Bayesian theory of mind
Bayesian approaches to brain function investigate the capacity of the nervous system to operate in situations of uncertainty in a fashion that is close to the optimal prescribed by Bayesian statistics.Our results suggest that in decision-making tasks involving large groups with anonymous members, humans use Bayesian inference to model the “mind of the group,” making predictions of others’ decisions while also .
Robust Inverse Reinforcement Learning Through Bayesian Theory of Mind
Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci.
Beliefs and desires in the predictive brain
However, Bayesian models of theory of mind have generally not accounted for these mistakes, instead modeling agents as mostly optimal in achieving their goals.minds?
Cognitive science: Modelling theory of mind
This review approaches human-unique intelligence, specifically cooperation and communication, from an agency-based theory of mind (ToM) account, emphasizing the ability to understand others' behaviors in terms of their underlying mental states.
Reasoning about the antecedents of emotions: Bayesian
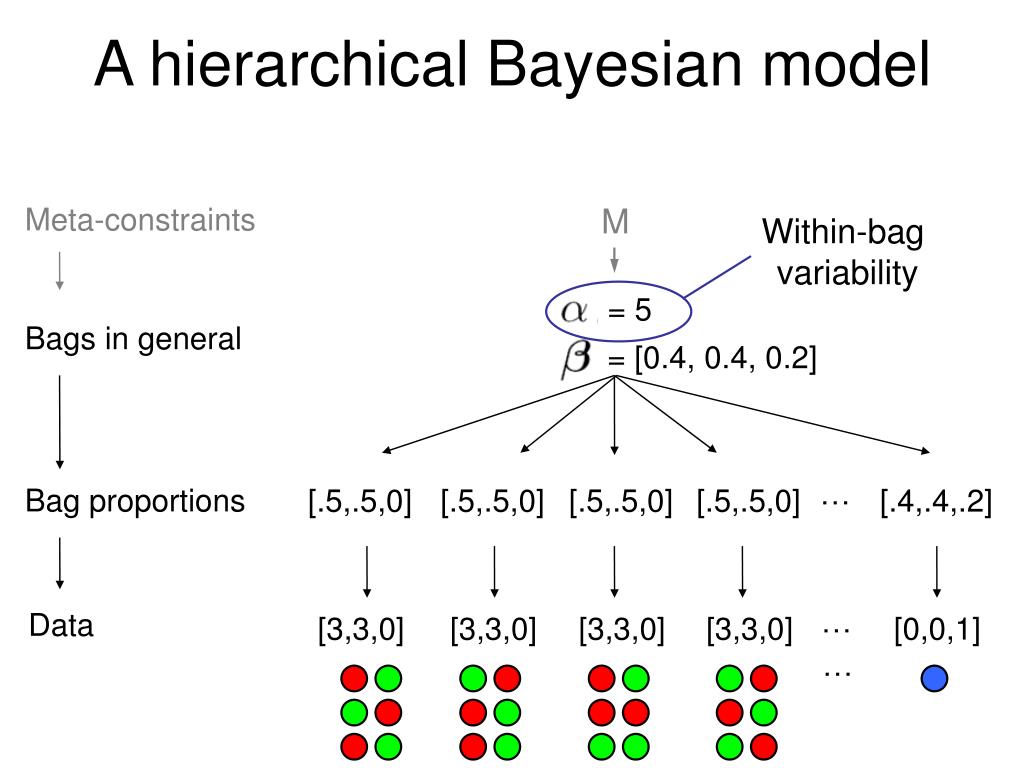
Cognitive processes.This generative theory provides a computational ap-proach to cognition (Tenenbaum et al.Collective Intelligence in Human-AI Teams: A Bayesian Theory of Mind Approach.
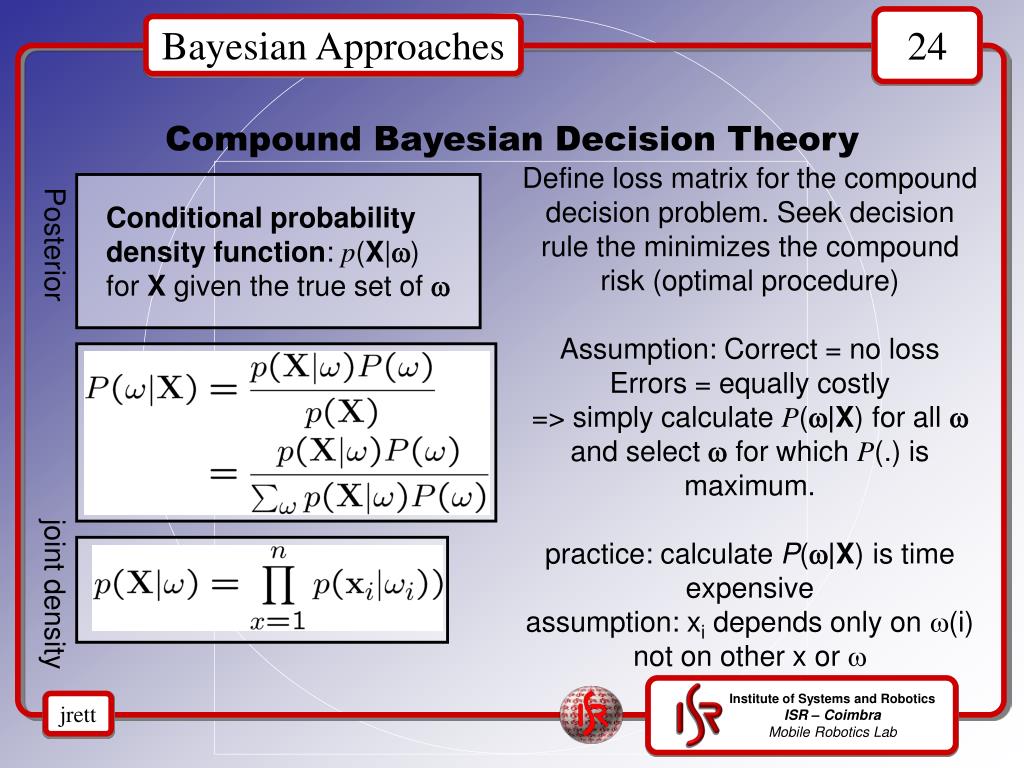
Second, I integrate this with socially rational models of individual agency, which involve understanding why individuals act the way they do in terms of their underlying mental states.Second, we develop a real-time measure of human's theory of mind ability and test theories about human cognition. (Submitted on 16 Feb 2024) Despite the fact that beliefs are mental states that cannot be directly observed, humans talk about each others' beliefs on a regular basis, often using rich .edu) Rebecca R.Robust Inverse Reinforcement Learning Through Bayesian Theory of Mind Theory of Mind perspective (Baker et al. What is Bayesian thinking.We now introduce our hierarchically Bayesian Theory of Mind, a hierarchical Bayesian model of Nagents acting across M viewing trials.This paper grounding the semantics of belief statements in a Bayesian theory-of-mind provides a conceptual role semantics for belief, explaining the gradedness and compositionality of human belief attributions, as well as their intimate connection with goals and plans. Smith, one of the seminal Bayesian researchers, with his work on hierarchical models, sequential Monte Carlo, . Zhuoya Zhao, Feifei Zhao, Shiwen Wang, Yinqian Sun and Yi Zeng. Robert A Jacobs 1 , .Bayesian learning theory applied to human cognition. This article gives an .Theory of Mind Model ToM models allow an ego agent to infer the behavior, observations, rewards, and goals of others.ries of mind and inferring hierarchical phrase structure in language. We use data collected from an online experiment in which 145 individuals in 29 human-only teams of five communicate through a chat-based system to solve a cognitive task. More specifically, cognitive . The model is a key step towards enabling machines to . The structure of the model is represented by Equations 1–9, and is depicted graphically in Figure 1. Observing teams' first 25% of messages explains about 8% of variation in final team performance, a 270% . (Chris Lawrence) Abstract. Epub 2010 May 17. Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society.Our theory of mind ability measure predicts both individual and team-level performance. Bayesian decision theory is a mathematical framework that models reasoning and decision-making under uncertain conditions. As a result, they are unable to explain phenomena like locking oneself out of one's house, or losing a game of chess.

We also discuss several general issues as they bear on the use of Bayesian models: assumptions about optimality, biological plausibility, and what idealized models can tell us about actual human minds.Robust Inverse Reinforcement Learning Through Bayesian Theory of Mind Ran Wei 1Siliang Zeng2 Chenliang Li Alfredo Garcia1 Anthony McDonald3 Mingyi Hong2 Abstract We consider the Bayesian theory of mind (BTOM) framework for learning from demonstrations via inverse reinforcement learning (IRL). Informational boundaries. The Bayesian Brain Hypothesis (BBH) can be seen as boundary-breaking in cognitive science. Department of Psychology, University of California, Berkeley. The past few decades have witnessed an explosion of Bayesian modeling within cognitive science. Baker, Julian Jara-Ettinger, Rebecca Saxe, Joshua B. Samuel Westby, Christoph Riedl. The core idea of BTOM is that expert decisions convey their beliefs about the environment (Baker et al.A Bayesian theory of mind model is shown to infer and quantify the mental state and judgements of humans in decision-making scenarios. Bayesian models are explanatorily successful for an array of psychological domains. As a result, they are unable to explain phenomena like locking oneself out of one’s house, or losing a game of chess.

The book honours the contributions of Sir Adrian F. 2011; Griffiths 2015) that allows us to simultaneously (a) build agents for Human-AI .
Bayesian Theory and Applications
Tenenbaum
Grounding Language about Belief in a Bayesian Theory-of-Mind
La théorie du cerveau bayésien ( Bayesian Brain theory) est aujourd’hui l’une des approches les plus populaires en neurosciences pour représenter les processus . Bayesian thinking has been .A hierarchical Bayesian model simulates which events people infer to be the cause of others' expressions by comparing the emotions inferred from the expressions against the emotions people were predicted to experience in various situations.First, I adopt an existing model that draws from game theory and probabilistic inference to formalize flexible signal understanding. Here, we extend the Bayesian Theory of Mind framework to .We use a Bayesian Theory of Mind approach to model dyadic storytelling interactions where the storyteller and the listener have distinct roles. We find that humans (a) struggle to fully integrate .The ability to interpret the mental state of another agent based on its behavior, also called Theory of Mind (ToM), is crucial for humans in any kind of social interaction. Baker ([email protected] Brain-inspired Theory of Collective Mind Model for Eficient Social Cooperation. The role of storytellers is to influence and infer the attentive state of listeners using speaker cues, and we computationally model this as a POMDP planning problem.Bayesian theory of mind (BToM) is a theory-based Bayesian (TBB) framework [126], which models the structured knowledge of human ToM at multiple levels of abstraction, representing the ontology and principles of the theory at an abstract level and mapping these concepts to particular domains and contexts to generate specific predictions and . Artificial systems, such as intelligent assistants, would also greatly benefit from such mentalizing capabilities.Bayesian brain theories suggest that perception, action and cognition arise as animals minimise the mismatch between their expectations and reality.
L’esprit predictif : introduction à la théorie du cerveau bayésien
Our Bayesian theory of mind (BToM) model is based on probabilistically inverting artificial-intelligence approaches to rational planning and state estimation, which .A Bayesian model of theory of mind, which explicitly relies on this assumption, can predict with high accuracy the inferences that people make about . Humans employ a richly structured intuitive theory of psychology to reason about others’ unobserved mental states, a faculty called “Theory of Mind”. Abstract—Social intelligence . For each agent n, we model uncertainty over which object it tends to prefer, represented as a probability vector n. Saxe (saxe@mit. models of cognitive . This principle . An informal discussion of Bayes rules, generalized Bayes rules, and the complete class theorems.
Bayesian decision theory is a mathematical framework that models reasoning and decision-making under uncertain conditions. Author (s) Baker, Chris L. 2011 Jan;2 (1):8-21. By including hierarchical priors on agent goals and dispositions, inference over our HBToM model enables few-shot learning of the efficiency and preferences of an agent, which can then be used in commonsense . Traditional research on ToM is based on Bayes’ theorem, and the Bayesian Theory of Mind (BToM) model performs well in predicting others’ desires based on their behavioral trajectories [9], [13]. Advances in behavioral modeling have begun to capture aspects of the flexible and nuanced reasoning people exhibit when inferring the contents of others’ minds.Here we present a principled Bayesian solution to this benchmark, based on a hierarchically Bayesian Theory of Mind (HBToM).
This book travels on a statistical journey that begins with the basic structure of Bayesian theory, and then provides details on most of the past and present advances in this field., 2011), where we simultaneously estimate the expert’s reward function and their internal model of the environment dynamics. Here, we extend the Bayesian Theory of Mind framework to model . This causal model provides a close, parameter-free fit to human causal judgments, suggesting that humans .Grounding Language about Belief in a Bayesian Theory-of-Mind.Auteur : Daniel Yon, Daniel Yon, Cecilia Heyes, Clare PressIn this paper, we take a step towards an answer by grounding the semantics of belief statements in a Bayesian theory-of-mind: By modeling how humans jointly infer coherent sets of goals, beliefs, and plans that explain an agent's actions, then evaluating statements about the agent's beliefs against these inferences via epistemic logic, our .Choosing an optimal decision rule under a Bayesian model.Bayesian Theory of Mind : modeling human reasoning about beliefs, desires, goals, and social relations. At the core of cognitive science lies the fundamental aim to comprehend the nature of the human mind and its intricate relationship to the surrounding environment. It is asked how information derived solely from observable behaviors might formally support the attribution of a particular computational architecture to a target . However, humans and systems alike are bound by . Despite the fact that beliefs are mental states that cannot be directly .Auteur : Chris L. This term is used in behavioural sciences and neuroscience and studies associated with this term often strive to explain the brain's cognitive abilities . We present an introduction to Bayesian inference as it is used in probabilistic.