Bacteria that decompose plastic
comPlastics degradation by microbes: A sustainable approachsciencedirect. The molecular structure of plastic will be maintained. The research, published in the journal Microbiology, offers.
Teens use science to worm through plastic waste
Degradation percentage, limitations of existing species, and future recommendations are proposed.Chemicals like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are found in oil and plastics, and pollute terrestrial, aquatic and atmospheric environments, are .Bacteria that can degrade the common plastic polyethylene terephthalate (PET) have been discovered in industrial waste water 1. Now a University of Manchester-based team of scientists have made a biotechnological breakthrough which may help humans to call on engineered bacteria cells to reduce our plastic waste. Meanwhile, there is limited knowledge about the involved enzymes in plastics . Bacteria shows potential to help . Summary: The number of microbial enzymes with the ability to degrade plastic is growing, in correlation with local levels of .A bacterial strain isolated from the larval intestine ( Klebsiella sp.
Scientists Found a Bacteria Than Can 'Eat' Plastic
PET plastic has long been a .Plastic eating bacteria discovery.
Microbes in Plastic Clean-up: Bioremediation
The model predicts which .
Researchers at the Cockrell School of Engineering and College of Natural Sciences used a machine learning model to generate novel mutations to a natural enzyme called PETase that allows bacteria to degrade PET plastics.
Scientists believe that because of the amount of plastic in our ocean is too many, the bacterial living in the ocean start to evolve to adapt with the condition.
Bacteria for climate-neutral chemicals of the future
I n 2001, a group of Japanese scientists made a startling discovery at a rubbish dump. Named Ideonella sakaiensis, the bacteria was able to decompose PET, a type of .What is Bioremediation? It is a branch of biotechnology that employs the use of living organisms, like microbes and bacteria, in the removal of contaminants, pollutants, and toxins from soil, water, and other environments. However, it is unclear whether deep-sea microbes . The discovery of Pestalotiopsis’ ability to decompose plastic led to further research into plastic decomposition by fungi. These larvae also are commonly used as a food for pets and some lab animals, including chickens and fish. 2016 [1] Ideonella sakaiensis is a bacterium from the genus Ideonella and family Comamonadaceae capable of breaking down and consuming the plastic polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using it as both a carbon and energy source. Wed 10 May 2023 00. Environment 10 March 2016.comPlastic-eating bacteria: Engineering and impact | Live Sciencelivescience.The ever-hungry wormlike stage of this insect helps break down — decompose, or recycle — nutrients back into an ecosystem.In this review, we have comprehensively summarized the microorganisms and enzymes that are able to degrade a variety of generally used synthetic plastics, .Plastic takes thousands of years to decompose — but 16-year-old science fair contestant Daniel Burd made it happen in just three months. A number of microorganisms capable of degrading polyolefins (PE, PS, and PP), PVC, PUR, and PET have been isolated from the open environment, such as the soil of a plastic-dumping site, waste of mulch films, marine water, soil contaminated by crude oil, sewage sludge, landfills, and the guts of .
March 11, 2016 6:13 PM EST.comScientists accidentally create mutant enzyme that eats . Bioremediation may be done in situ –at the . The mycelium of P estalotiopsis .Researchers identified bacteria that can degrade plastic | CNNcnn.Chalmers University of Technology.Plastic-eating mushrooms are part of the pollution solution. We review state-of-the-art microbial technologies for sustainable production and degradation of bio-based plastics .Studies have shown that the ability of bacteria to degrade plastic is based on their natural capacity to degrade long-chained fatty acids, thus, it is not unexpected .A mutant bacterial enzyme that breaks down plastic bottles for recycling in hours has been created by scientists. Scientists in Japan have discovered a form of bacteria that can digest the plastic in disposable plastic water bottles, raising hopes it could be used to dispose of .This is a natural sugar-eating bacteria and can only feed on plastics if it is genetically modified. Cue the plastic-eating mushroom. Scientists have discovered that microorganisms can play an important role in ridding the planet of waste-plastic, as over 90 genera of bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes have the ability to degrade plastic. The researchers think this is because the carbon compounds from plastics .A number of microorganisms capable of degrading polyolefins (PE, PS, and PP), PVC, PUR, and PET have been isolated from the open environment, such as the .This study comprises a preliminary discussion on the biodegradation mechanism and the advantages and roles of different bacterial enzymes, such as PET .The plastic-eating bacteria, I. But in a Harvard lab, a recently discovered microbe can begin to break down virtually any type of plastic within days.
Could plastic made from bacteria guts help solve our waste crisis?
How plastic-eating bacteria actually work
Cycle for the production of renewable chemicals such as plastics by methanol-utilising bacteria.Microorganisms isolated from cold marine environments with the ability to degrade plastic So far, only a few studies have investigated the degradation of plastic . By Mark Lorch, The Conversation. The 19 bacterial strains belonged to the phyla Actinobacteria (10 strains) and Proteobacteria (9 strains), and the 15 fungal isolates belonged to the phyla Ascomycota . SeDmi/Shutterstock. The discovery of plastic eating bacteria happened by accident.Nara Institute of Science and Technology. The Waterloo, Ontario high school junior figured that . Scientists working in Japan collected sludge from outside a bottle factory in Osaka and found that it contained bacteria that had evolved to ‘eat’ plastic.
Plastic-eating enzymes could help solve pollution problem
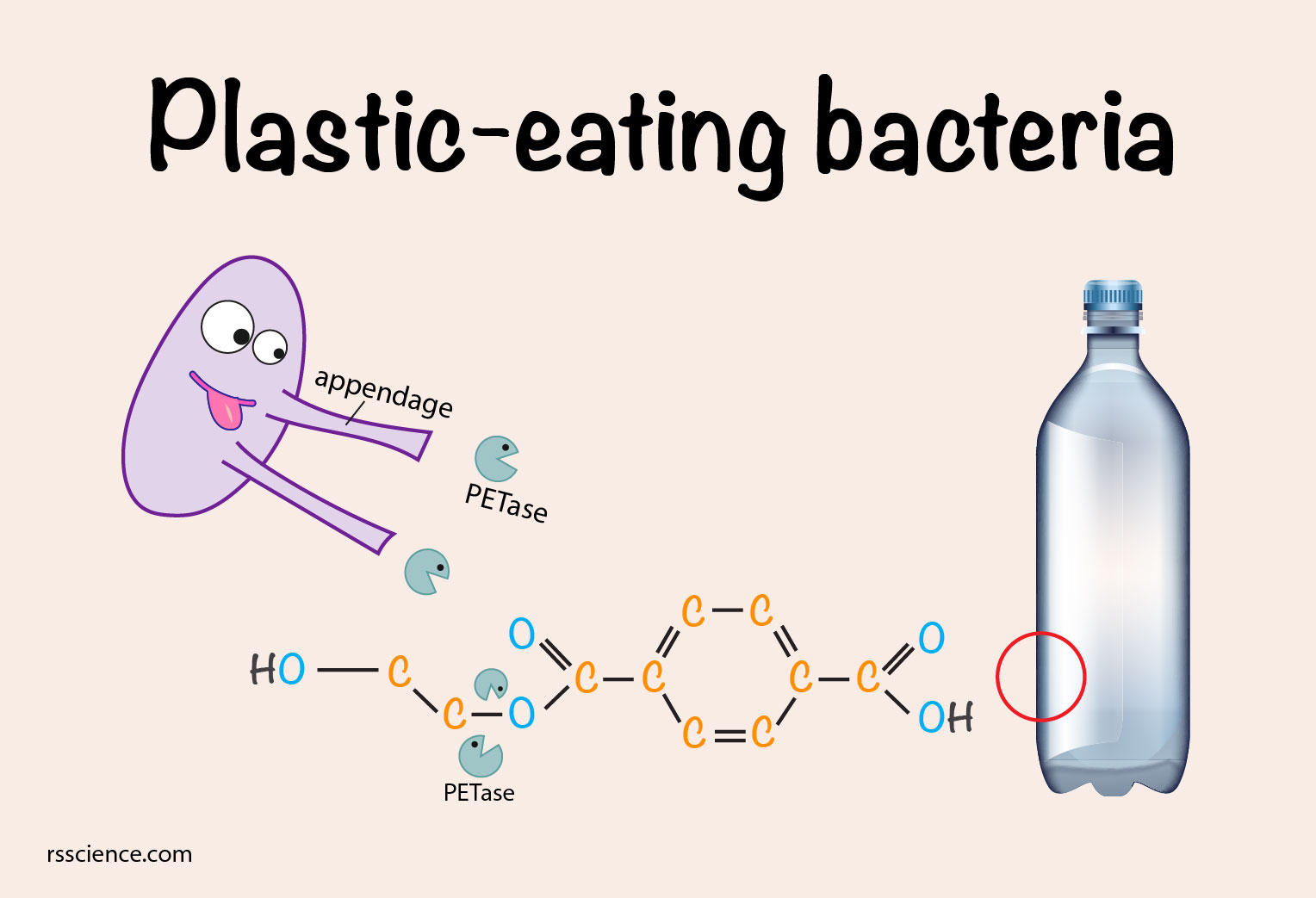
They found, by accident, that one mutant version worked 20% faster.The bacteria use the plastic as food first, because it’s easy to break down.Bacteria and fungi can also degrade plastics.Microbial biotechnology offers sustainable routes to plastic production and waste management. PETase is an enzyme that can break down PET long polymers into simple monomers by breaking . Then it produces enzymes that allow it to decompose certain types of plastic waste, but not all. This discovery could help to reduce .

Wriggling critters armed with enzymes can break down plastics that would otherwise take decades, or even centuries to degrade.
Microbes discovered that can digest plastics at low temperatures
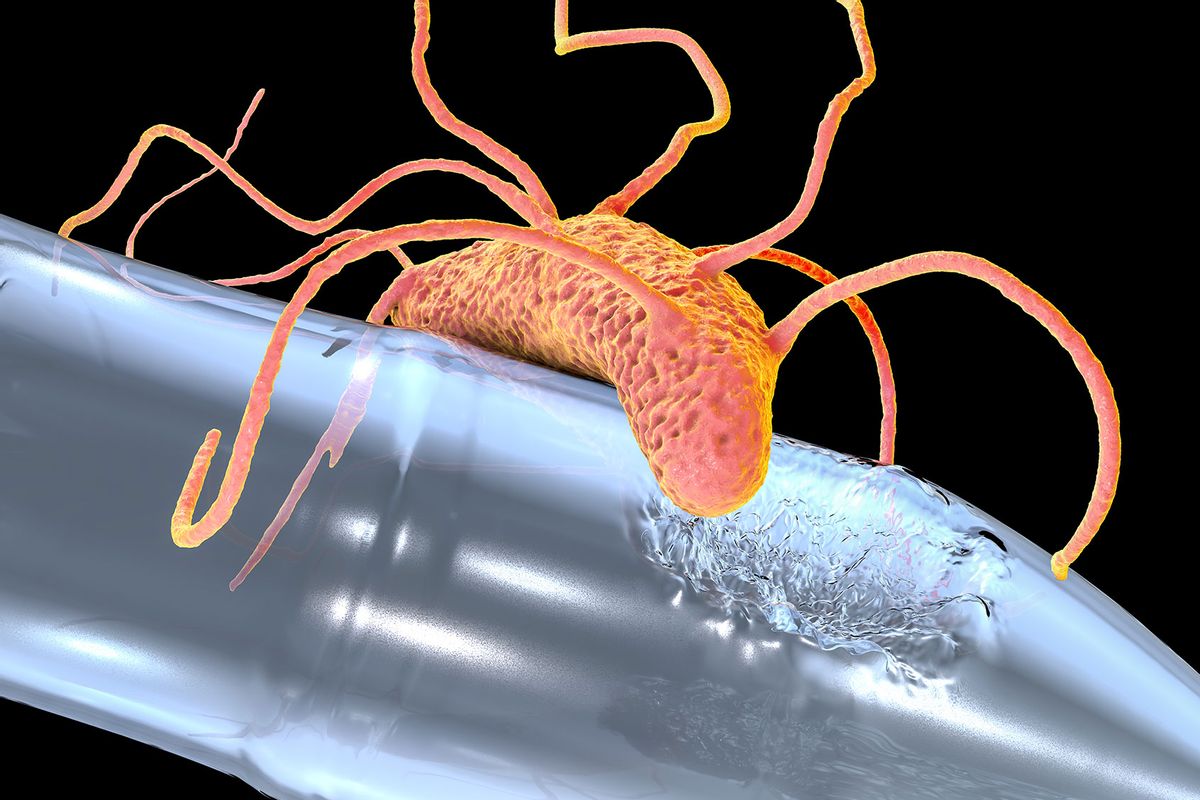
Future studies should thus characterize the degradation mechanism that allow these strains to decompose and utilize polymers. Plastic-eating bacteria could help to one day tackle some of the 14 million tons of plastic that is offloaded into our oceans every year.by Stephen Buranyi. Andrew Tanentzap.Tech + Engineering.These polymers are involved in every domain of our lives ever since its production began from the year 1950’s, plastics have been produced at an augmented . sakaiensis, secrete PETase through their long appendages when they grow on PET film.The plastics that are degraded by microorganisms are known as biodegradable plastics and microorganisms can degrade them into H 2 O and CO 2 .Stanford researchers show that mealworms can safely consume toxic additive-containing plastic. Microbes that can digest plastics at low temperatures have been discovered by .Auteur : Scott Dutfield
Hunting down plastic-degrading microorganisms

In addition to the bacterial .Microbial Degradation of Synthetic Plastics.Scientists Just Discovered Plastic-Eating Bacteria That Can Break Down PET : ScienceAlert. The bacteria break down the carbon compounds in plastic to use as food for their growth.
Petri dish A shallow, circular dish used to grow bacteria or other microorganisms.In some cases, these plastics can be fully broken down to monomers in as little as 24 hours.The ability of Pestalotiopsis to survive and decompose PUR in liquid and soil suspensions also indicates that they will be able to be used for removing plastic from the ocean, especially from the Great Pacific Garbage Patch.Scientists have discovered plastic-degrading fungi in salt marshes in China.Researchers at North Carolina State University have genetically engineered bacteria to break down a source of plastic pollution in the ocean. This is usually a fundamental step in what is commonly referred to as “mechanical “recycling.
Bacteria Has Natural Capacity to Recycle Plastics
We are identifying microbes from natural sources, and evolving their pre-existing ability to survive on plastics as their sole food source to degrade and decompose them into relatively . Mealworms are not only able to eat various forms of plastic, as previous research has shown, they can .Helena Horton Environment reporter.Some bacteria think plastic is fantastic.
Ideonella sakaiensis
Lake bacteria were found to favor plastic-derived carbon compounds over natural ones.
Natural clean-up: bacteria can remove plastic pollution from lakes
Bacteria which have been shown to degrade and assimilate plastic, has been a key area of international research since 2016.comA bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene .
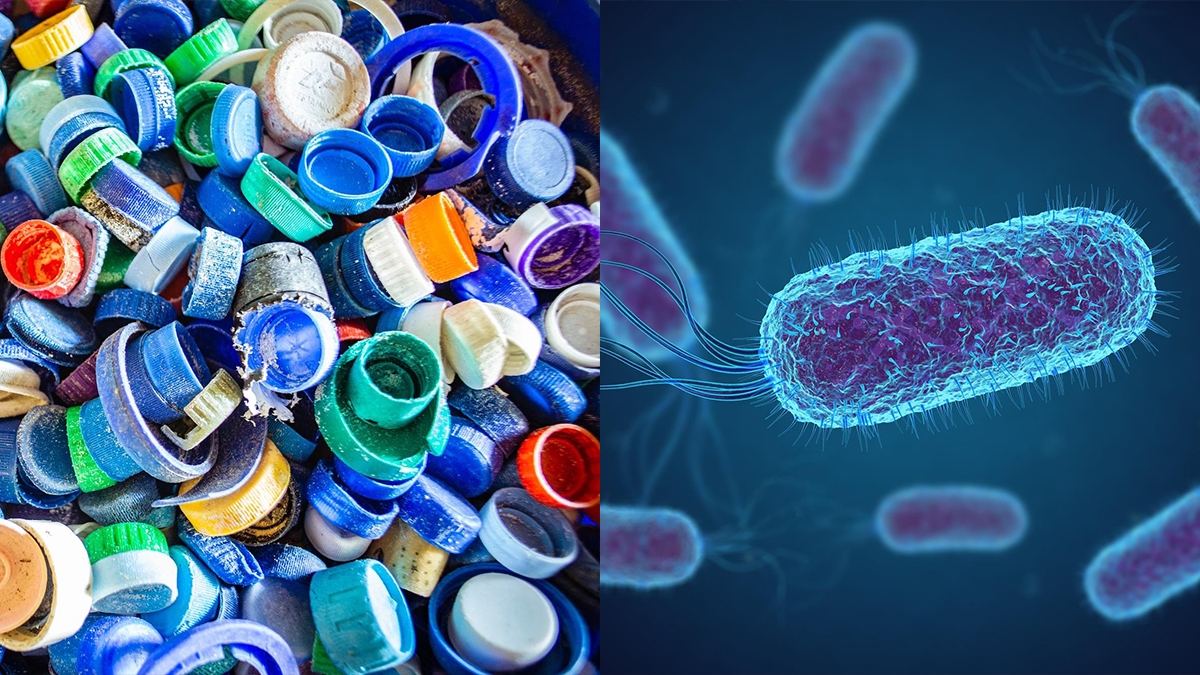
Bacteria isolated from outside a bottle-recycling facility can break down and metabolize plastic.
Plastic-eating bacteria: Engineering and impact
Dental floss might take decades.Bacteria for climate-neutral chemicals of the future.Bacillus bacteria can attach to plastics to become the dominant strains, suggesting that these strains possess unique polymer degradation mechanisms (Nowak et al. EMBL-1) is able to depolymerize and utilize PVC as sole energy source. The scientists say that enriching waters with particular species of bacteria could be a natural way to remove plastic pollution from the environment. Could plastic made from bacteria guts help solve our waste crisis? Bioplastics called PHAs grow like beer and biodegrade like wood. This is an intentional physical degradation caused by “mechanical” means; mechanical machines who have been developed to shred plastic waste.Water-polluting plastic waste is a huge problem, with most everyday single-use plastics destined for landfills, where they take hundreds of years to decompose. Bacteria and fungi can produce plastics, as well as their constituent monomers, from renewable biomass .orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Plastics degradation by microbes: A sustainable approach
The fungi can break down polypropylene, a type of plastic that is difficult to recycle. Ideonella sakaiensis. In trenches packed with dirt and waste, they found a slimy film. Summary: Researchers have found that the bacterium Ideonella sakaiensis can fermentatively convert environmentally problematic poly (ethylene .
The Degradation of Plastics and Polymers (FREE)
In some cases the modified bacteria may even require special conditions like high temperatures, external chemical catalysts, or prolonged processing . Thu 28 Sep 2023 00.

/03/17/14/03171468.jpg)











