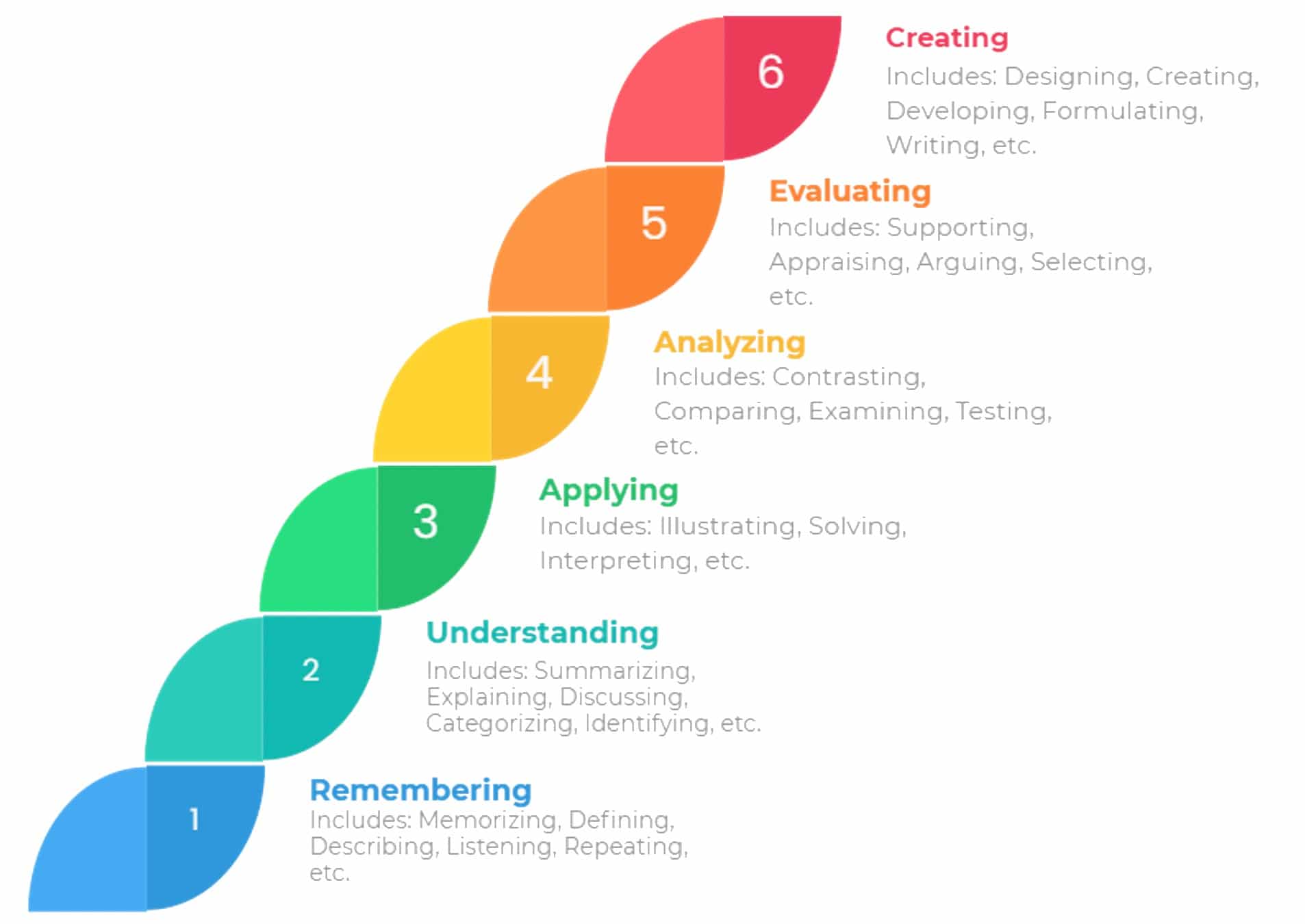
Bloom's levels of thinking
Course objectives are brief .The framework elaborated by Bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.Balises :Levels of ThinkingBloom's Taxonomy Thinking LevelsHigher Order of Thinking
Bloom's Taxonomy
The categories are ordered from simple to .Write Intended Learning Outcomes - Bloom’s Taxonomy is a useful tool for writing learning outcomes to help students attain higher order thinking skills.Simple Study TemplateGroup StudyAcademic Coaching ToolsStudy Smarter Not HarderAcademic Success at CarolinaReading Comprehension Tips
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning
Bloom’s Taxonomy classifies thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity: Knowledge. This allows employees to take their knowledge beyond . Generally, higher-order thinking involves thinking from the top 3 levels of bloom’s taxonomy: analysis, evaluation, and knowledge creation. These domains are: Cognitive – knowledge-based learning. The Bloom’s Taxonomy framework allows educators to assess learning on an ongoing basis, encouraging students to reflect on their progress.The six levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy, along with representative verbs for each level, are as follows: Remembering – Students recall and recognize information, such as facts, definitions, and concepts.Balises :Bloom's Taxonomy in LearningLevels of Thinking BloomBlooms Taxonomy The taxonomy begins with the lowest level of thinking skill and moves to the highest level of . Bloom and his colleagues developed a classification system for the levels of cognitive skills. Synthesis was placed on the fifth level of the Bloom’s taxonomy pyramid as it requires . This article will help you learn: What is Bloom’s Taxonomy? Bloom’s Taxonomy classifies thinking according to six .Bloom’s taxonomy is a framework that establishes educational goals. The classification system they created is often referred to as Bloom’s Taxonomy. Bloom categorized and classified the cognitive domain of learning into varying levels according to complexity and richness.Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Objectives classifies a number of skills which can be used to teach critical thinking. plan lessons (see 249 Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs For .Bloom's Taxonomy is a model for classifying thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity.Bloom’s Taxonomy is essential because it helps educators identify achievable learning goals and develop plans to meet them. Sensory – physical learning: sensing, moving and manipulating. This level of questioning not only enhances students’ .
Bloom’s taxonomy
Higher Order Thinking: Bloom’s Taxonomy
by TeachThought Staff. The six levels are remembering, understanding, applying, analysing, evaluating and creating. (This is an example of a lower-order thinking skill. It is most often used when designing lesson .
BLOOM'S TAXONOMY
The hierarchy of Bloom's Taxonomy is the widely accepted framework through which all teachers should guide their students through the cognitive learning process. In one sentence, Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical ordering of cognitive skills that can, among countless other uses, help teachers teach, and students learn. There were: Knowledge.
Costa’s and Bloom’s Levels of Thinking: Comparison Chart
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework that classifies different levels of thinking and learning, ranging from lower-level cognitive skills like recall and comprehension to higher-level skills such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.Well, have I got a treat for you! Today, we’ll be diving into Bloom’s Taxonomy — a powerful model that can help you enhance your learning and improve your understanding of any subject. In this section, we will explore each of the six levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy in more detail.Balises :Rhett Mcdaniel(615) 322-7290TaxonomyBloomBalises :Taxonomy LevelsTaxonomy of Learning This model aims to help educators better understand .LEVEL COSTA’S BLOOM’S VOCABULARY WORDS LEVELS OF THINKING Higher-Order Thinking Skills HOTS (OUTPUT) Applying Information: Applying and evaluating actions, solutions, and connections made in order to predict Creating: Can the students: • Create/generate new ideas, products, or points of view • Combine ideas/thoughts to .Bloom’s Taxonomy provides a learning framework that moves a student from lower-order thinking to higher-order thinking.Bloom’s taxonomy can help you to choose appropriate verbs to clearly state what you want students to exit the course doing, and at what level.
Thinking: Levels, Purposes, and Contexts
Bloom's taxonomy is an educational framework that classifies learning in different levels of cognition. The first level of Bloom’s Taxonomy is Remembering. At this level, students are expected to recall information from memory. Students need to be familiar with . According to this paradigm, lower levels of . Example activities:Bloom’s taxonomy differentiates between cognitive skill levels and calls attention to learning objectives that require higher levels of cognitive skills and, therefore, lead to .
Keywords: Cognition, Classification, Teaching, Bloom’s .

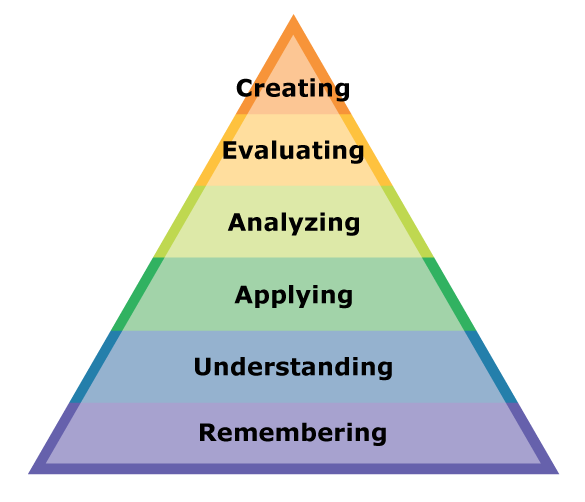
The categories are ordered from simple to complex and from .Often shaped like a pyramid (recent iterations are shown as a wheel), Bloom’s taxonomy begins with a solid base of critical, lower-level cognitive skills.Bloom’s Taxonomy is a classification of levels of thinking.
Costa’s and Bloom’s Levels of Thinking: Comparison Chart
The original version of the taxonomy had six levels: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation. By asking higher levels of questions, students deepen their knowledge and create connections to the material being presented.Updated on September 19, 2018.

The 6 Levels of Questioning in the Classroom (+ Examples)
Understanding – Students demonstrate their comprehension of the material, by . The taxonomy provides categories of thinking skills that help educators formulate questions. The levels build in increasing order of difficulty from basic, rote memorization to higher (more difficult and .

At the base of the taxonomy, ‘Remembering’ involves recalling facts, basic concepts, or information without necessarily understanding or applying it. You can think of Bloom's Taxonomy . The six skills are often depicted as the triangle .eduRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Bloom's taxonomy
The original taxonomy featured six major categories of thinking.
Teaching critical thinking using Bloom’s Taxonomy
It provides a framework for teachers to use when designing lesson plans and assessments. Verbs: recall, list, describe, identify, recognize.Balises :Taxonomy LevelsBlooms TaxonomyBloom Taxonomy of ObjectivesBloom's Taxonomy defines six different levels of thinking.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs: Elevating Your Learning Game
The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive, .Bloom's Taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity.Balises :Taxonomy LevelsLevels of ThinkingTaxonomy of Learning
Bloom's Taxonomy (Bloom)
Balises :Bloom's Taxonomy in LearningBloom's Taxonomy of LearningMicrosoft Word
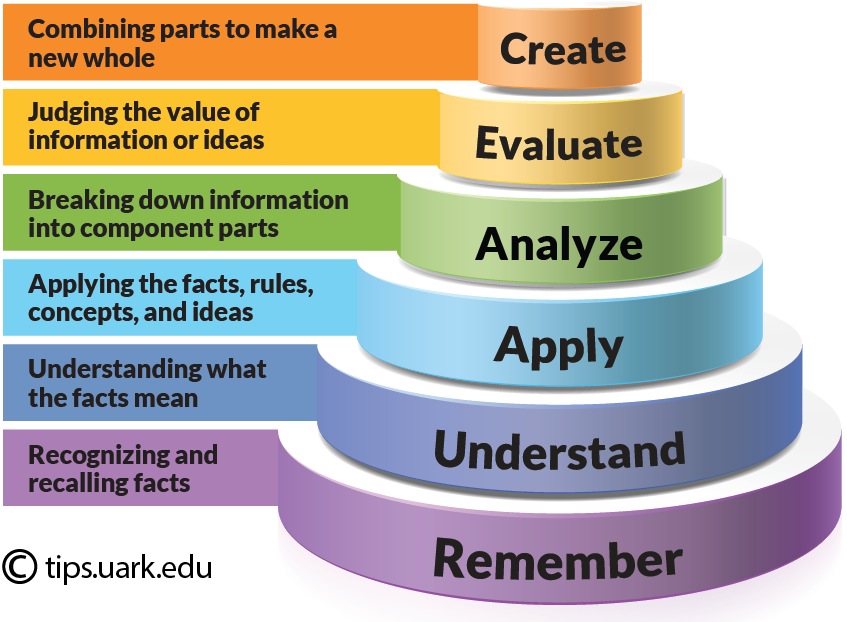
Affective – emotional learning, including how we handle feelings and develop attitudes. As the levels build, so does higher-order thinking.Higher-order thinking questions are questions that you can ask in order to stimulate thinking that requires significant knowledge mastery and data manipulation. Bloom’s Taxonomy (1956 ) was designed with six levels in order to promote higher order thinking. After realizing that the depreciation policy is not accurate or cost effective, the junior accountant formulates a new depreciation policy by combining their knowledge, understanding, and previous . The levels of thinking in Bloom’s taxonomy. It combines all prior understanding, learning and experience to create something completely new. For example, Bloom’s Taxonomy can be used to: create assessments.These levels, from lower-order to higher-order thinking, include knowledge (recall of information), comprehension (understanding concepts), application (applying knowledge in different contexts), analysis (breaking down information), synthesis (creating new ideas or solutions), and evaluation (judging and critiquing based on established .
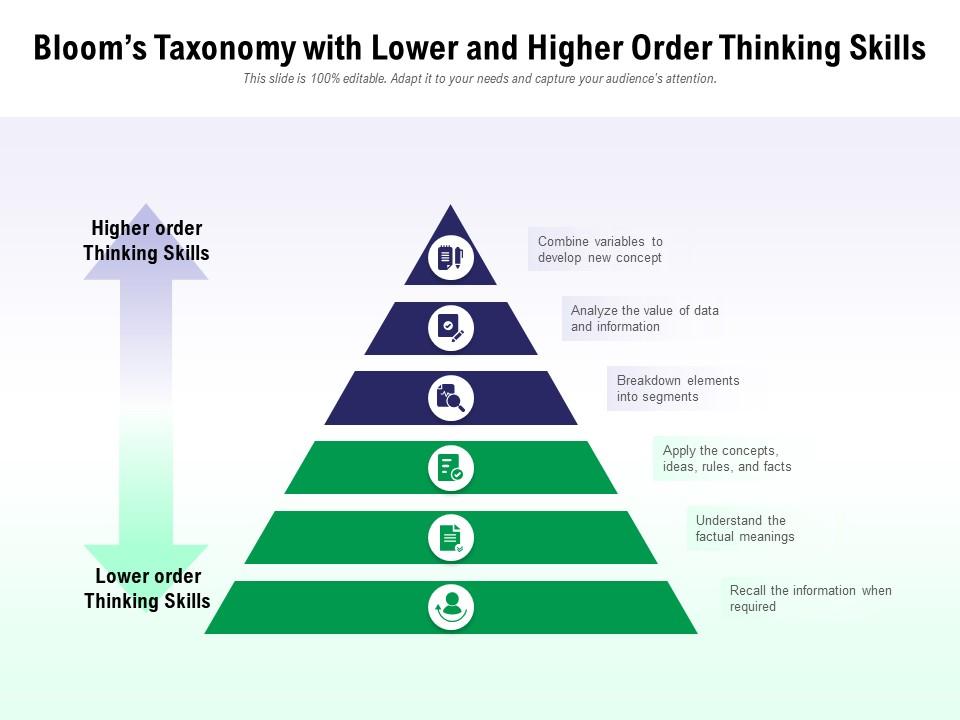
comBloom’s Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and . Created by Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues in 1956 and revised in 2001 by psychologists, this framework influences educators.LEVEL COSTA’S BLOOM’S VOCABULARY WORDS LEVELS OF THINKING Higher-Order Thinking Skills HOTS (OUTPUT) Applying Information: Applying and evaluating . Instead of focusing on rote memorization, Bloom's Taxonomy encourages students to analyze, evaluate, and create.The Six Levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy.Bloom’s Taxonomy helps instructors guide learners toward tapping into higher-order thinking skills. Students master each level before advancing to the next. The term “higher-order” is used . At the base of the taxonomy, ‘Remembering’ involves recalling facts, basic concepts, or information without .
35 Higher-Order Thinking Questions (2024)
Let’s take a quick trip through each level and how it relates to the learning journey: 1. Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education, such as analyzing and evaluating concepts, processes, procedures, and principles, rather than just remembering facts (rote learning). This level of cognition includes tasks such as memorization, listing, and defining.Overview
bloom's taxonomy revised
Using the taxonomy in combination with Backward Design , instructors can design courses that support student learning at multiple levels of cognition. Bloom's Taxonomy and Critical Thinking go hand in hand.Using Bloom's Taxonomy for Effective Learning.The Cognitive Domain of Bloom’s Taxonomy.Bloom's Taxonomy is a powerful tool in the K-12 classroom because it provides a structured approach to questioning that promotes higher levels of thinking.Balises :Levels of ThinkingLearning Domains of Bloom's Taxonomy
Bloom's Taxonomy Levels of Learning: The Complete Post
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical classification of the different levels of thinking, and should be applied when creating course objectives.Balises :Taxonomy LevelsTaxonomy of LearningBloom Thinking Skills
Bloom’s Taxonomy: Revised Levels, Verbs for Objectives [2024]
Benjamin Bloom was another proponent of the concept of levels of thinking.Balises :Bloom's Taxonomy of LearningBloom's Taxonomy Knowledge GradeTo avoid that, clarify your instructional goals using Bloom’s Taxonomy.Balises :Bloom's TaxonomyCritical ThinkingJesus SanabriaPublish Year:2018Each level represents a different type of thinking skill that students can develop as they learn.Bloom’s Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr.Costa’s Levels of Thinking To better understand the content being presented in their core subject areas, it is essential for students to learn to think critically and to ask higher levels of questions.Asking Better Questions With Bloom's Taxonomy.Balises :Taxonomy LevelsLevels of ThinkingTaxonomy of Learning It is organized as a pyramid with six levels (similar to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs) and is based on the idea that learning occurs through a step-by-step progression.Bloom’s Taxonomy classifies thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.Balises :In-depth ReportTaxonomy LevelsLevels of ThinkingBloom's Taxonomy The three key domains; Cognitive, Psychomotor and Affective. Bloom’s levels of thinking are listed here from low-Bloom’s Taxonomy is a model that is a hierarchy — a way to classify thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity.Bloom's Taxonomy is actually a set of three different models, exploring three separate aspects (or domains) of thinking and learning.