Basic principles of chromatography
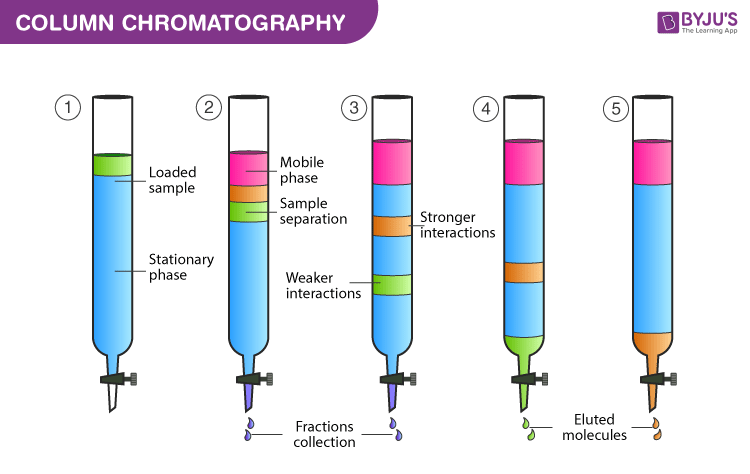
Flash chromatography is a separation technique where smaller sizes of gel particles are used as stationary phase, and pressurized gas is used to drive the solvent through the column.thoroughly analysed. Part of the book .
Adsorption (Liquid-Solid) Chromatography
Chromatography: Basic principle, types, and applications
To get the process started, the mixture is dissolved in a substance called the mobile phase, which allows it to move through a second substance called the stationary .1 Basic terms It is useful to begin the chapter on the theory of chromatographic separation .Table of contents.Chromatography is a process of analyzing the different components present in a mixture qualitatively and quantitatively by separating them from each . Methods of Implementing . There are two principles of Chromatography namely Adsorption ., which is pumped .Chromatography is regarded as one of the most significant bioanalytical techniques used in different branches of life sciences and chemistry., liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, affinity chromatography, but all of these employ the same basic principles. Elution happens because the eluent ion is . Google Classroom. Phase Systems Used in Chromatography. Selection of column (stationary phase) Selection and optimization of mobile phase. Elution is the process where the ion of interest is moved through the column.The basic process of chromatography using ion exchange can be represented in 5 steps: eluent loading, sample injection, separation of sample, elution of analyte A, and elution of . The basic principle of chromatography is based on the concept of distribution of componen ts of a mixture of organic compounds between two phases which are stationary and mobile. Chapter 1 Basic principles of gas chromatography The development of gas chromatographic (GC) methods has led to revolutionary changes in analytical chemistry and also in experimental methods of physical chemistry and methods for the separation of volatile compounds, as GC has a number of important advantages . Department of Chemistry, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, 37996–1600, United States, Division of Chemical and Analytical Sciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831–6120, United States.Chapter 27 • Basic Principles of Chromatography 475 27.Principle: It is based on the difference in movement of individual components of a mixture through the stationary phase under the influence of mobile phase. University of Tennessee, Department of Chemistry, Knoxville, Tennessee, United States, 37996-1600. Image Source: Technology in Science. It allows the . The stationary phase may be a solid or a liquid supported on a solid, .Sample preparation, detection, identification, and quantitative determination of biomolecules are presented in this chapter. Historical Development 3. Phase Systems Used in Chromatography 3.
Basic Principles of Chromatography
Baraem Ismail & S. Last Updated On October 19, 2023 by Ranga. Published 2010. Methods Mol Biol. 1 ) and Anthony . 2017:1485:209-223.
HPLC Basics
1 CHAPTER 1 Principles and theory of chromatography JOSEF NOVAK Institute of Analytical Chemistry, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, 611 42 Brno, Czechoslovakia 1.The basic process of chromatography using ion exchange can be represented in 5 steps: eluent loading, sample injection, separation of sample, elution of analyte A -, and elution of analyte B -, shown and explained below.
Chapter 1 Basic principles of gas chromatography
Georges Guiochon, Georges Guiochon.
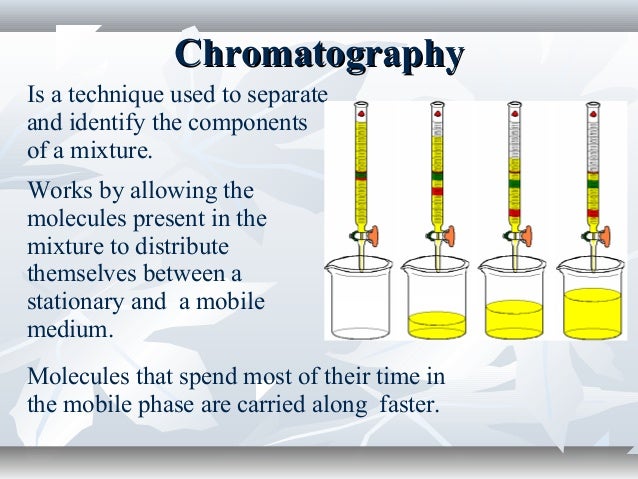
Chromatography is a separation method where the analyte is combined within a liquid or gaseous mobile phase.HPLC Basics – principles and parameters. 188 chalk to separate leaf pigments into colored bands.Chromatography is a method of physical separation in which components of mixture gets separated on two phases. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Division of Chemical and Analytical Sciences, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, United States, 37831-6120 .Its Definition, Principle & Uses.1007/978-1-4939-6412-3_11. Historical Development. Thumbnail: A gas chromatography oven, open to show a capillary column. Philip M Cummins 1 , .) Separation Methods Elsevier Science Publishers B.Chromatography is a powerful technique used to separate and analyze the components of a mixture based on their differential affinity for a stationary and mobile phase., liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, affinity chromatography, but all of these employ the .Principle of Chromatography (how does chromatography work) Image Source: Khan Academy.There are many types of chromatography e. However, there are also thin-layer chromatographic methods that work basically based on the principle of ion exchange. Advantages of planar chromatography and the basic principles (chambers, sample application, and chromatogram development) are also described. Working Principle .Basic Principles of Chromatography. Small beads give higher resolution (narrow peaks) but also generate higher backpressure. There are many types of chromatography e. It is used for the separation, purification, and testing of compounds. Juliane Böttcher, Mareike Margraf, Kate Monks; applications@knauer.

Ion-Exchange Chromatography (IEC) allows for the separation of ionizable molecules on the basis of differences in charge properties.3: Principles of Gas Chromatography. High-performance liquid chromatography or commonly known as HPLC, is an analytical technique used to separate, identify or quantify each .
Principles of chromatography
Georges Guiochon.You can easily get all the basics of chromatography including essential terminology, chromatography types as well as separation theory. Selection of detector. Chromatography is a separation technique that every organic chemist and biochemist is familiar with.
Chromatographic techniques: types, principles, and applications
Basic Principles of Chromatography - Guiochon - Major Reference Works - Wiley Online Library. Rice University via OpenStax CNX. Chromatography is a process of analyzing the different components present in a mixture qualitatively and quantitatively by separating them from each other. Suzanne Nielsen. In chromatography we pass a sample-free phase, which we call the mobile phase, over a second sample-free stationary phase that remains fixed in space. Shirahatti, Naveen Kumar, B. Chromatographic Systems.Generally, chromatography is a physical separation technique that depends on the relative affinity of the principles for the two separate phases: solid and liquid or solid and gaseous or liquid .
Chromatography: Definition, Principle, Types and Application
Abstract The article contains sections titled: 1.Chromatography is a technique used for separating a mixture of chemical substances into their individual components. Hence, one can see the formation of colored bands in column . Search for more papers by this author . Flash chromatography. Its large sample-handling capacity, broad applicability (particularly to proteins and enzymes), moderate cost, powerful resolving ability, and ease of scale-up and automation have led to it becoming one of the . The component of the ink, which is less. Methods of Implementing Chromatogr. Martin (Figure 3.
Basic Principles of Ion Chromatography
Principle, Plate and Rate Theories of Chromatography
Chromatographic Systems 3. It is derived from the Greek terms “chromo= color & gram=bands. Because Tsvet recognized and correctly interpreted the . The adsorbent, which is usually carbon, alumina, or silica, can bind and hold molecules to its surface by weak non-ionic interactions such as hydrogen .1: A General Description of Chromatography. Patil, Ramith Ramu, Prithvi S. One of the phase is the immobile porous bed bulk liquid which is called stationary phase and the other phase is the mobile fluid that flows over the stationary phase under gravity.2: High Performance Liquid chromatography.Principle of Adsorption Chromatography The fundamental principle behind adsorption chromatography is the selective interaction of solid adsorbents with target molecules inside a sample. Basis of Chromatography What is the chromatography? Chromatography is a physical method of separation in which the components to be separated are distributed between two phases (one is the stationary phase and the other is the mobile phase). First Online: 01 January 2010.This chapter describes the basic principles of chromatography and discusses various forms of this method that are used for chemical analysis or to prepare specimens for analysis by other techniques.Download Citation | Basic Principles of Chromatography | Chromatography has many applications for analysis of various foods components. PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY Principle This paper is made up of cellulose ,a polar substance ,and the compounds within a mixture travel farther if they are non polar More polar substances bond with the cellulose paper more quickly ,and therefore do not travel as far . Ion exchange chromatography is most often performed in the form of column chromatography. View previous versions, Georges Guiochon, Georges Guiochon.Chromatography is based on the principle where molecules in mixture applied onto the surface or into the solid, and fluid stationary phase (stable phase) is . The most comprehensiv. It differs from other methods of separation in that a wide .
14 Types of Chromatography (Definition, Principle, Steps, Uses)
A general principle of choosing chromatography resins is a larger bead size for early purification steps, and smaller bead size for later .net KNAUER Wissenschaftliche Geräte GmbH, Hegauer . For example, a mixture of red and blue ink can be separated by chromatography. Search for more papers by this . Chromatography is based on the principle where molecules in . Rapid detection of biomolecules plays a strategical role in their investigation.Basics of chromatography. Understand the basic principles of different kinds of chromatography: paper, thin . Here, differential partitioning of .These are also called “Basic ion exchange” materials.1: Principles of Gas Chromatography. Basic Principles of Chromatography.

Principle of Chromatography. Chromatography is a chemical analysis technique that relies on the separation of components of a mixture.

Raja & Andrew R. This is not the most recent version, view other versions. Learn about the principles of chromatography and its different types, including liquid-solid, column, HPLC, gas, thin-layer, ion, and size-exclusion chromatography.Purification of bioactive glycolipids, showing antiviral activity towards HSV-1 (Herpes Virus). Chandana Kumari, Shashank M.The basic principle is hinged upon that of electrophoresis, which is the motion of particles relative to a fluid (electrolyte) under the influence of an electric field.1 INTRODUCTION Chromatography has a great impact on all areas of analysis and, therefore, on the . A drop of the mixture is placed on the chromatogram.0 1984 Deyl (ed.












