Bipedalism in human
Human babies do not have prehensile feet, and moreover their hands have no hairy maternal body to cling to.Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where a tetrapod moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs.Human positional behavior research has focused on five interrelated issues of bipedalism: (1) the muscle activity and movements involved in walking or running; (2) the morphology uniquely adapted to bipedalism; (3) the timing of its evolution; (4) the .Some human traits, like bipedalism, evolved very early, while others, like large brains, did not evolve until relatively recently.
The Origins of Bipedal Locomotion
The most striking feature of modern human bipedalism compared with that of other vertebrates is that we walk with extended hips and knees ( 2 ), permitting .Fossils Upend Conventional Wisdom about Evolution of Human Bipedalism | Scientific American. It is essentially an extended period of growth with continued rapid development of the brain. November 1, 2022., the head is above the chest, which is above the pelvis, which is over the knees, which is above the feet). Attention is given to the work of John Napier and John Robinson who were pioneers in the interpretation of Plio-Pleistocene hominin skeletons in the .
Bipedalism in human evolution
Heather Scoville.
A change in the environment would have been at the origin of this evolution.Bipedalism Human skeleton walking.2 Occasional Bipedalism in Non-human Primates: Voluntary But Anatomically Constrained.One enduring hypothesis for this transition is that bipedalism evolved to reduce locomotor costs in early hominins, relative to the ape-like last common ancestor (LCA) of .

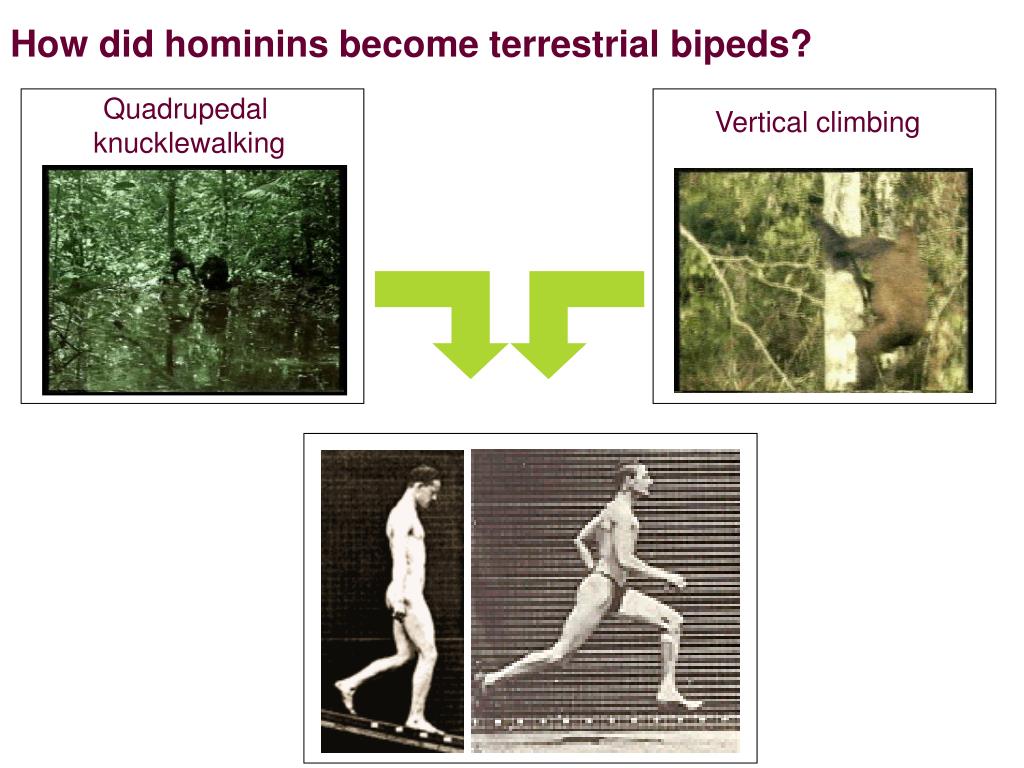
Human bipedalism is commonly thought to have evolved from a quadrupedal terrestrial precursor, yet some recent paleontological evidence suggests that adaptations for bipedalism arose in an arboreal context. Collins English Dictionary. claims that bipedalism came about as the result of Homo ancestors swimming, diving or foraging on the bottom of rivers, lakes or coastal shallows. This reduces the amount of muscle needed to be engaged during locomotion to “pull us up” and allows us to travel longer .66 million years ago are widely accepted as the oldest unequivocal evidence of obligate bipedalism in the human . The obstetric dilemma seeks to explain the helplessness of human infants.
Challenges to human uniqueness: bipedalism, birth and brains

There is no doubt that the evolution of bipedalism is a critical issue in the study of human origins.
Evidence that humans evolved from a knuckle-walking ancestor
It is from this broad ancestral locomotor repertoire that human bipedalism evolved.
In particular, the emergence of so many important fossil .
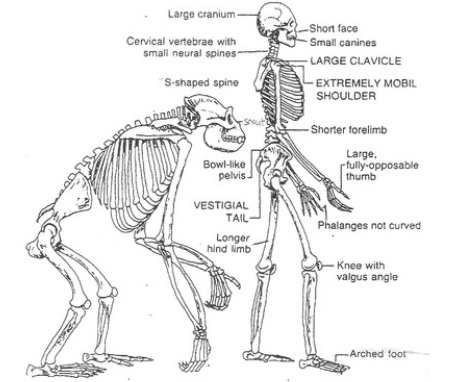
Adaptations to bipedalism include “stacking” the majority of the weight of the body over a small area around the center of gravity (i.1 Introduction. By Nevit Dilmen, CC BY-SA 3. All primates sit upright. Motion analysis, as applied to evolutionary biomechanics, has experienced its own evolution over the last 50 years. The obstetric .Bipedalism first appeared in the human lineage several million years ago and evolved to its modern form through a number of unique stages.Origin of Human Bipedalism As an Adaptation for Locomotion . To say these events were all . Here we show that it allows the most arboreal . An alternative .

When we swim or dive, our head, spine and feet tend to align.
HUMAN EVOLUTION / BIPEDALISM
However, as we have seen, there has often been a considerable degree of rather polarized debate and disagreement as to how, when, why, and in whom hominin bipedalism evolved.Many questions remain about the evolution of bipedalism. The Austalopithecine would have passed from forest to savannah. Author (s) Beth Blaxland, Fran Dorey. the condition or state of having two feet. Silhouette of Orrorin tugenensis for femur. Walking upright may have helped our oldest human ancestors survive in the diverse habitats near where they lived, including forests and grasslands.Bipedal locomotion is found in human species which are bipeds and that walk on two legs as their primary mode of locomotion.The human skeletal form underlies bipedalism, but the genetic basis of skeletal proportions (SPs) is not well characterized. Habitual bipedalism has developed several times within mammals, with macropods, springhare, kangaroo mice and rats, pangolins, jumping mice, and hominin apes (australopithecines and humans) and also other extinct groups .orgEvidence that humans evolved from a knuckle-walking ancestornature.Many studies since the nineteenth century have investigated the origin of human bipedalism.
Convergence of Bipedal Locomotion: Why Walk or Run on Only
Auteur : Heather Scoville
Bipedalism
Orange, blue, and violet lines represent three alternative phylogenetic hypotheses. Thorpe 1, Juliet M.
(PDF) The arboreal origins of human bipedalism
We define it as the period of time following infancy, when the youngster is weaned but is not able to care for itself. Modern human bipedalism develops during the first 9 years of life, is associated with anatomical (pelvic shape, limb length, large calcaneus and hallux) and mechanical (heel strike, toe-off) .24 August 2022. The animals best-known for their ability to practice occasional bipedalism are definitely the non-human primates (NHPs).These theories are in line with Wheeler's claim (albeit energetics only merits one paragraph in his excerpt): “Finally human bipedalism at low speeds uses less energy that does either true quadrupedalism or the knuckle walking used by African apes. Comparison between the legs of a modern human, . Evolutionary theory reminds us, however, of our ancestral .Human bipedalism is commonly thought to have evolved from a quadrupedal terrestrial precursor, yet some recent paleontological evidence suggests that adaptations .An understanding of the evolution of human bipedalism can provide valuable insights into the biomechanical and physiological characteristics of locomotion in modern . Other animals that . Here we review how an ever .Bipedal trackways discovered in 1978 at Laetoli site G, Tanzania and dated to 3. While visiting zoological parks, or hiking in the wild, many of us will have noticed the ease with which primates can .
The First Hominins and the Origins of Bipedalism
From this base rooted in comparative anatomy of living primates we trace changing ideas about the evolution of human bipedalism as increasing amounts of postcranial fossil material were discovered. Highly specialized postcranial adaptations, especially in the lower limb, characterize this unique form of locomotion. Almost a century and a half ago, Charles Darwin in The Descent of Man (1871: 141 . A leg bone and two arm bones of a hominin from Chad suggest that, seven million years ago, around the time .The arboreal origins of human. This reduces both dietary requirements (and the time and effort spent foraging) and the rate at which heat is .
Humans and other bipeds: the evolution of bipedality
Although it has been suggested that the bony labyrinth morphology of great apes is phylogenetically informative, 20, 37 neighbor-joining cluster analyses 20 and our .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Bipedalism
This may have resulted in self-accelerating push towards bipedalism.The oldest evidence for walking on two legs comes from fossils of the earliest humans known.

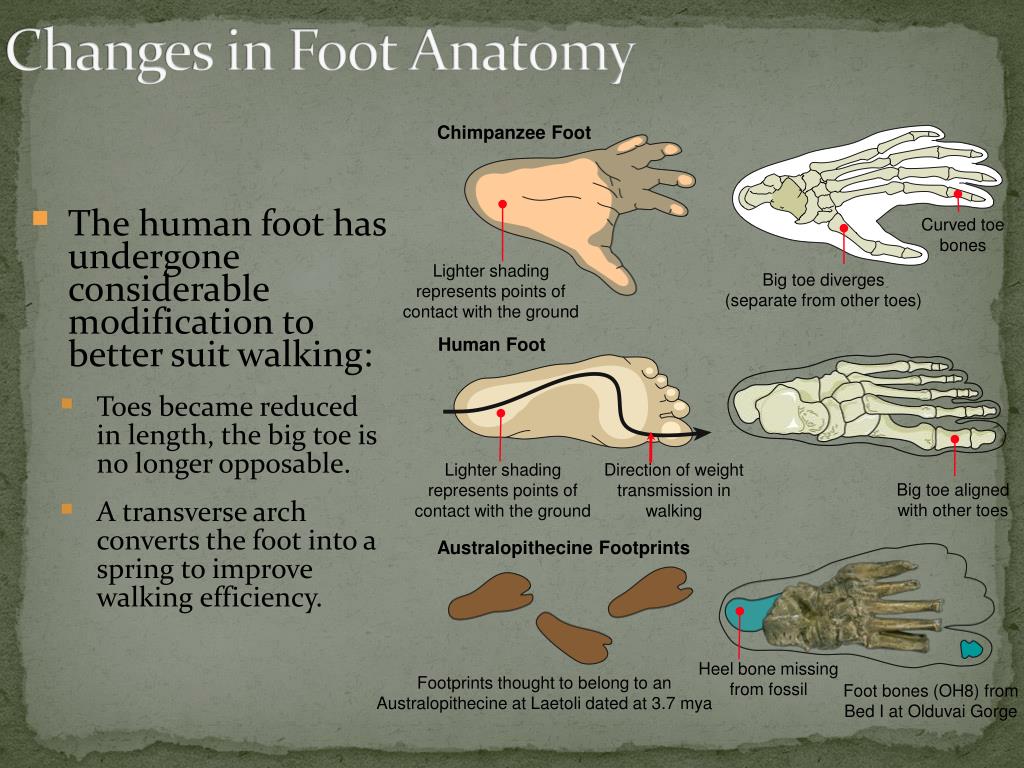
Partially bipedal hominins, with a big toe tending to face slightly forward, would have less prehensile feet.Human bipedalism was derived from a common Lufengpithecus-like locomotor mode.Although habitual bipedalism is unique to humans, it may have developed from occasional bipedalism in ancestors, without a quadrupedal stage.
Standing up for the earliest bipedal hominins
This would result in a more permanent straightening of the spine. 6 million years ago. One of the most obvious characteristics shown by humans that is not shared by . Hypotheses abound . Nevertheless, mechanically, all forms of bipedalism can . Copyright © HarperCollins Publishers. From Darwin and Huxley to the present, many researchers have added insights into this question but with .Bipedalism, a major type of locomotion, involving movement on two feet. Updated on January 01, 2018. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is .As human ancestors evolved, bipedalism became a big advantage, allowing us to grab things with our hands as we stood and walked around on our feet. We applied deep-learning models to 31,221 x-rays from the UK Biobank to extract a comprehensive set of SPs, which were associated with 145 independent loci genome-wide. Standing up for the earliest bipedal hominins. Thus they have to be carried by their mother.The existence of a childhood appears to be an important development on the road to becoming human.

Alternate-foot or striding bipedalism is a locomotor mode unique to humans (Figure 1). We still do not know why upright walking was selectively advantageous for our earliest ancestors and extinct relatives. For a long time, paleoanthropologists thought that large brains were the first hallmark of becoming human; however, research in the 20th century showed that bipedalism, or upright walking, was the first morphological trait on the road to humanity. Word Frequency.Of all extant primates, humans are the only obligate bipeds. The timing of human birth is seen as uniquely constrained by fetal head size and maternal pelvic width.