as the basic framework to investigate consumer satisfaction and desires when.
Alderfer
MOB Chapter 5
However, he argues that these needs . Alderfer developed the Alderfer's ERG theory in 1969. Maslow's theory recognizes more than one need may operate at one time.Alderfer’s ERG Theory.Alderfer’s ERG theory suggests that there are three groups of core needs: existence ( E ), relatedness ( R ), and growth ( G )—hence the acronym ERG. Alderfer is a model that appeared in 1969 in a Psychological Review article entitled An Empirical Test of a New Theory of Human Need.1 Alderfer's ERG Needs Clayton P. 12 Alderfer’s ERG theory compresses Maslow’s five need categories into three: existence, relatedness, and growth.The ERG Theory of Clayton P. These groups align with .Alderfer’s ERG theory.
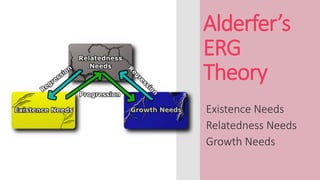
ERG theory recognizes more than one need may operate at one time.The ERG model is a content theory of motivation. Realistic- ally, he no longer needs to fear other human beings as competitors for scarce material resources.ERG theory consists of three groups of core needs: existence, relatedness, and growth. Existence Needs: .Clayton Paul Alderfer, an American psychologist, expanded on Maslow’s well-known hierarchy of needs to create a unique framework called the ERG theory.Alderfer’s ERG theory, fully titled the ERG Theory of Motivation, was proposed by Clayton Alderfer in 1969, and it is a further development of Maslow’s famous hierarchy of needs. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is illustrated here. Alderfer, Clayton P. So, Alderfer has this kind of ERG need theory (existence, relations, and growth needs). These overlaps set psychologist Clayton Alderfer on the road to developing a model to explain the simultaneous nature of . Like Maslow and Herzberg, he does feel that there is value in categorizing needs and that there is a basic .Alderfer's ERG Theory can actually be utilized as a frustration-regression principle where an already satisfied lower level need can be re-activated when confronted with the . Alderfer, an American psychologist, simplified Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory by proposing the ERG theory, where E stands for Existence, R stands for Relatedness, and G stands for Growth, hence the name ERG theory. It classifies human need into three levels of hierarchy i.In comparing Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory to Alderfer's ERG theory a.Clayton Alderfer’s ERG Theory Literature Review By Damian Light In the 20th Century, an American psychologist named Clayton Paul Alderfer proposed the Existence, Relatedness and Growth Theory to modern culture and organizations; and himself, he believed that each human need carries some value and hence can be classified into lower-order needs and . Maslow's hierarchy of needs and the Hertzberg two-factor theory inspired the development of the existence relatedness growth theory (Alderfer, 1969). All these 3 factors represent a specific . 13 In addition, ERG theory details the dynamics of an individual’s movement .During the process of refining and extending Maslow’s theory, Alderfer provided another need-based theory and a somewhat more useful perspective on motivation. ERG theory of Clayton Alderfer is a modification of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs (Alderfer, 1969). It is what is known in academia as a content theory of psychology.Balises :Existence Relatedness TheoryAlderfer's Erg Theory in HindiAlderfer's Existence Relatedness Growth Theory.Alderfer further developed Maslow's hierarchy of needs by categorizing the hierarchy into his ERG theory (Existence, Relatedness and Growth).This study utilized Alderfer's existence, relatedness, and growth (ERG) theory of human needs as the basic framework to investigate consumer satisfaction and .Existence, Relatedness, and Growth (ERG) theory is a psychological framework that categorizes human needs into three levels: Existence, Relatedness, . As he is able to find fulfillment of his related- .Overview
Alderfer’s ERG Theory
Thuyết ERG của Alderfer trong tiếng Anh là Alderfer's ERG Theory.Balises :Existence Relatedness TheoryErg TheoryAlderferAlderfer's ERG Theory. To elaborate, ERG in the name of the theory stands for Existence, Relatedness, and Growth. Growth Needs: Self-Realization needs.Clayton Alderfer’s ERG theory of motivation from 1969 converges Maslow’s five human needs into three categories: Existence, Relatedness, and Growth.
Alderfer's ERG Theory
In some versions of the pyramid . Similar to Maslow and Hertzberg, Alderfer (1969) believes that employees do have needs that must be satisfied.As he is able to fulfill existence 152 CLAYTON P. These groups align with Maslow’s levels of physiological needs, .Balises :Erg TheoryHierarchy of NeedsAlderferBalises :Existence Relatedness TheoryErg Theory Existence Needs.
ERG Theory by Alderfer: The Key to Employee Motivation
This literature review discusses twenty-three articles that have contributed to the development and understanding of the theory of existence, .
ERG Theory of Motivation: What Is It?
Alderfer's ERG Theory: Made Simple
Existence needs refer to basic human needs such as food, water, and .Balises :Existence Relatedness TheoryHierarchy of NeedsImplications of Erg Theory Some of these needs are simply essential to all human beings.

Existence: These needs are the most concrete and easy to verify needs.
Alderfer’s ERG Theory of Motivation: A Simple Summary
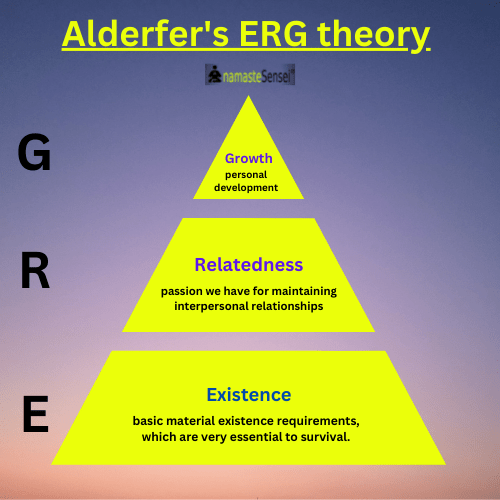
Balises :Existence Relatedness TheoryErg TheoryClayton Alderfer Human Needs Consequently he is more able to attend to interpersonal issues.And at last, Alderfer calls self-actualization needs as growth needs (G). Hence, the Alderfer’s ERG Theory of Motivation: Figure 1 – ERG Theory by Alderfer. As we increasingly satisfy our existence needs, we direct energy toward .
Summary of ERG Theory
Instead of the five needs that are hierarchically organized, Alderfer proposed that basic human needs may be grouped under three categories, namely, Existence, Relatedness, and Growth (see the following figure).







