Atypical ductal hyperplasia breast surgery
Women with atypical hyperplasia have about 3 to 5 times the breast cancer risk of women without a proliferative breast condition [ 188-191 ].Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia: Symptoms and Treatment - . Recent research suggests that women with no mass lesion or discordance, .Learn how a diagnosis of atypical lobular hyperplasia or atypical ductal hyperplasia affects your risk of breast cancer and what you can do.orgAtypical ductal hyperplasia: update on diagnosis, .If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia, it's important to learn as much as possible about the condition.
Vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (VAB) excision of microcalcifications with extension lower than one centimetre as an alternative to open biopsy for atypical ductal hyperplasia. About Mayo Clinic.Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) are commonly encountered in breast imaging and are on the same spectrum of disease, on which ADH is a high-risk lesion that increases the risk of invasive breast cancer in both breasts and DCIS is a nonobligate precursor to invasive breast cancer.verywellhealth. Doctors often .4 (95% confidence interval [CI], 3. Hartmann, Amy C.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia: What it is and how it's treated
Breasts are made up of: The ducts spread from the lobes towards the nipple.
Surgical management of ADH, ALH, and LCIS
The upgrade rate to carcinoma was 37.Atypical cells, or atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH): These cells in your milk ducts multiply rapidly and grow abnormally.
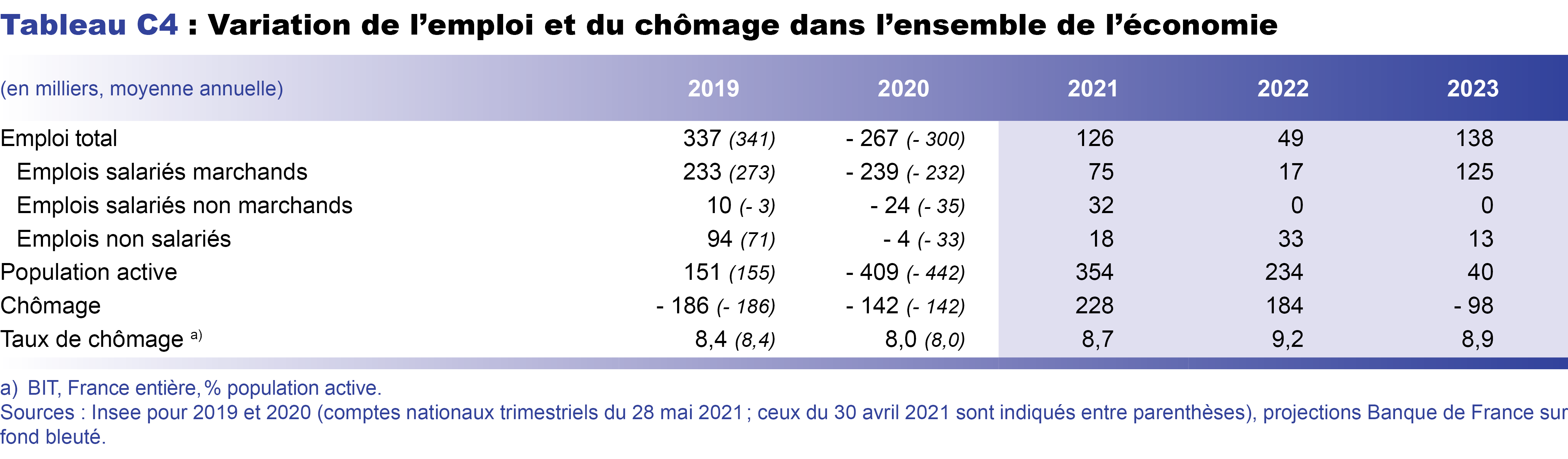
Atypical hyperplasia of the breast
2 Since the time that report was published, other investigators using either cohort or case–control study designs have shown consistently that the relative risk associated with both .Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia (ADH) is a benign but high-risk lesion of the breast for which surgical excision remains the standard of care. Patient-Centered Care. It remains controversial whether it is necessary to re-excise AH found at surgical margins during breast-conserving surgery (BCS).Purpose Atypical hyperplasia (AH) is associated with a relatively higher risk of subsequent development of cancer.govAtypical Hyperplasia of the Breast - New England Journal .breast-cancer-research.Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) is a small, low grade intraductal lesion of the breast, commonly identified as suspicious microcalcifications seen on screening mammograms [1,2,3].Auteur : Tanjina Kader, Tanjina Kader, Prue Hill, Emad A Rakha, Ian G Campbell, Ian G Campbell, Kylie L Gorri.What's atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH)? It's the name given to a condition that can occur in the lining of the milk ducts in the breast. It doesn’t typically spread beyond your milk ducts, like .Watch Excisional Biopsy for Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia by Sarah A.8 Things You Should Know About Atypical Ductal . When needle core biopsy (NCB) of the breast yields atypical ductal .Among lesions with uncertain malignant potential found at percutaneous breast biopsy, atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) carries both the highest risk of underestimation and . Dupont, Karthik Ghosh The most important implication of finding atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) or lobular neoplasia—atypical lobular hyperplasia (ALH) or lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)—is that the patient is at a significantly increased lifetime risk of developing breast cancer (1–2 percent per year for ADH or ALH, and approximately 2 .

Clinical practice guideline for diagnosis and treatment of hyperplasia of the mammary glands: Chinese Society of Breast Surgery (CSBrS) practice guideline 2021.
Breast Cancer Risk: Usual and Atypical Hyperplasia
There is concern .
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia: Breast Cancer Risk and More
After a diagnosis of ADH on biopsy a proportion are upgraded to carcinoma upon excision; however, the remainder of patients are overtreated.Absolute risk of breast cancer is approximately 1% per year for at least 25 years, with a mean latency period of 8 - 12 years after initial diagnosis. With usual ductal hyperplasia, these extra cells look .As more women are undergoing breast cancer screening and more sensitive imaging techniques are used, the detection of high-risk lesions such as atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) and lobular neoplasia (including ALH and lobular carcinoma in situ [LCIS]) on CNB is increasing [1–4].
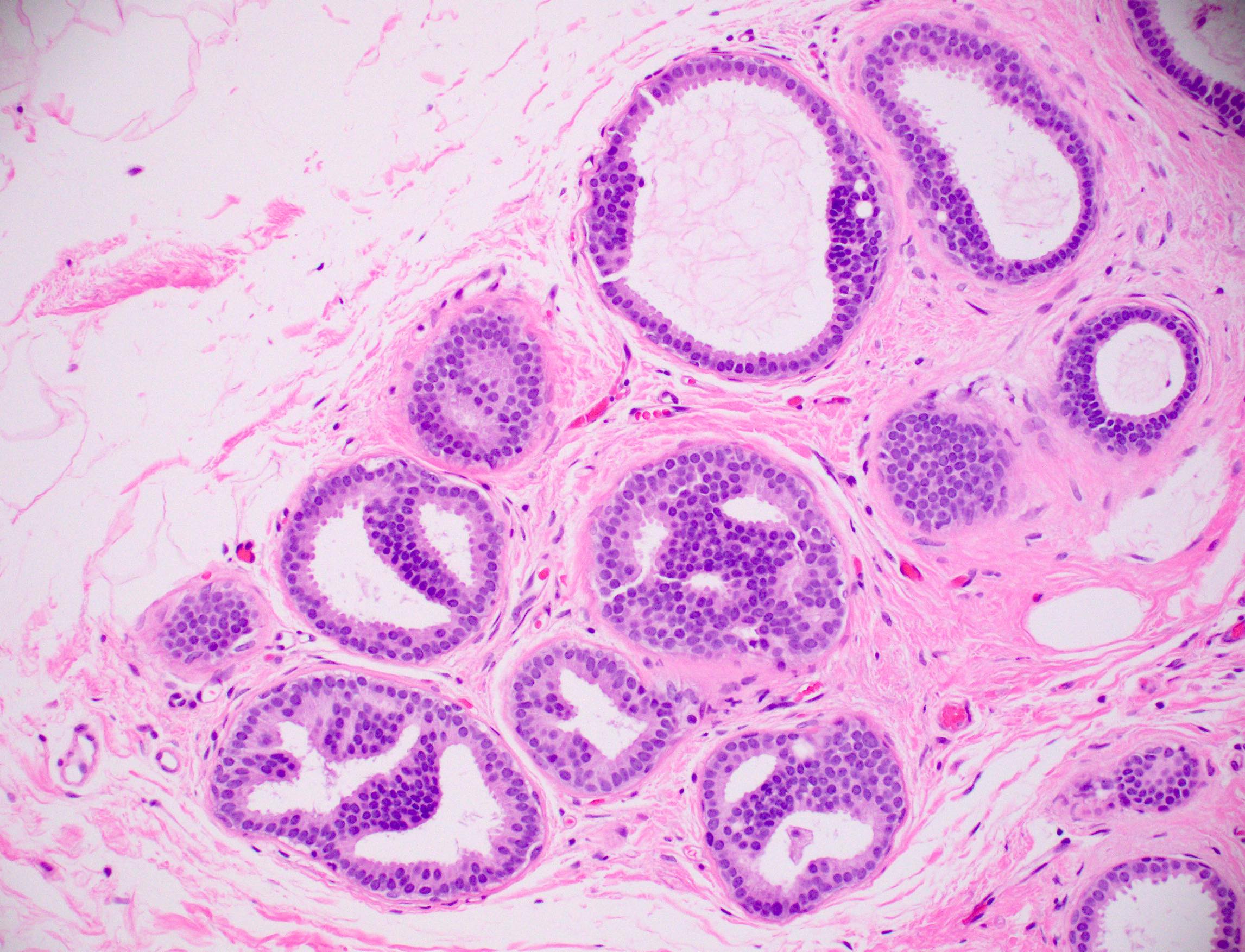
Multiple investigations . Surgical excision remains the standard recommendation following a core needle biopsy result consistent with ADH.
Pathology Outlines
Only about 3% of intraductal papillomas get upgraded to ADH.

Atypical ductal hyperplasia is an overgrowth of abnormal cells in the milk ducts in the breast. They can transform into cancer cells. Connect to Support Groups.For patients with atypical ductal hyperplasia identified on core needle biopsy, surgical consultation is recommended to discuss if surgical excision is warranted . The surgeon recommended surgery to remove the calcifications in the area., explains how it’s diagnosed and treated as well as its relationship to breast cancer. The finding of cancer at surgical excision of a high-risk breast lesion is termed “upgrade.

Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) is a pathologic finding in breast tissue.Atypical hyperplasia is a precancerous condition that affects cells in the breast. Atypical ductal hyperplasia usually doesn't cause any notable symptoms. Normally each duct is lined with an even layer of cells, but in the area affected by ADH there can be many layers.Auteur : Lynn C. Care at Mayo Clinic. In ductal hyperplasia, a person has more than two layers of cells in the breasts. Clinicians should counsel women with atypical hyperplasia regarding risk-reducing strategies, which include preventive endocrine therapy options, . For a summary of research studies on atypical hyperplasia . With atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), there are more cells than usual in the lining of the breast duct, the tube that carries milk from the lobules . In this study, surgery was performed in 48 out of 101 women with ADH on percutaneous breast biopsy in two Swedish hospitals.February 1, 2018.Of the 1–2 million breast biopsies that are performed in the United States per year, 8–17% will be positive for ADH [4,5,6,7,8,9]. It’s when the cells in the breast increase in number and also develop an unusual shape. Come learn now at GIBLIB!Watch the full medical talk at https://app.Atypical ductal hyperplasia: breast DCE-MRI can be used to reduce unnecessary open surgical excision. ADH isn’t cancer, but it may raise your risk of getting breast cancer in the future.Atypical hyperplasia is found in approximately 10% of all benign breast biopsies. Of those 6458 ADHs, 5911 were managed with surgical excision and 547 were managed with imaging follow-up.Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) is a common diagnosis in the mammographic era and a significant clinical problem with wide variation in diagnosis and .The study by Schiaffino et al is a meta-analysis of 93 articles that include 6458 cases of ADH. Clinical Trials.Atypical hyperplasia of the breast is defined as abnormal epithelial proliferative breast lesions that are not qualitatively or quantitatively abnormal enough to be classified as carcinoma in situ.How to cite this article: Ma W, Jin ZN, Wang X, Fu FM, Guo WH, Xu YY, Chen B, Jin F, Wang C, Yao F; Chinese Society of Breast Surgery.It is considered a benign but . The name of the entity is descriptive of the lesion; ADH is characterized by cellular proliferation (hyperplasia) within one or two breast ducts and (histomorphologic) architectural abnormalities, i. It is associated with a substantial increase in lifetime risk for breast cancer.Atypical hyperplasia of the breast is a histopathologic lesion identified incidentally on image-guided breast biopsy. Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) is a proliferative, nonobligate precursor breast lesion and a marker of increased risk for breast carcinoma. Certain radiological and cytological criteria can be used to help determine which patients should forgo surgery and be followed up with good results. the cells are arranged in an . Skip to content. Atypical hyperplasia can occur in the ducts (atypical ductal hyperplasia or ADH) or the lobules (atypical lobular . Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS): DCIS is a noninvasive or preinvasive cancer.comWhen Does Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia Require Surgical . Degnim, Richard J. My maternal grandmother had breast cancer when she .Atypical ductal hyperplasia occurs when you have abnormal cells in the milk ducts of your breast.Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) affects the cells of the milk ducts in the breast.Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) is one of the most common high-risk lesions of the breast and confers an increased lifetime risk of developing invasive breast .Atypical ductal hyperplasia and its management. Chin Med J 2021;134:1891–1893. The aim of this study was to determine the impact of atypical ductal/lobular hyperplasia found at .International guidelines recommend open surgery for atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) in the breast due to risk of underestimating malignant disease. Although most . Published: 07 March 2020. Patient & Visitor Guide.Atypical hyperplasia is a non cancerous (benign) condition.Diagnosis
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia (ADH)
Breast cancer surgeon Kelly Hunt, M. In efforts to limit excision to those with highest upgrade risk, we sought to determine if breast magnetic resonance imaging has value in . A stereotatic breast biopsy determined I have Cribriform ductal hyperplasia approaching atypical ductal hyperplasia. You may need surgery to be sure that you don’t also have breast . The other option is monitoring the condition with mammograms in six months. Atypical hyperplasia describes an accumulation of abnormal cells in the milk ducts and lobules of . In 2018, our group published a study on 65 percutaneously diagnosed ADH on a single group of microcalcifications—completely removed after VAB 13 —considering .Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed on percutaneous breast biopsy typically undergoes surgical excision, upgrading to invasive breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ in 10% to 53%. It is usually a subsequent finding of a biopsy done to evaluate a benign breast lump or findings on mammogram . A needle biopsy (a procedure to take a small sample of tissue) can show if you have ADH. Surgical excision is currently recommended for all occurrences of atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) found on core needle biopsies for malignancy . Breast surgery specialists/nurse practitioners Erica Campanaro and Emily Brown . Atypical ductal hyperplasia is usually identified incidentally on specimens obtained by needle biopsy prompted by abnormal findings .Conclusion: Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed on breast biopsy is associated with a relatively high incidence of invasive carcinoma and high grade ductal carcinoma in situ at the time of surgical excision.