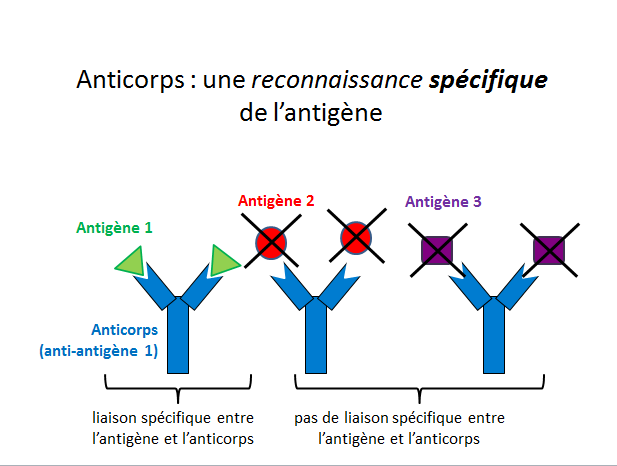
Anatomy of the lower jaw

Nasal notch; Infra-orbital margin; Infra-orbital foramen; Canine fossa; The nasal notch is a curved margin of the bony anterior nasal aperture.The muscles of mastication (Latin: musculi masticatorii) or masticatory muscles are a group of paired muscles responsible for the movements of the lower jaw at the temporomandibular joints (TMJs).comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
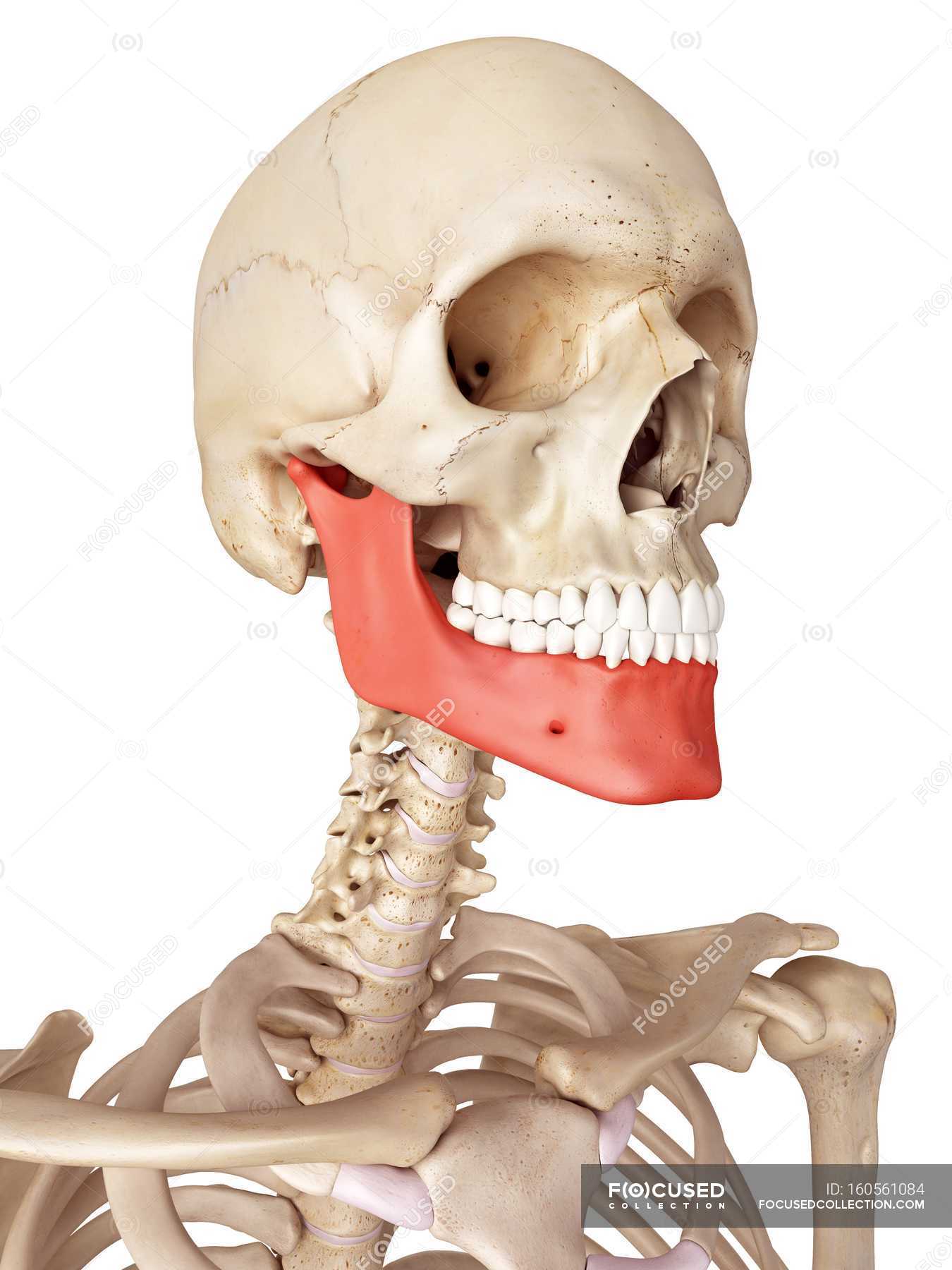
Mandible
And the infra-orbital margin is the lower margin of the orbit formed partly by the .Unlock with Premium. There are four muscles: Masseter.
It is normal to have a .
The mandible: Anatomy, structure, function
They may not all be uniform in size, and may also vary in number. It is commonly known as the lower jaw and is located inferior to the maxilla. It is the joint between condylar head of the mandible and . In birds, the mandible .5 feet (2 meters) . The teeth in the lower jaw are also rooted to this bone. The mandible is the bone of the lower jaw, carrying the lower teeth and forming part of the temporomandibular joint with the temporal bones of the skull. To compensate for the short jaw, babies' anatomy tend to favor jaw opening over jaw closing, allowing for an easy, drop down in jaw position and a wide gape. They are therefore innervated by a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), the mandibular .Incisors are the teeth that are present right in the front, on both the upper and the lower jaw.
The Anatomy of Teeth and Jaws
A motor and sensory branch of the trigeminal nerve. Author Information and Affiliations.The lower jaw is the largest and strongest bone in the human skull. This is the bone that moves as the mouth opens and closes.On the lower jaw, the mandibular premolar has a single root and the molars have one to two roots. Structure [edit | edit source]. It forms the mandibular dental arch and houses the .The lower jaw is formed by an unpaired mandible.Lower jaw (ramus of mandible) The ramus is the paired vertical part of the mandible that unites with the body and extends upward from it.Lower jaw (alveolar process of mandible) The alveolar process is the upper horseshoe-shaped portion of the body. Location of the masseter muscle: The masseter muscle spans . Each ramus of the mandible features several landmarks. The mandible plays a significant role in feeding ability.jaw, either of a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth of vertebrate animals, usually containing teeth and including a movable lower jaw and fixed upper jaw .
TMJ Anatomy
It is controlled by four bilateral muscles in the face. The main function of the mandible is to facilitate mastication (chewing) and all of the muscles of mastication attach to the mandible.
Mandible animation.Anatomy, Head and Neck, Mandible. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles.Auteur : The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Mandible
Each of its surfaces features different landmarks . It is composed of a horseshoe-shaped body which lodges the teeth, and a pair of rami which projects upwards to form a temporomandibular joint.The mandible hosts the .Jaw jerk reflex.
Mandibular Nerve: Function, Location, and Treatment
The flexibility and other movements of the jaw develop with the arrival of the permanent teeth.The submandibular glands are located in the submandibular triangle, which is underneath the mandible (lower jaw bone) and above the hyoid (tongue) bone. The mandible and maxilla are extensions of the bird’s skull, . The mandible, or lower jaw, is the bone that forms the lower part of the skull, and along with the maxilla (upper jaw), forms the mouth structure.Overview
The Mandible (Lower Jaw): Anatomy, Structures, and Function
The two central incisors usually remain smaller in size than the others.

It forms the mandibular dental arch and houses the mandibular teeth .
Understanding the Canine Jaw: Anatomy of Dogs Explained
This anatomy and the circular chewing motion enable an effective grinding of food.The premolar teeth (Latin: dentes premolares), also known as premolars and bicuspids, lie between the canines and first molar teeth.
Anatomy of Jaw Motion
The unpaired lower jaw has a body and two branches. Lateral pterygoid.Lower jaw (alveolar process of mandible) The alveolar process is the upper horseshoe-shaped portion of the body . This fusion is not complete even in the advanced age of a cow and thus forms the mandibular symphysis.Mandibular anatomy.Regarder la vidéo22:28The masticatory muscles attach to the mandible, and thus produce movements of the lower jaw at the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) to enable functions such as chewing and grinding.The human mandible, commonly known as the lower jaw, is the largest and strongest bone in the skull. These movements include: Protrusion (protraction), which moves the .The temporomandibular joints (TMJs) allow the lower jaw to move smoothly. Clinical aspects.Also, the upper jaw teeth are slightly wider. The teeth are divided into four quadrants within the .The mandible is the largest and strongest bone of the human skull.Therefore, these muscles are positioned within the head and neck around the mentioned joint.netMandible | Encyclopedia | Anatomy. The presence of interdental space . In addition, proper positioning of the upper and lower front teeth (the incisors) is required for the pronunciation of sibilants such as [s].In contrast to . Each of its surfaces features different landmarks described below.
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Mandible
Movement of the lower jaw opens and . Let’s take a closer look at some of the most important features of a bird’s beak. The jaw jerk test is rather straightforward and can be quickly performed. Test your knowledge on the anatomy of the tooth with this quiz. The two halves of the mandible bone fuse incompletely at the midline of the body.Each human has two jaws - the upper and lower jaw.
Jaw Definition & Meaning
The mandible (or lower jawbone, Latin: mandibula) is the only movable bone of the skull and the largest, strongest facial bone. Medial pterygoid. If left untreated, they can destroy the entire structure of the tooth and, in . The oral cavity houses four maxillary premolars (4, 5, 12, 13) in the upper jaw and four mandibular premolars (20, 21, 28, 29) in the lower jaw.Mandible jaw bone anatomy, parts, function & mandible . It is a single bone connected to the skull by the . Articulating Surfaces The temporomandibular joint consists of articulations between three surfaces; the mandibular fossa and articular tubercle (from the squamous part of the temporal bone ), and the .Browse Getty Images' premium collection of high-quality, authentic Jaw Anatomy stock photos, royalty-free images, and pictures. Updated on February 20, . Attached to it are major muscles for chewing .The mandible or lower jaw is the largest bone in the human skull. Responsible for the feeling in the chin and lower jaw. Types of teeth. Lower jaw (base of mandible) The base is the lowest, thickened part of the body of the mandible.The term “jaw” is referred to one or paired bones forming the framework of the oral cavity.; The lower jaw is formed by an unpaired mandible. The upper jaw (maxilla) holds the upper teeth, shapes the middle of the face, and supports the nose. In young children the jaw only moves up and down like a regular hinge. The mandible is the largest and strongest bone of the human skull. There are a total of 12 incisors, 6 each on either jaw, and they are small and sharp. The chewing surface of the upper and lower cheek teeth is not straight; it has an inclination of about 10 to15 degrees, formed by the chewing mechanism to help break down feed.In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin mandibula, 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lower – and typically more mobile – component of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). With a patellar hammer, tap the examining finger (not the patient’s chin) in an inferior direction. This joint allows for smooth and controlled movements of the jaw. The anterior surface of the body features the following structures:.Despite the wide variety of colors, shapes, and sizes, all bird beaks consist of the upper jaw (maxilla), lower jaw (mandible), and the keratinized outer layer (Rhamphotheca) that covers them. These animations were all mad. Dental caries are the most obvious and most common cause of all dental complaints.The muscles of mastication are associated with movements of the jaw ( temporomandibular joint ).Mastication, or the act of chewing, involves adduction and lateral motion of the jaw bone.A baby's lower jaw is generally short, as it's growth tends to be inhibited by the chin to chest position babies take in utero. The Mandible (Lower Jaw) (Inferior Maxillary Bone) The mandible, the largest and strongest bone of the face, serves for the reception of the lower teeth.: either of two complex cartilaginous or bony structures in most vertebrates that border the mouth, support the soft parts enclosing it, usually bear teeth on their oral margin, and are . It is a sturdy and dynamic bone that connects to the skull through the temporomandibular joint.

In this dissection we will . At the core of this intricate system is the mandible, commonly known as the lower jawbone. It is commonly known as the lower jaw and is located inferior to the .

appRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Mandible (Lower Jaw Bone)
Here, the symphyseal surfaces are extremely rough . Jaw Anatomy stock photos are available in a variety of sizes and formats to fit your needs. In contrast to the maxilla, the mandible is movable.Each side of the jaw (quadrant) contains two premolars.comMandible bone: anatomy and labeled diagram | GetBodySmartgetbodysmart.Cow lower jaw bone anatomy – mandible.
Bird Beaks and Skulls: Anatomy, Function, and Evolution
The mandible is the bone of the lower jaw, carrying the lower teeth and forming part of the temporomandibular joint with the temporal bones of the skull. The Anatomy of the Mandibular Nerve. The upper jaw is not movable as the maxilla is a fixated part of the skull. The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing joints with the cranium's temporal bones. By Adrienne Dellwo.The base is the lowest, thickened part of the body of the mandible.The temporomandibular joint (TMJ), or jaw joint, is a synovial joint that allows the complex movements necessary for life. It’s one of the branches of the inferior alveolar nerve, which is a branch of the trigeminal nerve ’s mandibular division. In craniometry, the midpoint on the lower border of the body is known as the gnathion. Overall, every adult has 8 . The movements of the lower jaw happen at the temporomandibular joint ( . The mental nerve is a sensory nerve that provides feeling to your lower lip, the front of your chin, and a portion of your gums.1 – Parts of the Skull: The skull consists of the rounded cranium that houses the brain and the facial bones that form the upper and lower jaws, nose, orbits, and other . The lower jaw (mandible) supports the bottom row of teeth and gives shape to the lower face and chin.In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the temporomandibular joint – its articulating surfaces, ligaments and clinical correlations.app | Learn anatomy | . When we chew food and speak the jaw movements can be forward and backward, sideways and circular. It’s the only large skull bone that can move and is essential .Structure of the tooth.such as [p, b, m, f, v]. The body of the lower jaw (corpus mandibulae) is curved by the convexity .The canine jaw consists of several components that work together harmoniously.