Antimicrobial use in food production
Despite antimicrobial use being the chief driver of resistance, US federal agencies do not collect or report farm-level use data nationally, despite recommendations for such collection from the Government Accountability Office [40–42].Its three main objectives are to determine and shape the patterns, purposes, and impacts of antibiotic use in food-producing animals, scrutinize antibiotic drug susceptibilities of bacteria in food-producing animals, production environments, and .The use of antibiotics has been very beneficial to human health, animal wellbeing, and food production, however, there are no alternatives to antimicrobials in treating infectious diseases.Food Animal Production and Antimicrobial Use Practices Since World War II, food animal production in the United States has been characterized by greater intensity (i. For the purposes of these guidelines, “food-producing animals” is considered an equivalent term to “food animals”. Subtherapeutic doses enhanced animal growth rates and feed efficiency while reducing mortality (Teillant and Laxminarayan 2015). Since 2000, meat production has plateaued in high-income countries but has grown by 68%, 64%, and 40% in Asia, Africa, and South America, respectively. Antimicrobial use in food animals selects for antimicrobial resistance in bacteria, which can spread to people. Microbial pathogens are the cause of many foodborne diseases after the ingestion of contaminated food.Auteur : Shashi B Kumar, Shanvanth R Arnipalli, Ouliana ZiouzenkovaIdentifying foodborne antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, including Salmonella and Campylobacter, in all 50 states using whole genome sequencing, . The transition to high-protein diets in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) has been .The available economic evidence strengthens the rationale for restricting antimicrobial use in U. Antimicrobial-resistant bacteria and/or antimicrobial resistance genes (transfer in pathogenic bacteria) may contaminate food at any stage, from the field to retail.
The use of antimicrobials in animal husbandry and the .We provide a baseline to monitor efforts to reduce antimicrobial use and assess how three global policies might curb antimicrobial consumption in food animal .Background: The administration of antimicrobial drugs to food animals at low doses for extended durations for growth promotion and disease prevention has been linked to the global health crisis of antimicrobial resistance.
Larson
Global trends in antimicrobial use in food-producing animals
Global use of antimicrobial substances in animal production for food (milk, eggs, and meat) was .
Benefits and risks of antimicrobial use in food-producing animals
Background: The administration of antimicrobial drugs to food animals at low doses for extended durations for growth promotion and disease prevention has been .Download PDFMetricsCitationPeer ReviewSurveillance of Antimicrobial Use in US Food Animal Production.
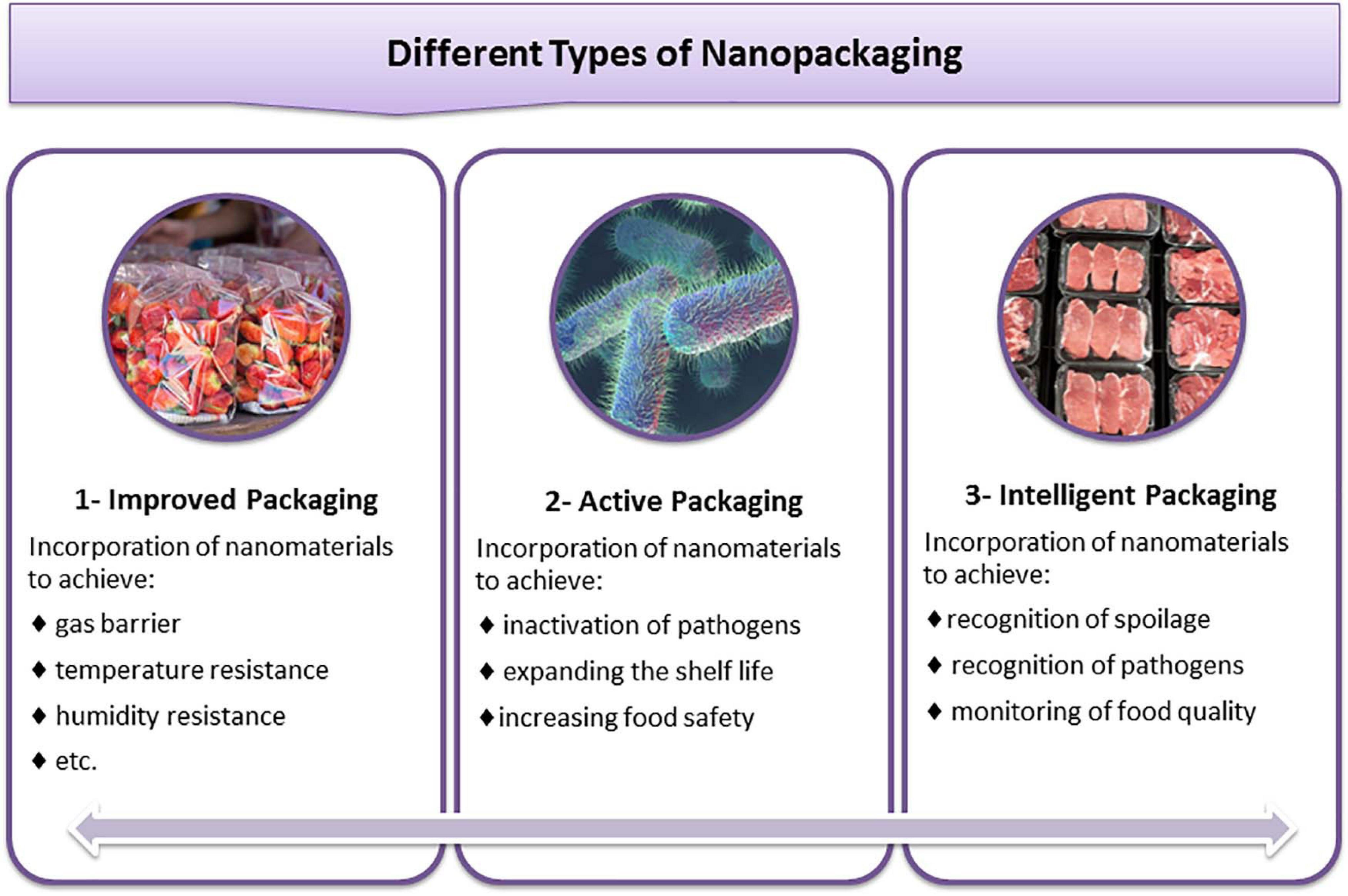
Food Safety through Natural Antimicrobials
Research highlights that foods .It is undeniable that rational use of antimicrobials plays a vital role in the production of food animals and protecting public health, while irrational and .Global utilization of antimicrobials in the production of food animals has been estimated at 63,151 (±1560) tons in 2010 and it is estimated to increase by 67% to 105,596 (±3605) tons by 2030. It is upon this . However, a major drawback of antimicrobial use is the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens in food-producing animals.Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance: An Overview of Priority Actions to Prevent Suboptimal Antimicrobial Use in Food-Animal Production Guillaume Lhermie 1,2* Yrjö T.Globally, antimicrobial usage was estimated at 99,502 tonnes (95% CI 68,535–198,052) in 2020 and is projected, based on current trends, to increase by 8. The term “food-producing animals” includes all terrestrial and aquatic animals (that is, includes aquaculture) used to produce food.The dominant model of food animal production in the United States and increasingly in other countries is characterized by large-scale, high-throughput confinement operations with herds or flocks that can range in size from hundreds to hundreds of thousands of animals [1, 2].It is reported that the food animal and livestock production sector used about 63,151 tonnes of antibacterial substances globally in 2010 and is expected to enhance by 67% by 2030 (Laxminarayan et al.Auteur : Timothy F. In terrestrial animal production, potential sources are feed, humans, water, air or dust, soil, wildlife, rodents, arthropods, and equipment, says EFSA.

A literature review was conducted on antimicrobial use and resistance in food animal production in Southeast Asia for the period 2011–2020, to assess the scope and extent of antibiotic use and resistance.Antimicrobial use is likely to increase with even exacerbated outcomes unless cost-effective, safe, and sustainable alternatives to antibiotics, especially .In FY 2019, FDA’s Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) developed a five-year action plan for supporting antimicrobial stewardship in veterinary settings.
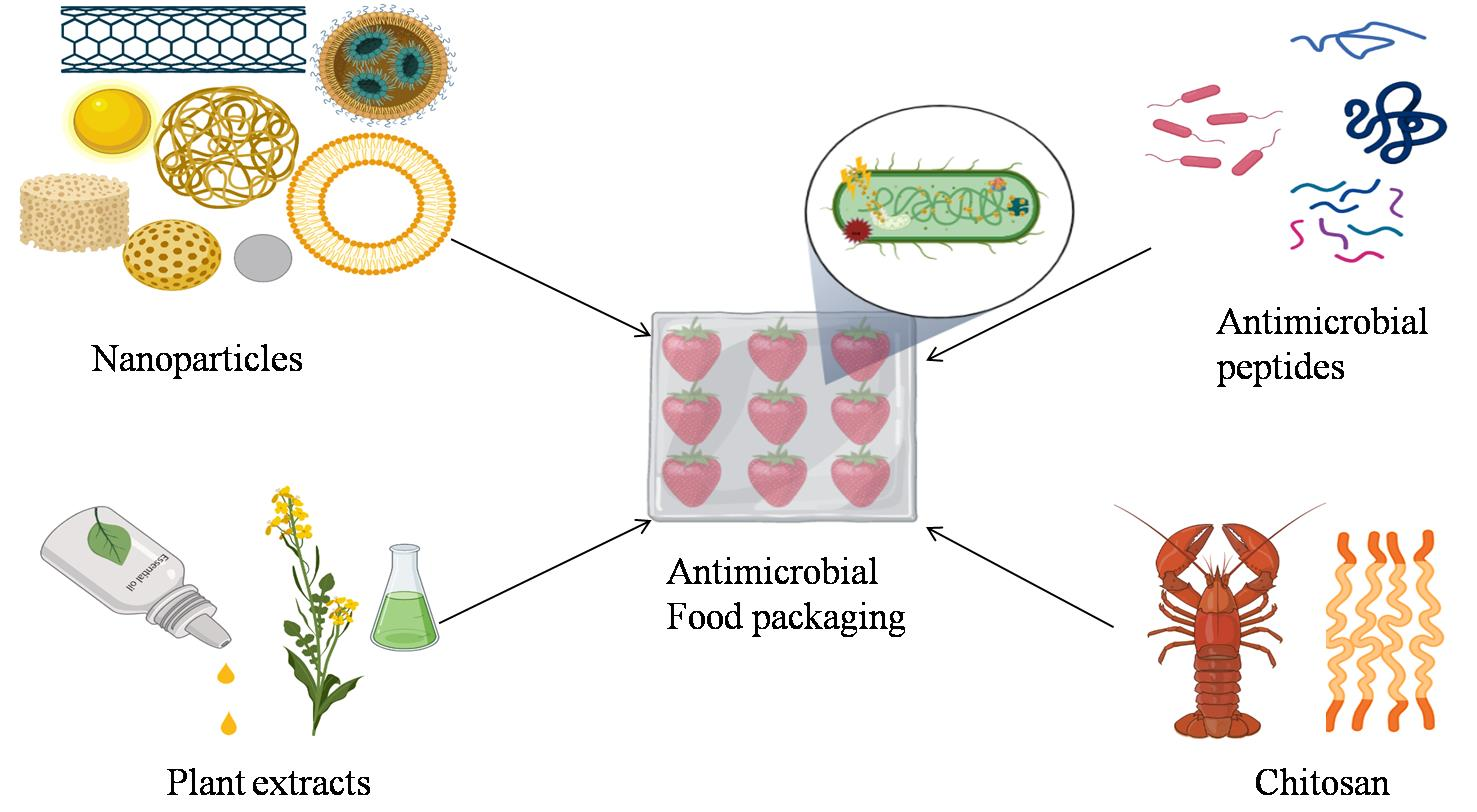
Many microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, parasites) are able to contaminate foodstuffs and cause a variety of .The ongoing occurrence of foodborne diseases and the imperative need for efficient spoilage and pathogen control in food products constitute a critical challenge for . The work of ANSES.
Antimicrobial Resistance Through Food: Role of Food Safety
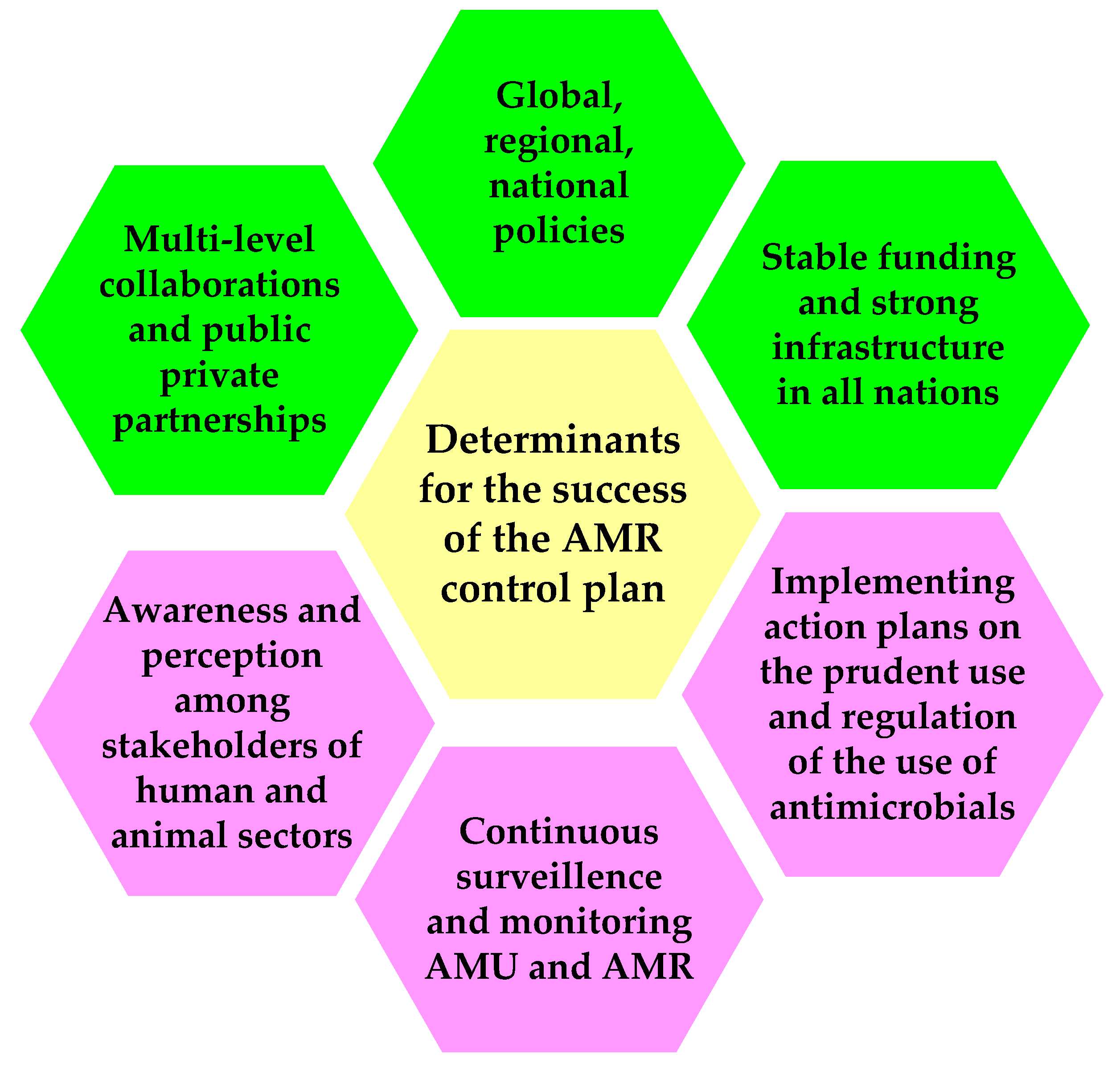
Antibiotic use plays a major role in the emerging public health crisis of antibiotic resistance.The control of antibiotics in food animal production is an important factor in combating antimicrobial resistance worldwide, because (i) antibiotics widely used in food-producing animals are identical to, or use a similar mechanism, to antibiotics used to treat bacterial infections in humans; (ii) the volume of animal antibiotic use, including for growth .This review examines current research on FPH production methods and their antioxidant and antibacterial activities.Scale of Antibiotic Use in Animals and Humans.1015950 farming, and how antimicrobial-resistant bacteria and AMR were transferred via food consumption (24).Microbiological risks in food. Furthermore, in existing studies, neither the risks to human health nor the benefits to animal production have been well studied.Antimicrobial drugs are used globally to treat infections in humans and animals and prophylactically in production agriculture.These animals are typically supplied with drinking water and . Internationally, multiple jurisdictions have responded by restricting antimicrobial use for these purposes, and by . To reduce the use of .The RENOFARM initiative aims to provide countries with policy support, technical assistance, capacity building, and knowledge sharing to help reduce the need . Landers, Bevin Cohen, Thomas E. The additional 34% rise will depend on the implementation of intensive farming systems by 2030.Antimicrobial resistance is an emerging global threat to public health.FDA has released the 2021 Summary Report on Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Use in Food-Producing Animals, which showed that domestic sales and distribution of . Several preservation methods have . Although the majority of antibiotic use occurs in agricultural . Few researches were involved in consumers' knowledge and attitude toward antimicrobial use (AMU) in food production.3390/antibiotics11010066.In our review, we found that the use of antibiotics in food animals is widespread, yet poorly characterized. This study was designed to investigate the knowledge and awareness, perception, and attitude of Chinese .WHO has launched new guidelines on use of medically important antimicrobials in food-producing animals, recommending that farmers and the food industry stop using .(1) Introduction: Antimicrobial agents have played an important role in improving the productivity of worldwide livestock production by reducing the impact of livestock diseases.Antimicrobials are frequently used in food animal production. The resistant bacteria in food animals can be transferred to humans through the food chain.
Reducing antimicrobial use in food animals
In addition to subsidising antibiotic research and tackling human overuse, most actors have also committed to reducing antibiotic consumption in food .PMCID: PMC8772955.

Medically important antimicrobials Antimicrobial classes used in human .
This review presents the current and comprehensive antimicrobial usage practices in food animal production across Sub-Saharan Africa and highlighted the overall regional drivers as well as the public health, environmental, and economic impact of antimicrobial use in the production of food animals.Auteur : Vanmathy Kasimanickam, Maadhanki Kasimanickam, Ramanathan Kasimanickam
Global trends in antimicrobial use in food-producing animals
2 minutes read.Antibiotics in Our Food System.Antimicrobial consumption by animals is currently twice than that used by . The alarming situation is not the resistance by a single species of bacteria to a particular antimicrobial but to more than one class of . The rise of dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a public health crisis, and routine antibiotic misuse in industrial agriculture is .Animals used in production of food.Antimicrobial use (AMU) in animal production is a key contributor to antimicrobial resistance (AMR) worldwide., fewer but larger farms) and scale of production ( figure 1 ), improved infectious disease management, and better nutrition [ 5 ]. food animals, and available data suggest that restrictions on growth promotion may not be detrimental to production in the long run, although additional research could be useful. Gröhn 1 Didier Raboisson 3 1 Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA Individual producers rarely report data on .Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) can be induced by overuse or misuse of antimicrobials.The widespread use of antimicrobials in the animal feed surged as manufacturing and production costs decreased.In Africa, there is dearth of information on antimicrobial use (AMU) in agriculture and food production systems and its consequential resistance in pathogens . This practice provides some .The animal production industry is a major user of antimicrobial agents which are necessary to meet the increasing demand of animal proteins for the growing world population. A recent study provides a . Therefore, food animal producers are important participants to prevent overuse and misuse of .Modern animal production practices are associated with regular use of antimicrobials, potentially increasing selection pressure on bacteria to become resistant. The use of antimicrobials in food .Two-thirds (66%) of global antimicrobial consumption growth (67%) is due to the increasing number of animals raised for food production. Share: Fertilisers of faecal origin, irrigation, and water are the most significant sources of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in plant-based food and/or aquaculture.


Descriptives of antimicrobial use and resistance, consensus regarding antimicrobial use and resistance indicators were arrived at through relevancy rating by a panel of 40 judges in the field of .Globally, antimicrobial usage was estimated at 99,502 tonnes (95% CI 68,535-198,052) in 2020 and is projected, based on current trends, to increase by 8.The global scale-up in demand for animal protein is the most notable dietary trend of our time. It is commonly asserted that agricultural production systems must use fewer antibiotics in .Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains of major interest for different types of food stakeholders since it can negatively impact human health on a global scale. Reducing use of antimicrobials—particularly those deemed to be critically important for human medicine—in food production animals continues to be an important step for preserving . As consumption of animal protein and associated animal production is forecast to increase markedly over coming years in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), accurate monitoring of AMU has become .Antibiotics are frequently used in food animal production in developing countries to promote the well-being and growth of animals.











