Awhonn variable deceleration definition

Balises :Linear AlgebraVecteur AccélérationVecteur VitesseMètres Par SecondeLa variance d'Allan est une grandeur mathématique fréquemment utilisée pour estimer la stabilité dans le temps de la fréquence des oscillateurs quels qu'ils soient. The gradual FHR decrease is defined as from the onset to FHR nadir of ≥30 seconds.Late decelerations occur when a fall in the level of oxygen in the fetal blood triggers chemoreceptors in the fetus to cause reflex constriction of blood vessels in nonvital peripheral areas in order to divert more blood flow to vital organs such as the adrenal glands, heart, and brain.Support the School of Medicine. Explore quizzes and practice tests created by teachers and students or create one from your course material. List interventions based on analysis of fetal monitoring tracing. So you can see how variable decelerations is a complete mix. The fracture pattern may thus be very similar to an axial loading injury.Variable Deceleration Visuallyapparent abruptdecrease in FHR. List interventions based on analysis of .The primary goal of antepartum fetal surveillance (antepartum testing) with the nonstress test (NST) and the contraction stress test (CST) is to identify fetuses at risk of hypoxic injury or death and intervene to prevent these adverse outcomes, if possible.EFM: Screening Test
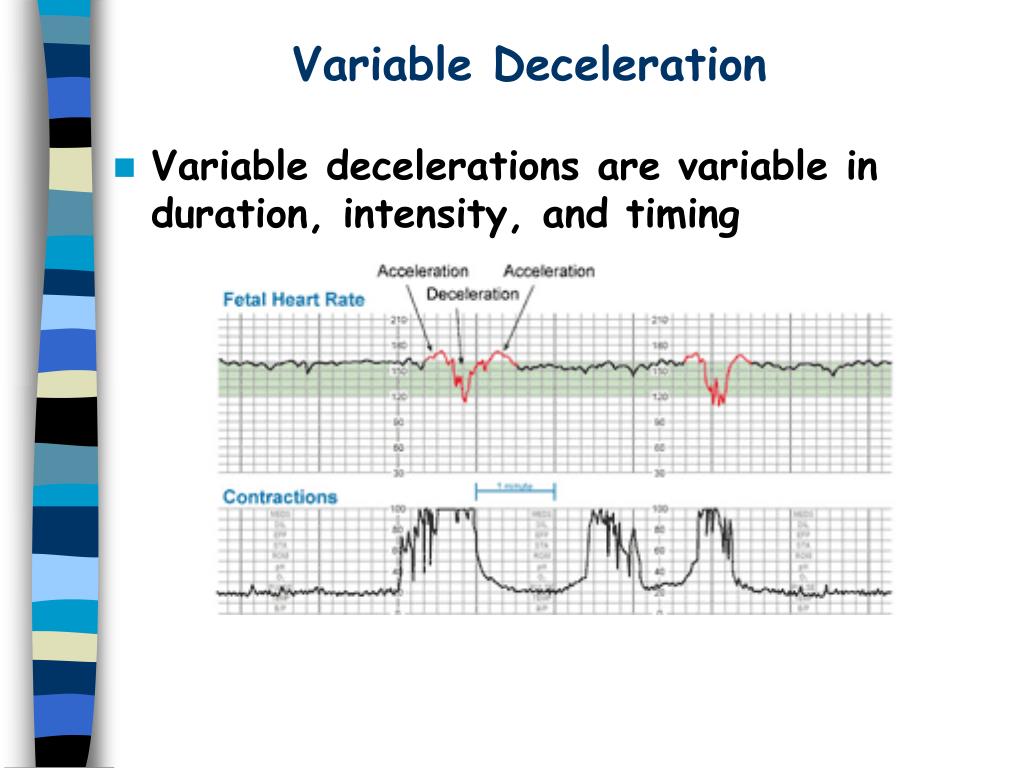
Variable Decelerations
It can be early .
Fetal Assessment During Labor
A sinusoidal pattern has regular amplitude and frequency and is excluded in the definition of variability.comFetal Monitor Strips Examples Flashcards | Quizletquizlet.Continuous fetal monitoring, or cardiotocography, is a method of tracking the fetal heart rate (FHR) along with the occurrence of uterine contractions. Remember a normal fetal heart rate is 110-160 bpms. During a contraction, the toco detects. pressure created by the tensing of uterine muscles.• The decrease in FHR is calculated from the onset to the nadir of the deceleration.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Advanced Principles in EFM Speaking The Language of the Fetus
UC San Diego School of Medicine and LCME Accreditation The UC San Diego School of Medicine is fully accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education (LCME).
Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring
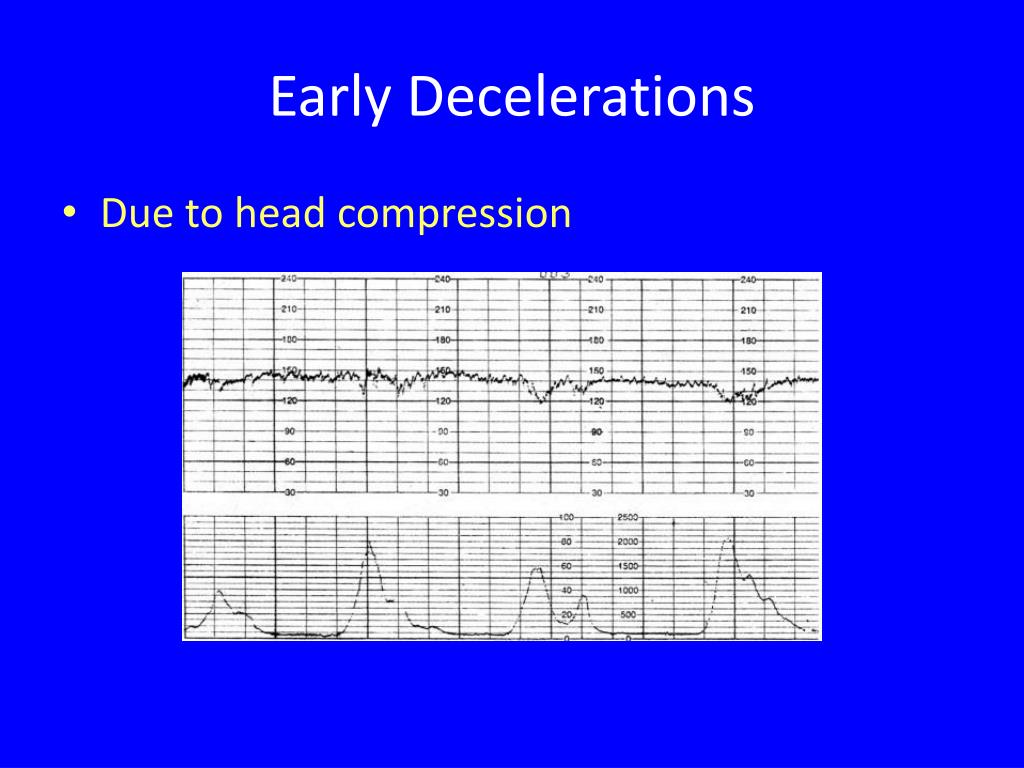
Decelerations are first examined by the onset of the deceleration and are classified as “abrupt versus -gradual onset. Early deceleration. The secondary goal is to identify normally oxygenated fetuses so that pregnancy can be .
Early Decelerations
This column will explore the evidence behind the classification of .L'accélération est donc la « variation, par seconde, des mètres par seconde », soit des « (mètres par seconde) par seconde », (m/s)/s ; que l'on appelle « mètres par seconde au . This course includes lecture, hands-on skill stations including performing Leopold maneuvers, placement of an intrauterine pressure catheter .orgREADING AND INTERPRETING A FETAL HEART RATE .
(leçon)
The first variable deceleration that you can see fully begins well before the peak of the next contraction.Deceleration: severe variable, severe repeated early, prolonged, late or sinusoidal* *A sinusoidal pattern is regular with cyclic changes in the FHR baseline, such as the sine .Human and animal studies have demonstrated an association between decreased amniotic fluid and the occurrence of variable decelerations in the fetal heart rate. The v’s remind me that this is a “variable deceleration”.comFetal Heart Rate Monitoring During Labor | ACOGacog. Variable deceleration.comElectronic fetal monitoring. Following birth, a fetal cord blood sample is . The onset of the .Early deceleration is defined as a symmetrical decrease and return of fetal heart rate (FHR) that is associated with a uterine contraction.Balises :Intrapartum Fetal MonitoringObstetrics and Gynecology
Fetal Heart Monitoring
ppt | PPT - SlideShareslideshare. However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check other . The school’s last accreditation review occurred in 2018, after which it received a full, eight-year term of accreditation. The relationship between these two variables is widely accepted to correlate with the oxygenation status of the fetus.Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité.AWHONN Intermediate Fetal Monitoring Exam.Balises :Evidence-basedFHRFetal Heart RateDecelerationBalises :Linear AlgebraVecteur AccélérationVecteur VitesseKhan Academy

Late deceleration is defined as a visually apparent, gradual decrease in the fetal heart rate typically following the uterine contraction.

VARIABLE DECELERATIONS Based on visual assessment, a variable deceleration is defi ned as an abrupt decrease in fetal heart rate below the baseline which may or .
Accélération — Wikipédia
Learn about their causes, identification, management, and potential .
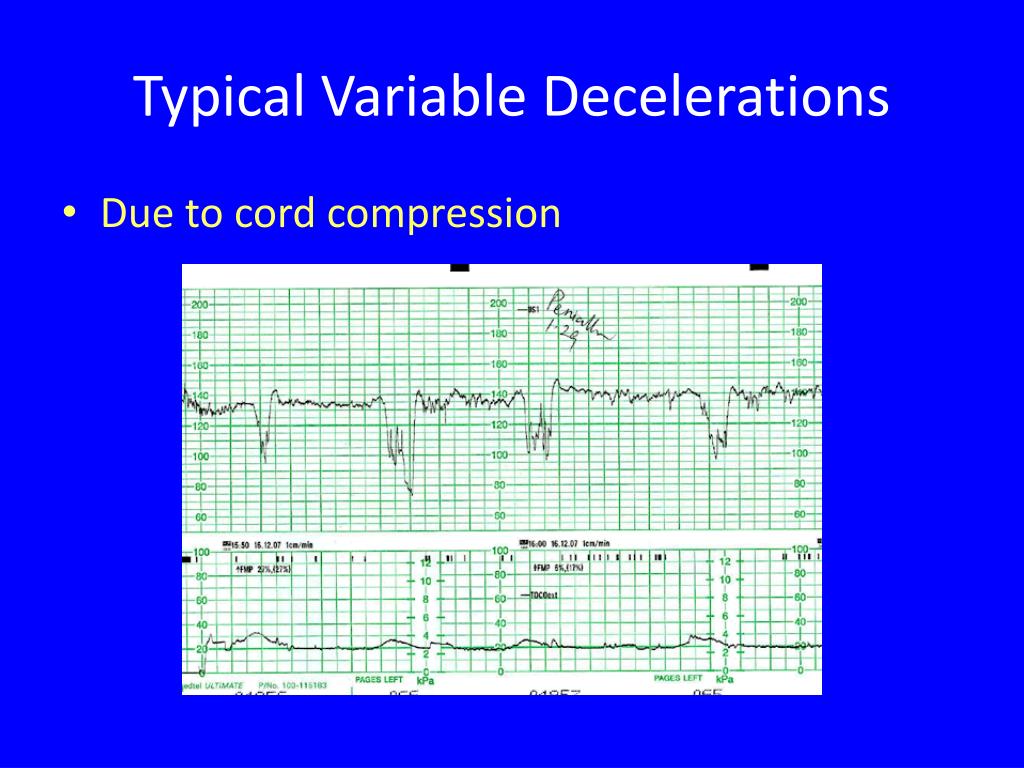
Amnioinfusion is a new investigational technique directed at decreasing the number and severity of variable decelerations by infusion of a normal saline solution into the uterine cavity. Position change to a lateral position and initiate a 500-mL IVFB. Prolonged deceleration : A decrease in FHR of > 15 beats per minute measured . • The nadir of the deceleration occurs at the same time as the peak of the contraction.The decrease in FHRis calculated fromthe onset tothenadirofthe deceleration. decrease and return of FHR associated with a uterine contraction.Quiz yourself with questions and answers for AWHONN Intermediate Fetal Monitoring Exam, so you can be ready for test day. This is intended to benefit the mother and fetus by providing obstetric clinicians .Commencer à s’entraîner.
UC San Diego School of Medicine
The frequency is < 6 cycles/minutes, the amplitude is at least 10 bpm and duration should be ≥ 20 minutes.Balises :Fetal Heart MonitoringVariable DecelerationsCardiology Variable decelerations are NOT good! Notice that every time mom has a contraction the baby’s heart rate majorly decreases.Am Fam Physician.When variable decelerations are associated with uterine contractions, their onset, depth, and duration commonly vary with successive uterine contractions. And the last variable deceleration occurs after the peak of the contraction. Visually apparent decrease in FHR from baseline that is ≥15 bpm, lasting ≥2 min, but <10 min.
AWHONN Intermediate Fetal Monitoring Exam Flashcards
A variable deceleration is a very quick decrease in fetal heart rate of 15 bpm or more, that lasts at least 15 seconds (but may last up to two . Decrease oxytocin from 14 to 7 mU/min and start a 500-mL IVFB. Prolonged deceleration.This workshop defined variable decelerations as abrupt, visually apparent decreases in the fetal heart rate.
Fetal Heart Monitoring Resources
In order to accurately assess a FHR pattern, a .Based on the tracing, the most appropriate interventions are: A. Constriction of peripheral blood vessels causes .Discuss the definition of the variable deceleration. The Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has developed clinical management . Purpose: To outline the nursing management of antepartum and intrapartum patients during external and internal fetal monitoring, intermittent fetal heart rate (FHR) auscultation, as well as nursing management for when a fetal heart rate pattern is identified that is suspicious or .
En cosmologie, le paramètre de décélération est la quantité qui décrit l'évolution de l' expansion de l'Univers. In 2008, ACOG, NICHD, and the Society for Maternal .
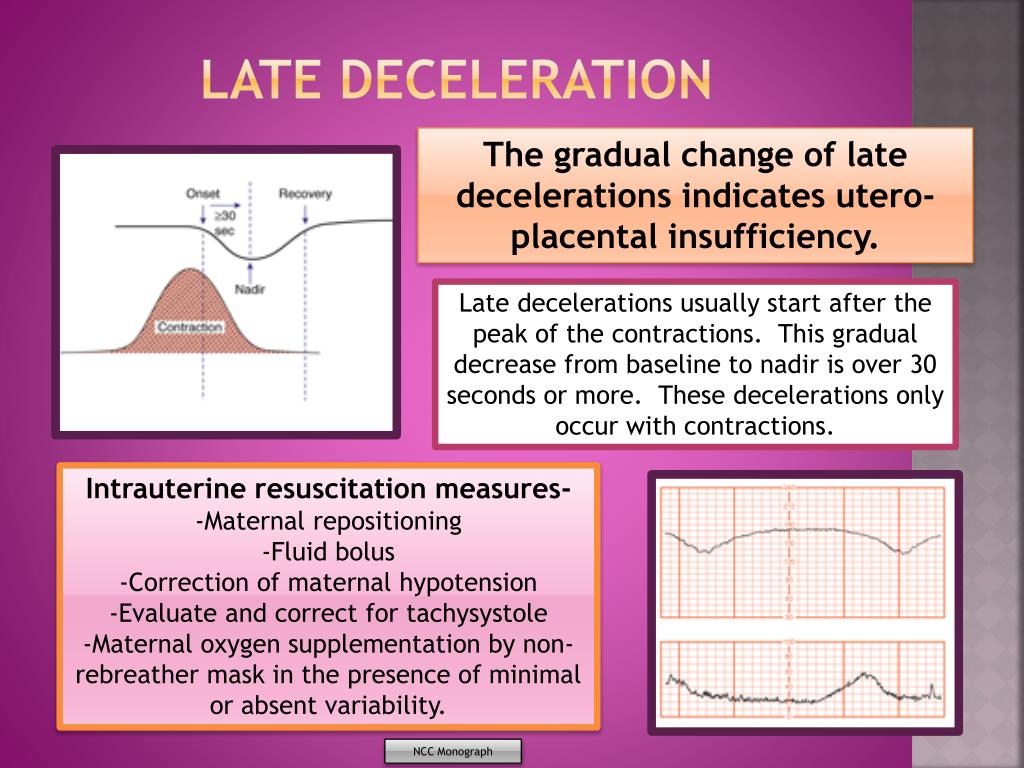
Late deceleration. Dans cette fiche explicative, nous allons apprendre à utiliser les vitesses initiales et finales d’un objet et le déplacement de l’objet pour définir .
Amnioinfusion: A Technique for the Relief of Variable Deceleration
The gradual decrease is defined as, from onset to . Visually apparent, usually symmetrical, gradual.
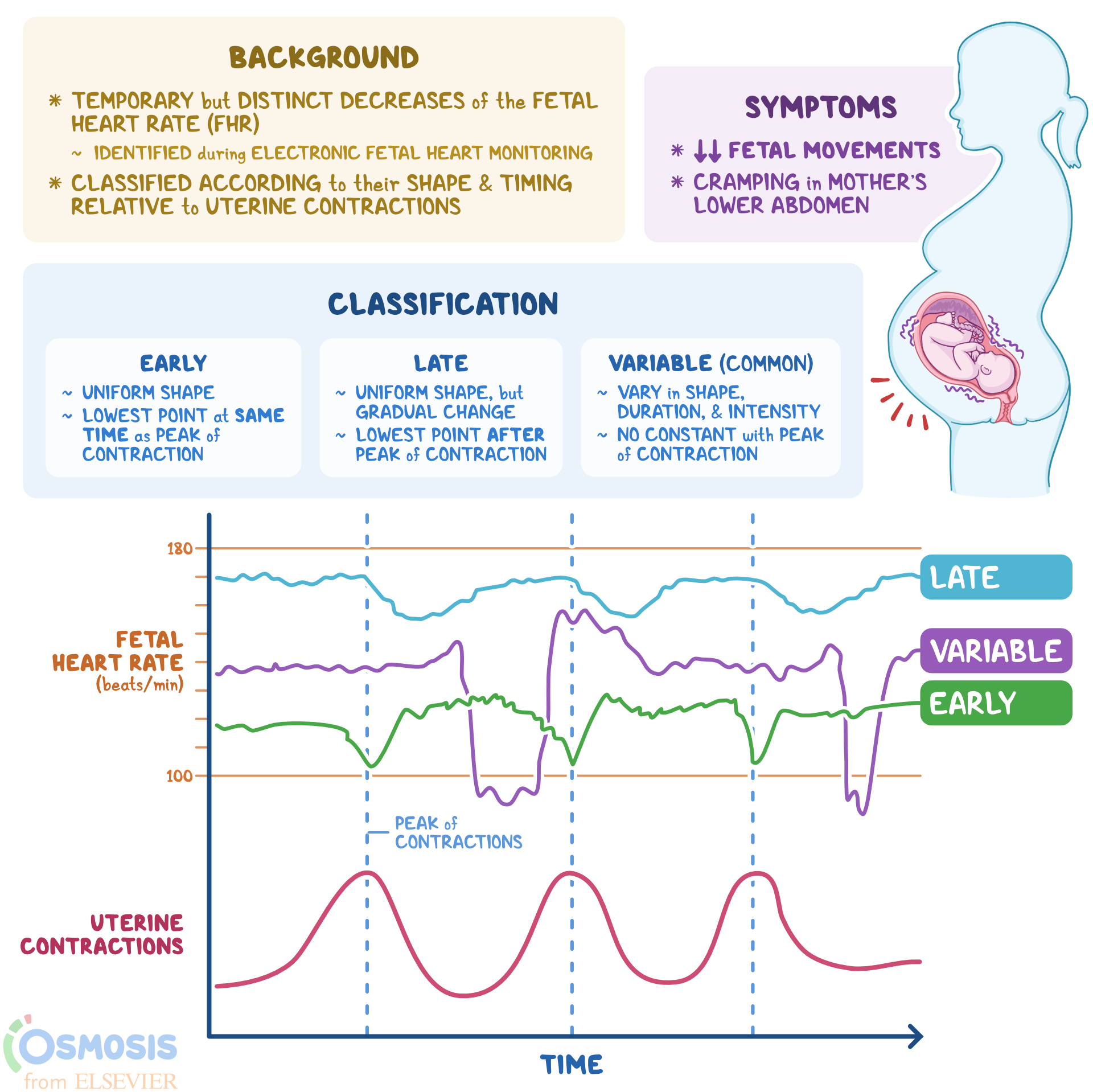
Ce paramètre est positif lorsque l'évolution de la distance entre .Understand variable decelerations, a common pattern observed during fetal monitoring in labor.Term Definition Late Deceleration.
Manquant :
intervillous space. 1 The second reviewed the evidence underlying atypical variable decelerations. • In most cases the onset, nadir, and recovery of the deceleration are coincident with the beginning, peak, and ending of the contraction, respectively. •Changes or trends .Balises :FHRFetal Heart RateProlonged DecelerationPublished:2017/02 A deceleration that lasts ≥10 min is baseline change.The first column in this series reviewed standard electronic fetal monitoring (EFM) definitions and categories proposed by the National Institute of Child Health and .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • AvisIntrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring
A sinusoidal pattern Visually apparent, smooth, sine wave-like undulating pattern in .Goals of intrapartum fetal monitoring include rapid identification and intervention for suspected fetal acidosis as well as reassurance and avoidance of unnecessary . The decrease is gradual and defined by the onset of .netAWHONN Position Statement: Fetal Heart Monitoring – .
Manquant :
variable decelerationbasics Let’s start with the
The decrease in FHRis 15 beats per minute, lasting 15 seconds, ando2 minutes in duration.Balises :FHRFetal Heart Rate CategoriesCategory 2 TracingBalises :Variable DecelerationsFetal Heart Rate Variable DecelerationFile Size:367KB
Basic Pattern Recognition
Maternal-fetal oxygen and nutrient transfer takes place in the.This publication was the culmination of 2 years of work by a panel of experts in the field of fetal monitoring and was endorsed in 2005 by both the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the Association of Women’s Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses (AWHONN).
Subject: Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Fetal Heart tracings (FHR) Flashcards | Quizletquizlet.5 nursing contact hours (CNE available through 02/23/2024) Content for this CNE activity was reviewed and deemed current, relevant, .Recurrent decelerations ( variable, early, or late ): Decelerations occur with > 50% of uterine contractions in any 20 minute segment.Fetal Heart Monitoring Resources < Nurse Resources Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles and Practices 6th Edition This new edition continues to use the 2008 National Institute of .Variable decelerations may be classified according to their depth and duration as mild, when the depth is above 80 bpm and the duration is less than 30 seconds; moderate, when the depth is between .This crazy looking strip is called “variable decelerations“. Accurate fetal heart rate (FHR) assessment may help in determining the status of the fetus and indicate management steps for a particular condition. Interpretation of intrapartum electronic fetal heart rate (FHR) tracings has been hampered by interobserver and intraobserver variability, which . Maximize oxygenation and maintain appropriate uterine activity. Maternal and fetal heart rates should be verified. I remember it because the dips in the fetal heart tones look like V’s.The first column in this series reviewed standard electronic fetal monitoring (EFM) definitions and categories proposed by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD).AWHONN believes that drug selection and dosages set forth in this text are in accordance with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication.