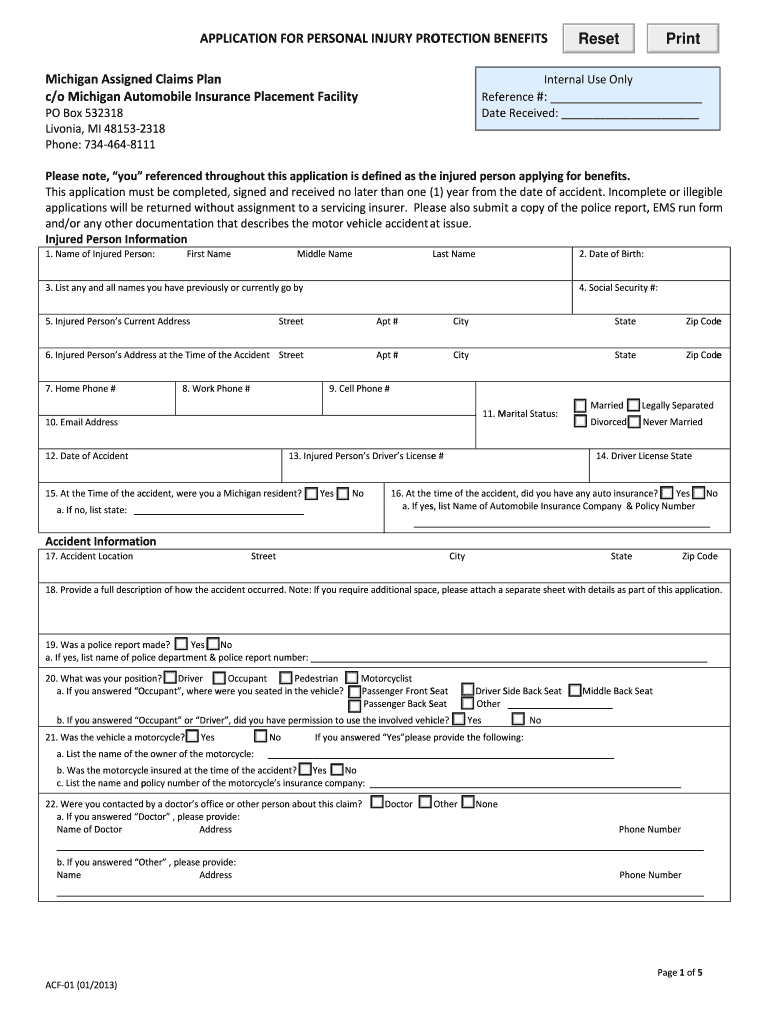
Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells

The process by which organisms break down glucose into a form that the cell can use as energy.
Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used; instead, organic or inorganic molecules are used as final electron acceptors. At the metabolic level, yeasts are characterised . Glucose is the primary source of energy for the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. However, many organisms have . In animals and some bacteria, anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid from glucose. When yeast cells are prevented from getting enough oxygen, they stop respiring aerobically, and start to respire anaerobically instead. Yeast can respire anaerobically (without oxygen), breaking down glucose in the absence of oxygen to produce ethanol . When yeast cells are reproducing rapidly during beer or wine production, the oxygen runs out.You may be familiar with this process from products like sauerkraut and yogurt.Yeast is a unicellular fungus that can convert glucose into carbon dioxide and ATP when oxygen is present.Yeast is used to make alcoholic drinks.24%, fructose was 18. In aerobic organisms undergoing respiration, electrons are shuttled to an electron transport chain, and the final electron acceptor is oxygen. Ethanol, a type of alcohol, and carbon dioxide are produced .When the sum of theoretical ATP production rates from anaerobic glycolysis and respiration are plotted against glucose consumption rates, a general trend can be observed. The respiration in yeast results in ethanol and CO2.Aerobic organisms respire pyruvate completely to CO 2 with oxygen (O 2) as the terminal electron acceptor, thereby making maximal use of energy transformations for . Comparing Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration. can be demonstrated by removing oxygen from yeast’s surroundings.comigcse biology (edexcel) 6 mark experiment questionsthestudentroom. Yes No. Last Updated: October 23, 2020. Anaerobic respiration: The respiration which takes place in the absence of oxygen is known as anaerobic respiration.Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O 2). When the sugar is fully dissolved, aerate the solution with the aquarium aerator pump and airstone, as shown in Figure 4, below. A student reads the following statement in a textbook: ‘Respiration and metabolism are linked to temperature.

This is an important step in the manufacture (making) of both bread and alcohol.Anaerobic respiration also happens in plant cells. In plant and yeast cells, glucose is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide.Critical parameters and procedures for anaerobic cultivation of yeasts in bioreactors and anaerobic chambers. In industrial fermentation processes, the asexual reproduction of yeasts is advisable to ensure the preservation of the genotype and to maintain stable fermentation behaviour that does not derive from it for as long as possible. This process, known as fermentation, allows yeast to partially break down glucose molecules, resulting in the production of . In anaerobic respiration, the process occurs in the absence of oxygen.Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is called fermentation.Aerobic respiration occurs in most of the higher species including plants and animals. Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain.Anaerobic Cellular Respiration. The cells of most living things make ATP from glucose in the process of cellular respiration.One of the most prominent features of the baker’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the rapid conversion of sugars to ethanol and carbon dioxide at both . Examples of an anaerobic respiration equation are the following: Denitrification: NO3− → NO2−→ NO + N2O → N2.They have no cell nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles within their cells.
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
pdf), Text File (.
Anaerobic Respiration In Yeast
Anaerobic respiration is the type of respiration through which .Yeast Respiration - ppt and experiment guide | Teaching . The contents of a cell between the plasma membrane and .As a result of sporulation, yeast cells suffer from genetic variability. Although yeast cells can utilize a wide range of carbon sources, presence of glucose suppresses molecular activities involved in the use of alternate carbon sources as well as it represses respiration and gluconeogenesis.Anaerobic respiration in plants.
Anaerobic Respiration
You need to be able to . Anaerobic converts glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide in yeast cells due to different circumstances within the different types of cells, instead of lactic acid as in muscle cells.) of sugar in ½ cup of warm water.
An Aerobic Exercise: Yeast Metabolism with and without Aeration
Anaerobic respiration breaks down glucose to extract energy in the absence of oxygen.While you might expect the cell would perform .This activity describes a mini- to microscale setup that offers an affordable, reproducible, and accurate method to compare the aerobic and anaerobic respiration of Saccharomyces boulardii, a strain of . in the absence of oxygen.Anaerobic respiration is the process by which energy is released in cells in the absence of oxygen.Anaerobic respiration mainly takes place in muscle cells during vigorous exercise.Compare anaerobic respiration in the muscle cell of an animal with anaerobic respiration in a yeast cell. The chemical reaction of lactic acid fermentation is the following: Pyruvate + NADH ↔ lactic acid + NAD+.
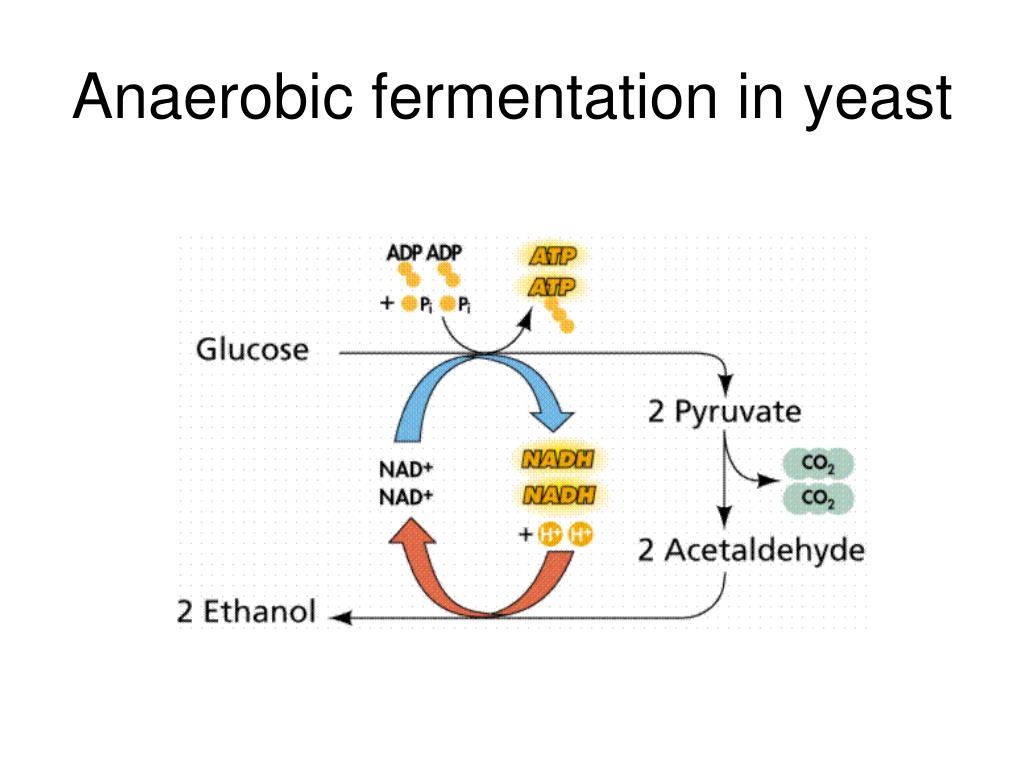
Seek medical assistance. Yeast is used to . Lactic acid fermentation converts pyruvate (a slightly oxidized carbon compound) to lactic acid. Further studies of yeast and muscle revealed the pathway of glycolysis and demonstrated that under anaerobic conditions pyruvate in yeast was converted into ethanol, whereas muscle converted it to .
Energy Metabolism by the Yeast Cell
Cellular respiration in humans is an example. Set up five water baths of varying temperatures: 20, 30, 40, 50 and 60°C.
Practical: Investigating Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast
In 1897, Eduard Buchner carried out fermentation by cell-free extracts and opened the way to determine the main biochemical steps.This occurs routinely in mammalian red blood cells and in skeletal muscle that does not have enough oxygen to allow aerobic respiration to continue (such as in muscles after hard exercise). The liquid paraffin acts as a barrier between any oxygen present and the yeast solution, thus preventing aerobic respiration from taking place. Stir slowly and gently. After 5 minutes, stop aerating the . fermentation: An anaerobic biochemical reaction.
Is Yeast Aerobic or Anaerobic?
The most common yeasts used in fermentation processes (Saccharomyces genus) will produce alcohol in both a beer wort and in bread dough immediately regardless of aeration.Anaerobic respiration in muscle cells: glucose -> lactic acid The lactic acid build up in muscles requires oxygen to be broken down and thus creates an oxygen debt, resulting in the animal breathing faster and more deeply to acquire a higher partial pressure of oxygen in their blood.

When we exercise vigorously, our muscles have a higher demand for energy than when we are resting or exercising normally. The electron transport chain, where the majority of ATP is formed, requires a large input of oxygen.By: Katy McLaughlin, Ph. Glucose is not broken down completely, . In the process, NADH is oxidized to form NAD+.
Cellular respiration review (article)
Upon a strictly biochemical point of view, fermentation is a process of central metabolism in which an organism converts a carbohydrate, such as starch or sugar, into .
Ethanol, a type of alcohol, and carbon.ukRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
The Role of Yeasts in Fermentation Processes
The yeast switches to anaerobic respiration. Methylene blue dye can be used as an indicator for aerobic respiration in yeast.Dissolve 1 teaspoon (tsp.Anaerobic Respiration In Yeast Name Date In biology, . Ethanol and carbon dioxide are produced. Take the yeast suspension and stir using a glass rod.Crabtree Effect. How did you do? Stuck? View related notes.This process occurs in three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport.This occurs routinely in mammalian red blood cells and in skeletal muscle that has insufficient oxygen supply to allow aerobic respiration to continue (that is, in muscles used to the point of fatigue).It was due to the yeast cell respiration in consuming oxygen (O2) and producing carbon dioxide (CO2), where the decrease in DO levels of sucrose was 14.Handle yeast in a suspension form; use non-latex disposable gloves.Living things’ cells power their activities with the energy-carrying molecule ATP (adenosine triphosphate). As the ethanol concentration in the environment increases, the yeast cells begin to get damaged, slowing their growth. It was difficult to keep the temperature of the water bath constant, which could . Increased glucose consumption rates can result in higher ATP production rates.docx), PDF File (.Most (not all) genera and species of yeast can ferment sugars to ethanol anaerobically. All organisms respire in order to release energy to fuel their living processes. The microorganisms like yeast break down .
Chapter 8
The first step of fermentation in brewing is where complex sugars or polysaccharides are broken down into monosaccharides, for example glucose by yeast.Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is called fermentation; Fermentation is economically important in the manufacture of bread (where the production of carbon dioxide makes dough rise) and alcoholic drinks (as ethanol is a type of alcohol) The process outlined above is the same in plants. The production of energy requires oxygen.This is for two reasons; firstly because less energy is produced by anaerobic respiration than by aerobic respiration and, secondly, because the ethanol produced is actually toxic to the yeast.Respiration - AQA.Practical: Investigating Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast. Example 1: Identifying the Site of Anaerobic Respiration in Animal Cells.txt) or read online for free. Fermentation includes .Surprise! Yeast is actually both aerobic and anaerobic! This means yeast can survive and thrive both in the presence and absence of oxygen! Pretty cool, right? Let’s look at how . Yeast is used to make alcoholic. Cellular respiration. Fermentation is economically important in the manufacture of bread (where the carbon dioxide produced helps the .Anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast is different from the same process in muscle cells.They are used to investigate the effects of temperature and substrate concentration on the rate of anaerobic respiration in yeast; These dyes can be added to a suspension of living yeast cells as they don’t damage cells; Yeast can respire both aerobically and anaerobically, in the first experiment it is their rate of anaerobic .The latter two stages require oxygen, making cellular respiration an . Glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide; In yeast cells, this is called fermentation. The fermentation method used by animals and some bacteria like those in yogurt is lactic acid fermentation (Figure 4. The Crabtree effect is the occurrence of alcoholic fermentation under aerobic conditions. In this instance, as much glucose as possible is . This is why research on yeast fermentation has (and still does) receive . Anaerobic respiration in yeast is used during brewing and bread-making: Image caption, Anaerobic respiration by yeast helps bread dough rise . The respiration can be aerobic, which uses glucose and oxygen, or .Anaerobic respiration in yeast.anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration in animals . Using a 20 cm3 syringe take up 5 cm3 yeast suspension.Anaerobic respiration. Boil the glucose solution to sterilise it and remove any oxygen, .
Anaerobic respiration
02%, glucose was 16.