Applied overhead equation
Suppose the company produces two products, A and B. In order to perform the traditional method, it is also important to . The first step is calculating total manufacturing overhead costs for a specific period or accounting cycle.
In other words, it’s the amount of costs incurred by the company during in a production process that can’t be directly traced back to a specific product or service, but should be included in . This last situation is called underapplied overhead. Managing and accurately tracking these expenses can mean the difference between a successful construction project and one that loses money. Khadija Khartit. If the total manufacturing overhead is $100,000, the allocation would be: . Overhead cost = Recovered overhead - Actual overhead variance.
Applied Overhead: What it is, How it Works, Example
0 To adjust for overapplied or underapplied manufacturing overhead, some companies have a more complicated, three-part allocation to work in process, finished . If your overhead allocation rate is $100 per .Applied overhead. AO = R * T AO = R ∗ T. Determine direct materials and direct . Job Order Costing.Overhead Rate: In managerial accounting , a cost added on to the direct costs of production in order to more accurately assess the profitability of each product. To calculate a predetermined overhead rate, divide the manufacturing overhead cost by the units of .Over the fiscal year, the actual costs are recorded as debits into the account called manufacturing overhead. We know overhead is applied using estimated or budgeted overhead and a base. When the overhead is applied to the jobs, the amount is first calculated using the application rate. The resulting figure, 20%, represents our company’s overhead rate, i. Last updated 03/15/2024 by. The predetermined overhead rate is an estimation of overhead costs applicable to “work in progress” inventory during the accounting period. By definition, overhead cannot be traced directly to jobs. MOC is the manufacturing overhead cost. Most company use a predetermined overhead rate (or estimated rate) instead of actual overhead for the following reasons: . Multiple choice question. total cost equation. If the situation is reverse and the . POR = MOC / UA POR = MOC /U A.overapplied overhead. Some key points on overhead rate calculations: The allocation measure in the denominator should have a causal relationship with overhead . Traditional allocation involves the allocation of factory overhead to products based on the volume of production resources consumed, such as the amount of direct labor hours consumed, direct labor cost, or machine hours used. Actual overhead costs may be different and we will not have all of those costs until late . The amount assigned could be based on an estimate, rather than the .This video explains what a predetermined overhead rate is and illustrates how to calculate and apply the predetermined overhead rate with an example. Thus, it helps in product pricing and aids in deciding the fixed price to . These costs may include rent, utilities, salaries and wages of support staff, depreciation, insurance, and other expenses that . Also, there can be other bases for allocating fixed overheads apart from production units.For example, the actual overhead rate for a company is $10 an hour, Therefore, actual overhead is $10,000 by the equation $10 x 1,000 hours.If the overhead was overapplied, and the actual overhead was $248,000 and the applied overhead was $250,000, the entry would be: Figure 8. = 44,000 - 62,000 = 18,000 (unfavorable) The total overhead cost variance can be analyzed into a budgeted or spending variance and a volume variance. Applied overhead = 0.comExamples of Overhead Costs: Top 11 Examples | Cost .accountingnotes.Applied overhead is the amount of overhead cost that has been assigned to a cost object.debit overhead, credit COGS. Process Costing. Overhead costs are all costs that . If the total labor paid for the job is $66, the overhead applied to the job is $2. a costing system used in situations where many different products, jobs, or services are produced each period.The overhead rate is applied to determine the amount of overhead to be charged to a job. Investopedia / Matthew Collins. Direct costs typically are direct labor, . Subtract the budgeted overhead costs from the actual overhead costs to determine the applied overhead.If manufacturing overhead has a credit balance, the overhead is overapplied, and the resulting amount in cost of goods sold is overstated. = 2 x 20,000 = $40,000.Enter the average overhead allocation rate and the total number of hours into the calculator to determine the applied overhead. actual < applied.The following equation is used to calculate the predetermined overhead rate. Bamigbola Paul.The formula is: Manufacturing Overhead Applied = Overhead Allocation Rate x Actual Amount of Chosen Allocation Base. Fact checked by. net operating income net operating assets cost of goods manufactured cost of goods sold, The difference between overhead applied to work in process and actual overhead is . Follow these steps to accurately calculate your company’s manufacturing overhead applied: Step 1: Determine Your Total Manufacturing Overhead Costs.
Applied Overhead Calculator
Manufacturing overhead = Indirect materials + Indirect labor + Utilities + Physical costs + Financial costs + Additional manufacturing expenses.50 times that amount, or $165.Standard overhead = Standard rate per hour x Actual hours. Applied overhead = Predetermined overhead rate x Actual activity base units. Fixed overhead budget variance = $19,000 – $17,500 = $1,500 (F) With the result above we can conclude that the $1,500 of the fixed overhead budget variance is favorable, in which it means that the company ABC spends less than the budgeted cost in this area by . For example, if your total monthly sales were $850,000, and your monthly overhead costs were $400,000 your overhead rate for the month would be calculated as follows: $400,000 / .Understanding applied overhead is integral to accurate job costing and ensuring a construction project's profitability.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Gross margin minus selling and administrative expenses equals Blank______.Updated July 31, 2021.

If actual factory overhead is $95,000 then underapplied overhead is $5,000 ($95,000 – $90,000).Applied Factory Overhead. The adjusting entry is: Figure 8.The equation for the overhead rate is overhead (or indirect) costs divided by direct costs or whatever you're measuring.You can use the following formula to calculate applied overhead: Applied overhead = estimated amount of overhead costs / estimated activity of the base . Hence, applied overhead is a crucial financial aspect of any construction project. A more likely outcome is that the applied overhead will not equal the actual overhead.netRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
(Definition, Formula and Example)

Calculate overhead rate percentage; Once you’ve calculated all of your indirect expenses, you’ll need to complete another calculation for your overhead rate percentage.
Overhead Absorption
2490 x 6,000 = 1,494. It is said to be an “unfavorable” outcome, because not enough jobs were produced to absorb all of the . Since we will be using the concept of the predetermined overhead rate many times during the semester, lets review what it means again.comApplied overhead definition — AccountingToolsaccountingtools. Where POR is the predetermined overhead rate. Where AO is the applied overhead .
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance
Predetermined Overhead Rate Calculator
Accounting For Actual And Applied Overhead
Manufacturing overhead is part of a company’s manufacturing operations, specifically, the costs incurred outside of those related to the cost of direct materials and labor.The formula is: Applied overhead = predetermined overhead rate (total amount of overhead cost / total activity) x base unit's estimated activity.Apply overhead to products or services: Multiply the overhead application rate by the specific amount of chosen allocation base incurred during the production of each .Overhead Rate = $200,000 / 50,000 hours = $4 per direct labor hour This $4 per hour overhead rate would then be applied to the number of direct labor hours for each job to allocate overhead costs.
Overhead Rate
DM cost + DL cost + applied overhead.Component Categories under Traditional Allocation. Overhead Rate = $40k ÷ $200k = 0.
Overhead Absorption Rate: Formula, Examples and Guide

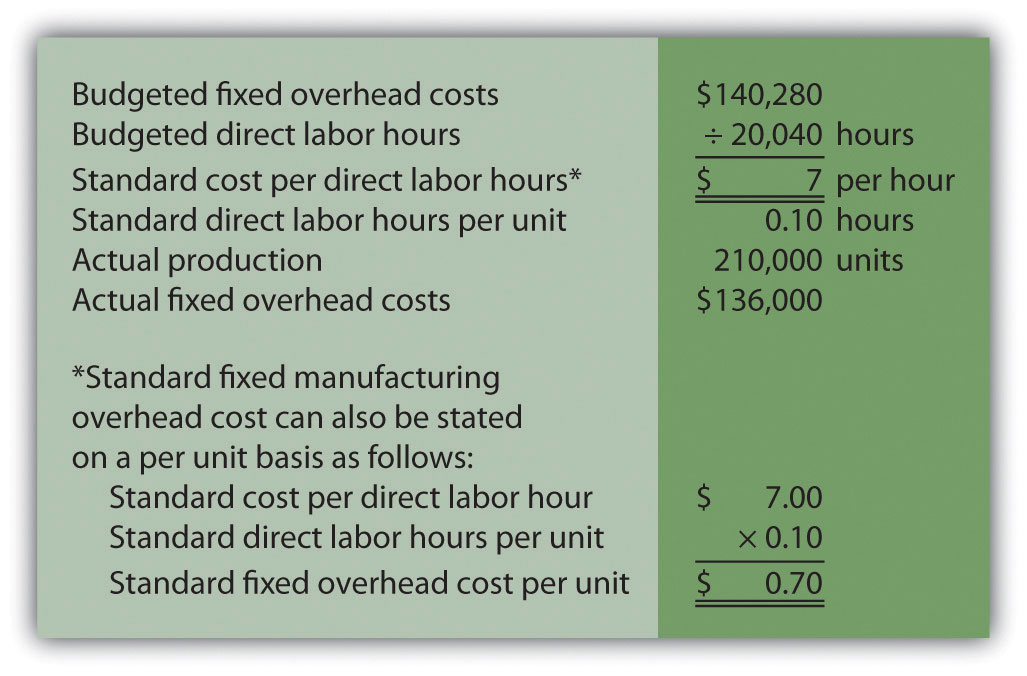
Standard Fixed Overheads = Budgeted Fixed Overheads ÷ Budgeted Production. These allocation .You can calculate applied manufacturing overhead by multiplying the overhead allocation rate by the number of hours worked or machinery used. If the total production overhead is $15,000 and the cost of direct materials is $60,000, . In our example, $10,000 minus $8,000 equals $2,000 of underapplied . They are considered the direct cost and are recorded using a cost accounting methodology. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like PDR equation, applied overhead equation, COGM . See the Explanation of Standard Costing. What Is Applied Overhead? Applied overhead is a type of direct overhead expense that is recorded.Find your predetermined overhead rate by using this formula: Predetermined overhead rate = estimated overhead / estimated activity Your result from this equation will be an amount in dollars and cents. The following graphic shows a case where $100,000 of overhead was actually .
Fixed Overhead Budget Variance
This dollar and cent amount returns in step three when it's time to find the applied overhead rate. Manufacturing Overhead = Cost of Sales – Changes in Finished Goods and Work in Process – Raw Materials used and Merchandise Purchased – Wages and .

We must now take the $40k in overhead costs and divide it by the $200k in monthly revenue assumption.
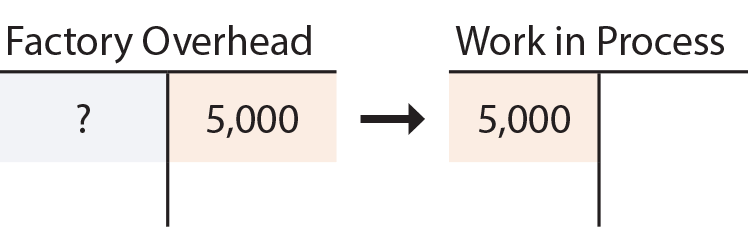
income statement. 15,000 machine hours are actually worked and overhead applied to production is therefore $90,000 (15,000 hours × $6).
Predetermined Overhead Rate
Step 1: Identify your total overhead expenses.Calculating Manufacturing Overhead Applied: Step by Step Guide.Definition: Applied overhead is the amount of indirect costs that can’t be specifically matched to the production of a product but must be assigned to a cost object.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Applied Overhead & Actual Overhead
Include all indirect expenses . The cost is mainly used to determine the expenses incurred during the production process.Applied overhead is the expenditure rate that is applied to a cost item.
Over-applied and Underapplied Overhead
5 Under- or Over-applied Overhead.Applied overhead are those factory costs that are linked to a particular unit of production. sales rev - adjusted COGS - S&A expenses = operating income - income tax expense = net income. In more technical .
Applied Overhead: Definition, Examples, and Strategic Insights
UA is the unit of allocation.Applied overhead is a fixed amount of cash added to a unit’s production cost in order to take into account the indirect costs of production.The following formula is used to calculate an applied overhead.Manufacturing overhead assigned to units of output.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 1 min
How to Calculate and use the Applied Overhead Formula
If a job in work in process has recorded actual labor costs of 6,000 for the accounting period then the predetermined overhead applied to the job is calculated as follows.
How to Calculate Manufacturing Overhead
An item to which the costs incurred in producing goods or services would be allocated is .
How to Calculate Applied Overhead
A costing method used when essentially homogeneous products are produced on a continuous basis. It plays a crucial role in project management and .9 By: Rice University Openstax CC BY SA 4.

Product A requires 40% of the total machine hours, while Product B requires 60%.