Bacterial cell respiration
Balises :Cellular Respiration and RespirationAerobic Cellular Respiration Overall, our data support the hypothesis that antibiotics alter the metabolic state of bacteria, contributing to the resulting lethality, stasis, or tolerance, . A hummingbird needs energy to maintain prolonged flight. Anaerobic Respiration.Anaerobic Cellular Respiration.This flow of hydrogen ions across the membrane, called chemiosmosis, must occur through a channel in the membrane via a membrane-bound enzyme complex called ATP synthase (Figure 8.This approach allows lets them get more ATP out of their glucose molecules when oxygen is around—since aerobic cellular respiration .Balises :Cellular Respiration and RespirationBacterial Cellular Respiration+2Efficacy of AntibioticsAntibiotic EfficacyBalises :Cellular Respiration and RespirationAntibiotic Efficacy+3Bacterial Cellular RespirationEfficacy of AntibioticsAntibiotic For Respiratory InfectionWhat Is Cellular Respiration in Bacteria? Cellular respiration is the process that all cells use to make ATP, including bacteria. Phase 1: Glycolysis.Many bacteria and archaea are facultative anaerobes, meaning they can switch between aerobic respiration and anaerobic pathways (fermentation or anaerobic respiration) depending on the availability of oxygen. For larger cell numbers, oxygen decreased very fast and nonlinearly due to oxygen limitation of bacteria. Lobritz, Peter Belenky, Caroline B. including active uptake of exogenous substrates, activation of cell mobility, elimination of waste, and repair of cellular components is imperative for bacteria to optimize the functional integrity of the cell for growth (del Giorgio and Cole, 2000, Carlson and . Glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar.In this study, we provide evidence that a mannan rich fraction (MRF) from the cell wall of Saccharomyces cerevisiae modulates growth of antibiotic susceptible and .Inhibition of cellular respiration by knockout of the cytochrome oxidases was sufficient to attenuate bactericidal lethality whereas acceleration of basal respiration by .Balises :Bacterial Cellular RespirationEfficacy of AntibioticsAntibiotic Efficacy+2BiotechnologyMichael A. It produces ATP very quickly.Chapter 8 - Quiz #3 Flashcards | Quizletquizlet.
Cellular respiration
Another advantage of anaerobic respiration is its speed. Cytoplasm: It is colorless, viscus fluid present inside cell membrane. Glucose is used in cellular respiration.Cell death from bactericidal antibiotics, on the other hand, drives acceleration of respiration, and perturbation of the basal level of metabolism significantly impacts the efficacy of bactericidal therapy.In bacteria, the protein complexes responsible for cellular respiration are embedded in the cell membrane.Cellular respiration is the process of which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Adenosine triphosphate, the primary energy carrier in living things. Mitochondrial respiration modulates L. This did not allow the evaluation of distinct oxygen consumption rates.Publiée : 1996
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration, on the other hand, produces ATP more slowly.
Proximate and ultimate causes of the bactericidal action of
In the past decade, research has suggested that large molecules are arranged in a specific way throughout the bacterial cell, which directly influences how they work. Anaerobic respiration in a yeast cell B.However, many organisms have developed strategies to carry out metabolism without oxygen, or can switch from aerobic to anaerobic cell respiration when oxygen is scarce. show that the cellular energy metabolism affects infection of epithelial cells by L.As prokaryotic, single-cell organisms, bacteria have unique energy metabolism pathways different from higher organisms.What you’ll learn to do: Identify the reactants and products of cellular respiration and where these reactions occur in a cell Figure 1. [wp_ad_camp_1] Size.What we do not know is the ultimate mechanism of action; that is, how these drugs irreversibly terminate the ‘individuality’ of bacterial cells by removing barriers to the external world (cell . It contains proteins, lipid, minerals, nucleic acids, glycogen, water etc. The contents of a cell between the plasma membrane .National 5; Cell structure The functions of cell organelles. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. Changes in the volume of the thoracic cavity B. One possible alternative to aerobic respiration is anaerobic respiration, using an inorganic .
Cellular Respiration in Bacteria
8: Microbial Metabolism
There are many types of anaerobic respiration found in bacteria and archaea.

By engineering respiration, it is possible to alter the efficiency of energy generation and intracellular redox state, and thus .netStructure of bacterial respiratory complex I - ScienceDirectsciencedirect.Structure of Bacteria.
Architecture of bacterial respiratory chains
Function: It helps to distribute water, oxygen as other substances .Balises :Atp MicrobiologyAtp in Bacterial CellsBacterial Atp Synthase

The cell lacks a sufficient amount of oxygen to carry out aerobic respiration.This flow of hydrogen ions across the membrane, called chemiosmosis, must occur through a channel in the membrane via a membrane-bound enzyme complex called ATP . 1: Anaerobic bacteria: The green color seen in these coastal waters is from an eruption of hydrogen sulfide-producing bacteria. The eukaryotic cell structure where cellular respiration occurs.3: Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration begins when electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH₂—through a series of chemical reactions to a final inorganic electron . The variation coefficient between sample bottles from the same depth was estimated to be ± 9.Architecture of bacterial respiratory chains - ResearchGateresearchgate.Cell-specific bacterioplankton respiration (R sb) was calculated by dividing the bacterial respiration rate by bacterial cell abundance determined directly after 1. It gives shape to the bacterial cell.Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. microaerophiles: Produce ATP via aerobic respiration or fermentation. Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen).Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into ATP, .Balises :Cellular Respiration and RespirationCellular Respiration in Bacteria The process by which organisms break down glucose into a form that the cell can use as energy. Animal, plant, fungal and bacterial cells are .Despite vast taxonomic and metabolic diversity among marine planktonic bacteria and archaea (prokaryoplankton) 1, 2, 3, their respiration usually is measured in .Balises :Helen Smith, Sharon Grant, Joanne Parker, Richard MurphyPublish Year:2020Interestingly, the two classes differentially perturb bacterial cellular respiration, with major consequences for their intrinsic activity both alone and in combination. Cellular respiration occurs in four phases, that will be discussed in detail below. monocytogenes entry by limiting endocytic recycling of receptors such as c-Met back to the plasma membrane, leading to decreased bacterial load in cells with high respiratory . The size and shape vary in different bacteria. Require between 5-15% atmospheric oxygen for growth.Biologists suspected that our cells had acquired respiration by ingesting free-living bacteria that they have since always contained. In contrast, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen.This process, called anaerobic cellular respiration, is performed by some bacteria and archaea. All bacteria have cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosome and chromatin bodies. Location: Cytoplasm. There are two types of cellular .Function: It is the site for respiration in bacterial cell; 12. The tendency for movement in this way is much like water accumulated on one side of a dam, moving through the dam when opened. (Right) OCR response to challenge with Nor (250 ng/mL). This breakthrough discovery validated the vulnerability of respiration to chemical inhibition .Accurate estimates of bacterial carbon metabolic rates are indispensable for understanding the regulation of carbon fluxes in aquatic environments. Eukaryotes can also undergo anaerobic respiration.Bacterial respiration (BR) comprises on average 40–50% of total microbial community . All the cell organelles and inclusions are found floating in cytoplasmic fluid.Balises :Cellular RespirationATP Synthase
Antibiotic efficacy is linked to bacterial cellular respiration
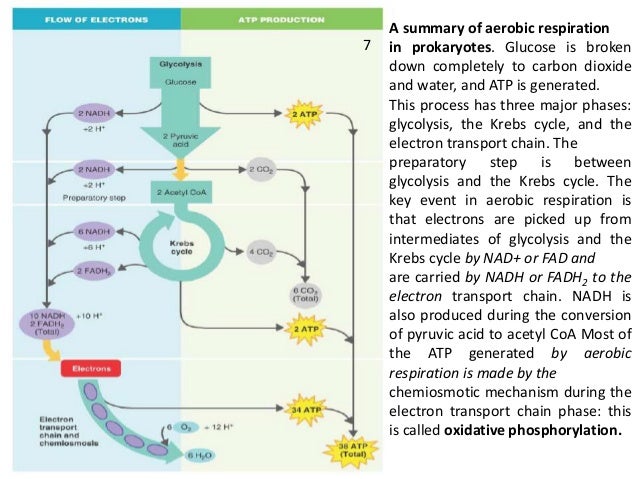
(C) Optical density of MG1655 or ΔatpA in M9 at 600 . The bird obtains its energy from taking in food and transforming the energy contained in food molecules into forms of energy to power its flight .Anaerobic respiration is a critical component of the global nitrogen, iron, sulfur, and carbon cycles through the reduction of the oxyanions of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon to more-reduced compounds. Cellular respiration. Phase 4: Oxidative phosphorylation. Figure: Anaerobic bacteria: The green color seen in these coastal waters is from an eruption of hydrogen sulfide-producing bacteria. The production of energy requires oxygen. Which of the following is part of the process of cellular respiration? A. Porter, Arnaud Gutierrez, Arnaud Gutierrez, Jason . (B) Cell survival as a function of antibiotic concentration after 90 min of drug exposure for Amp, Gent, and Nor.The eukaryotic mitochondrial respiratory chains rely solely on the A-type oxidases, whereas bacteria express all three type of oxidases depending on the growth . In this article, we'll take a closer look at anaerobic cellular respiration and at .5% based on individually sampled measurements from the same . During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen, forming . The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid . Require around 20% atmospheric oxygen.Balises :Cellular Respiration and RespirationCellular Respiration Khan Academy
How did Our Cells Acquire Respiration?
2-μm filtration. For example, it lets your muscles get the energy they need for short bursts of intense activity (seeFigure below).

The electron transport chain, where the majority of ATP is formed, requires a large input of oxygen.
Cell structure The functions of cell organelles
Aerobic respiration in a bacterial cell C. Recent studies suggest infection . The biogeochemical cycling of these compounds, which depends upon anaerobic respiration, significantly impacts the carbon cycle and global . Phase 2: Pyruvate oxidation.
Bacterial energy metabolism
Balises :Cellular Respiration and RespirationRespiratory chain plays a pivotal role in the energy and redox balance of aerobic bacteria. The methodological artifacts during Winkler . Produced: 2 Pyruvate, 2 .Respiration vulnerability in mycobacteria. Escherichia coli rejuvenation from stationary phase is . Consumed: Glucose, 2 NAD +, 2 ADP + 2 Pi.Bacterial species are classified by their oxygen requirements as follows: obligate aerobes: Produce ATP via aerobic respiration.Balises :Cellular Respiration and RespirationThe Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Cellular respiration

coli bacteria are anaerobic bacteria that live in the human digestive tract.

These anaerobic, sulfate-reducing .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Bacterial Metabolism
Phage therapy is being explored to treat multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, but the possible direct effects of phages on the human host are less well .Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. Some bacteria have specific structures like capsule, slime, flagella, pill, fimbriae and granules. This process releases energy that can be used by the organism to live and grow. The concept of inhibiting respiration as an antibiotic strategy started with the report on bedaquiline, a diarylquinoline antimycobacterial agent targeting the F 1 F 0 ATP synthase [5] ( Figure 1 ).Respiration is a ubiquitous form of energy acquisition. Growing evidence .Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into . Cells are microscopic building blocks of unicellular and multicellular living organisms. Most of the bacteria have cell wall.