Beta lactam ring antibiotics
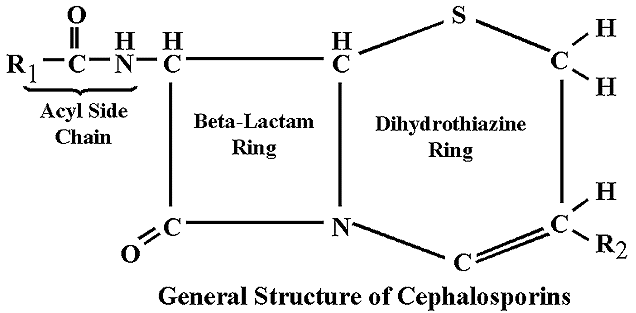
3 This β-lactam ring is generally fused with another heterocycle, and this bicyclic core is functionalized in several key positions, .Beta-lactam antimicrobials, named after the active chemical component of the drug (the 4-member beta-lactam ring), include the 6-membered ring-structured penicillins, monobactams, and carbapenems; and the 7-membered ring-structured cephalosporins and cephamycins.β-Lactam antibiotics are bactericidal agents that interrupt bacterial cell-wall formation as a result of covalent binding to essential penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), enzymes that are .-lactam antibiotics consists of a -lactam ring (4-Membered cyclic amide). • Structural aspects of β-lactam antibiotics and their influence on . Bradford
β-Lactams: chemical structure, mode of action and mechanisms
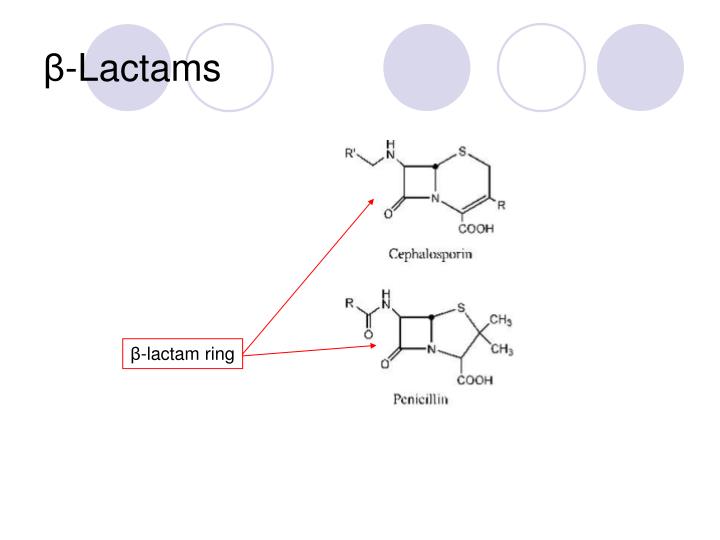
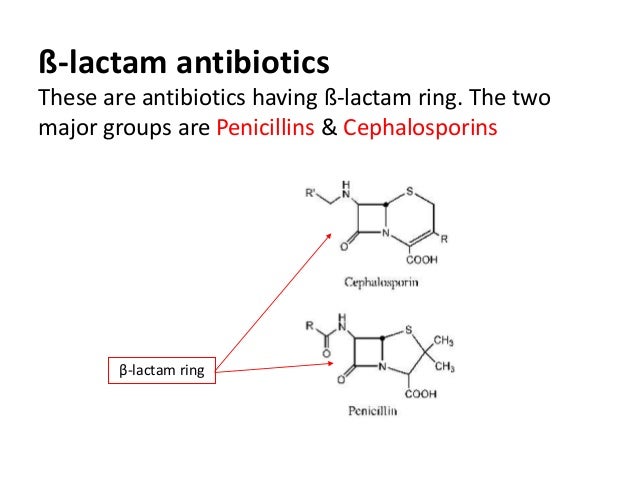
These antibiotics (most of which end in the suffix - cillin) contain a nucleus of 6-animopenicillanic acid (lactam plus thiazolidine) .The reactive β-lactam ring is able to acylate the active serine residue of the transpeptidase, leading to a stable acyl–enzyme intermediate that is still appended with a bulky substituent (the second ring of the β-lactam antibiotics), thus preventing the access of an incoming .
This ring mimics the shape of .So named because of the presence of a four-membered β-lactam ring in the molecules, the β-lactam antibiotics comprise four main classes of drugs that possess .This review discusses, with a focus on structural aspects, the different classes of beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, monobactams .Beta-lactamases are a diverse class of enzymes produced by bacteria that break open the beta-lactam ring, inactivating the beta-lactam antibiotic.
Beta-lactam antibiotics: Mechanisms of action and resistance
Selecting an Antibiotic The 4 ring structure . Additionally, allelic .The principal antibiotic families of which the β-lactam ring is part of the core structure are the penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams, which are also .The β-lactam antibiotics comprise four main classes of drugs, penams (penicillins), cephems (cephalosporins), monobactams, and carbapenems.
Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
They kill bacteria by preventing peptide cross-linking in .β-Lactam antibiotics mimic the terminal d-Ala-d-Ala moiety of the pentapeptide.
Beta-Lactam Antimicrobial Use in Animals
This review discusses, with a focus on structural aspects, the different classes of beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, monobactams and penems) in .
1,2 The antibiotics in this group are characterized by a reactive four-membered β-lactam ring, .The beta lactam ring in all of the first, second, third generation cephalosporins and aztreonam are hydrolyzed by β-lactamases while most of fourth generation cephalosporins are also affected by ESBL .
Cephalosporins as key lead generation beta-lactam antibiotics

There are five relevant . The beta-lactams include some of the most effective, widely used, and well-tolerated agents available for the treatment of microbial infections. Penams are a large group of β-lactams that include penicillins.The combined use of beta-lactamase inhibitors with broad spectrum activity β-lactam antibiotics has been an effective strategy to circumvent the resistance issue. In addition to their chemical structure, the major difference between these .
Origins of the β-lactam rings in natural products
(H) A carbacephem. Other antibiotics that do not fit into the classes listed above include chloramphenicol, , , , , , , , and . These groups will be .Bacterial beta-lactamases, a group of enzymes capable of disrupting the beta-lactam ring structure by hydrolysis, are the most frequently reported source of penicillin antibiotic resistance, especially to natural penicillins (Raj 2021).All beta-lactam antibiotics contain the same core 4-member “beta-lactam” ring (highlighted in red).(B) A carbapenam.The structural characteristics of a β-lactam ring provide higher reactivity for β-lactam antibiotics to inactivate penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) than a linear, five- or .4062/biomolther.Our focus here is on degradation rates for β-lactam antibiotics. Some beta-lactamases are encoded on mobile genetic elements (eg, .
betalactam
Penicillins can .(F) A monobactam. 1,2 The antibiotics in this group are characterized by a reactive four-membered β-lactam ring, which is essential to their bactericidal activity.Auteur : Neelanjana Pandey, Marco Cascella
Structural Insights for β-Lactam Antibiotics
Some beta-lactamases are encoded on mobile genetic elements (eg, plasmids); others are encoded on chromosomes. Antibiotics are listed . Therefore, semi-synthetic penicillins (methicillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, dicloxacillin), which are resistant to .A beta lactamase inhibitor used to enhance the effectiveness of beta lactam antibiotics.Introduction The β-lactams are the most widely used class of antibiotic. The beta-lactam ring is part of the structure of several antibiotic families, principally the penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams, which are therefore also called beta-lactam antibiotics.(C) An oxapenam. They are characterised by a β-lactam ring in their molecular structures (Fig 1); clinically relevant classes of β-lactams include This has a lethal .
Frontiers
4 Enzymatic hydrolysis of beta-lactam antibiotics.Keywords: hydrolysis, decomposition, chemical informatics, lactam antibiotics, antibiotic allergy (including penicillin and cephalosporin β-lactams), antimicrobial activity, deactivation Citation: Turner J, Muraoka A, Bedenbaugh M, Childress B, Pernot L, Wiencek M and Peterson YK (2022) The Chemical Relationship Among Beta . Beta-lactamases are a diverse class of enzymes produced by bacteria that break open the beta-lactam ring, inactivating the beta-lactam antibiotic. Beta-lactamase production is among the most clinically important . Benzylpenicillin: A penicillin used for the treatment of infections caused by gram-positive cocci, in particular streptococcal infections.β-Lactam antibiotics are bicyclic or monocyclic azetidinone ring-containing compounds (Fig. This now allows for .
Beta-lactam
They are called beta-lactams because of the unusual 4-member ring that is common to all their members.
beta-Lactams
Furthermore, the occurrence of bla CTX-M-15, bla TEM-1, and bla OXA genes, also attributed resistance to the beta-lactam class of antibiotics.
β-Lactams and β-Lactamase Inhibitors: An Overview

Background The emergence and spread of β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella spp.Penicillins and cephalosporins are the major antibiotics that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, and Other β-Lactam Antibiotics
That is why we call this a beta-lactam ring. The most effective way for bacteria to counteract these chemicals has been by producing β . • Monobactams work only against aerobic gram-negative bacteria (Neisseria, Pseudomonas). These antibiotics, a group that includes the penicillins and cephalosporins, are covalent .Biosynthetic studies have shown that the β-lactam class of natural products can be divided into at least four different subgroups based on the origin of the β-lactam ring.β-Lactam nucleus is the core of the biological activity of a large class of antibiotics characterized by the presence of this four-membered ring and differentiated . This classification depends on the chemical nature of the ring fused to the β-lactam . This form of penicillin is typically used in intravenous or long-acting injectable formulations due to poor oral .Carbapenems, cephalosporins, monobactams, and penicillins are subclasses of beta-lactam antibiotics, a class of antibiotic characterized by a chemical structure called a beta-lactam ring.
There are five relevant ring systems, including the penam, penem, carbapenem, cefem and monobactam ring structure. The important groups of drugs included in this category are the penicillins, cephalosporins and cephamycins, carbapenams, monobactams, and carbacephams.β-Lactam antibiotics: one of the most relevant antibacterial drug classes worldwide.Looking for our lactam ring, it's an amide in a ring, and we can see that here is our lactam.Beta-lactam antibiotics are among the most commonly prescribed drugs, grouped together based upon a shared structural feature, the beta-lactam ring.Monobactams • Monobactams are a subgroup of beta-lactam antibiotics, wherein the beta-lactam ring is alone and not fused to another ring (other beta-lactams have at least two rings).
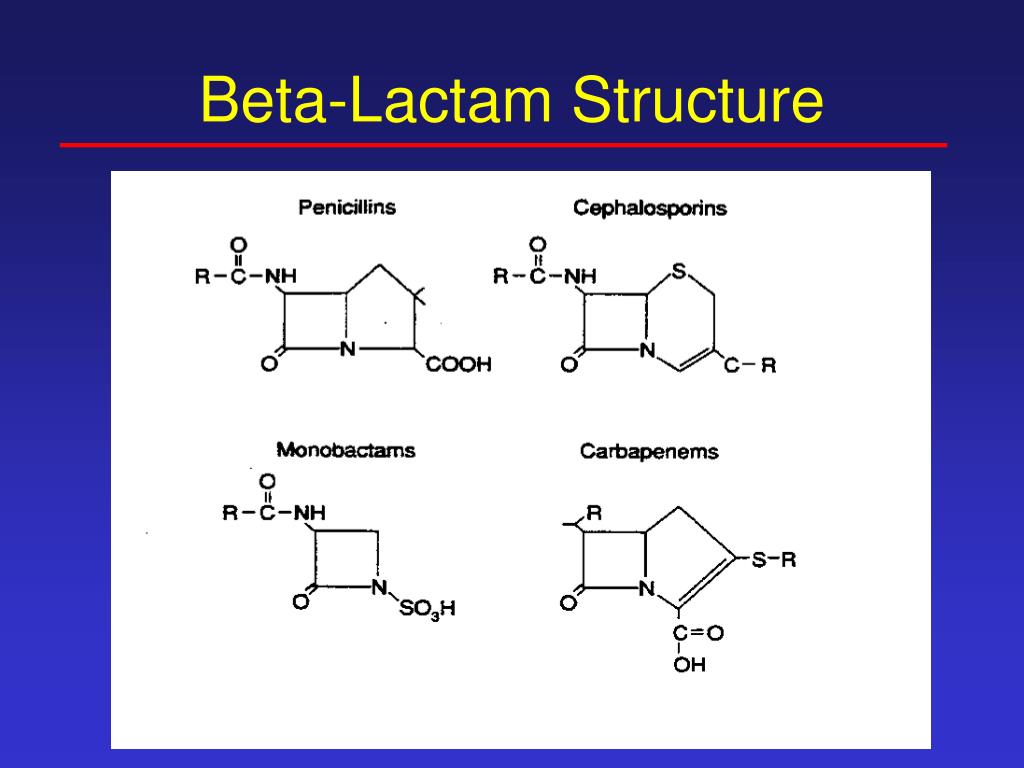
If we wanted to classify this lactam, the carbon next to the carbonyl is the alpha carbon.Beta-lactam antibiotics are those that contain 4-member, nitrogen-containing, beta-lactam ring at the core of their structure.Cephalosporins are the second major group of beta-lactam antibiotics.The β-lactams are the most widely used class of antibiotic. Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems*, Monobactams* (*Beta-lactamase resistance) -lactam antibiotics are the most important class, that frequently used in the treatment of bacterial infection, these are the bactericidal drugs means they kill the bacteria by inhibiting cell .
Beta-lactam antibiotics (video)
This class divided into four subtypes:
Beta Lactam Antibiotic Agent
During World War II there was a huge . They are classified in penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, penems (also known as thiopenems) and monobactams. β-lactams, which inhibit bacterial cell-wall synthesis [28–30], account for the majority of global antibiotic consumption . β-Lactam Antibiotics Bearing More Than One β-Lactam Ring. An interesting approach aimed at improving the biological activity of β-lactam antibiotics and fight resistance against them has been the introduction of more than one β-lactam unit inside the same chemical structure.The β-lactam antibiotics is a family of bactericidal drugs structurally-related containing the β-lactam ring in their chemical structure.
:format(jpeg):mode_rgb():quality(90)/discogs-images/R-10288317-1494711109-2652.jpeg.jpg)





