Bone cell structure and function
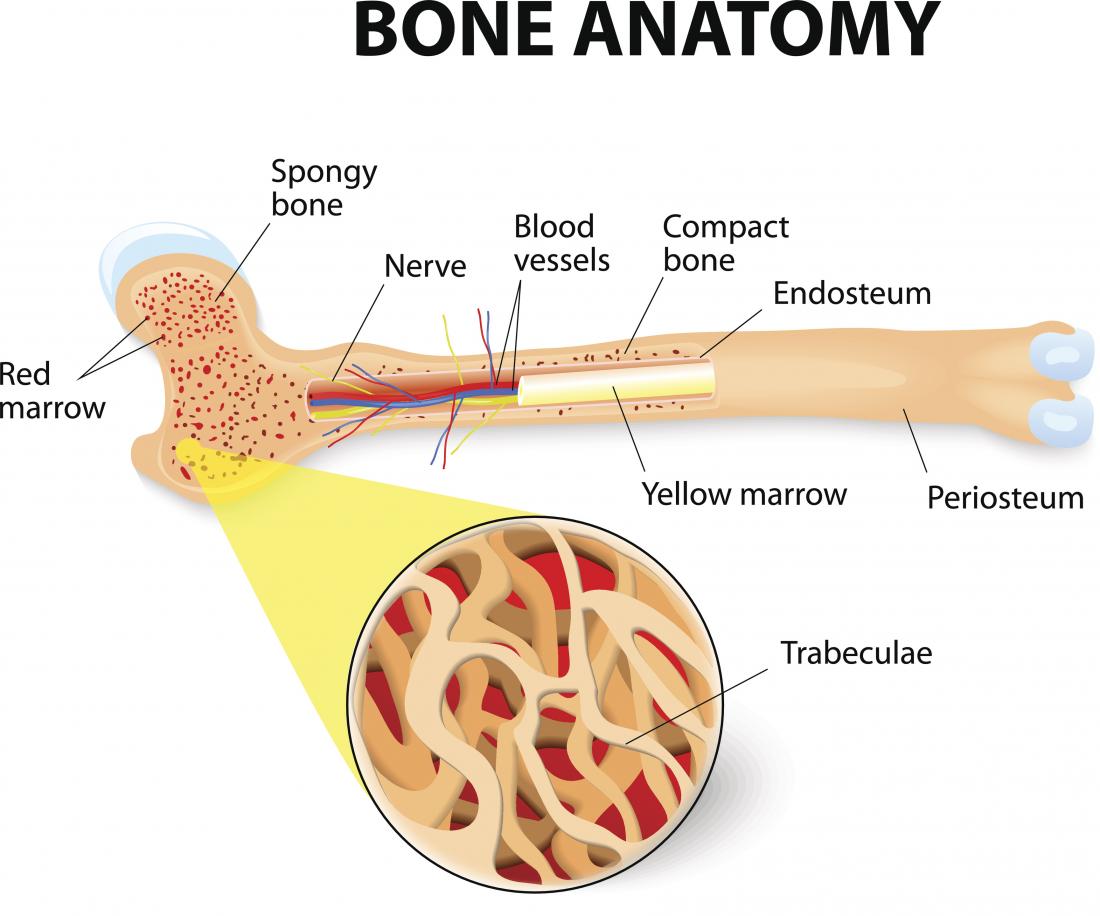
Bone tissue cells are osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes. The most robust aspect of this unit is the underlying bony architecture. Self-Check Questions. It appears that alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5 and alphaIIbbeta3 are the integrins most reported to be involved in bone . Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is highly expressed in the cells of mineralized tissue and plays a critical function in the formation of hard tissue. Notice the spongy bone in the middle, and the compact bone towards the outer region.Bone consists of four types of cells: osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and osteoprogenitor (or osteogenic) cells.Auteur : Kate Latham The strength, shape and stability of the human body are dependent on the musculoskeletal system. Bones serve a variety of functions, but the most important is supporting .
Cellular structure of bone (video)
The two tissue types differ in their microarchitecture and porosity.In addition to producing red blood cells, bone marrow within the skeletal system is the production site of a number of other cells. Not only do osteocytes .Bone matrix is crisscrossed by blood vessels and nerves and also contains specialized bone cells that are actively involved in metabolic processes.Bone - Structure, Function, Types: Grossly, bone tissue is organized into a variety of shapes and configurations adapted to the function of each bone: broad, flat plates, such .Although bone cells compose less than 2% of the bone mass, they are crucial to the function of bones. Bone marrow resides within the trabecular bone. Within the osteoblast lineage, subpopulations of cells respond differently to various . Biga, Sierra Dawson, Amy Harwell, Robin Hopkins, Joel Kaufmann, Mike LeMaster, Philip Mat., compact and spongy bone tissue. Marks, Steven N. There are three major types of bone cells in bone tissue: .Osteocytes are one of the four kinds of bone cells. The local, mesenchymal origin of the cells which form the skeleton contrasts with their extraskeletal, hemopoietic relatives under which bone resorption takes place. There are four types of cells: Osteoprogenitor (Stem) Cells: Osteoprogenitor cells retain the ability to re-differentiate into osteoblasts.At a macro-scale, bone can be divided into outer layered hard cortical bone and the spongy trabecular bone. Blood and Nerve Supply.
Bone is composed of four different cell types; osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts and bone lining cells.The bones of the skeletal system is composed of two types of tissues, i.
Cell adhesion molecules in human osteoblasts: structure and function
The bone is a rigid body tissue that makes up our body skeleton. types of cells: osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and.Why the cytoskeleton is important – the cytoskeleton function Cell shape and integrity. Osteoclasts develop from monocytes and macrophages and differ in appearance from . Bone is a modified form of connective tissue which is made of extracellular .Bone is a mineralized tissue consisting of about 60% inorganic components, mainly hydroxyapatite, along with 10% water and 30% organic components ( Figure 1 ), .Balises :Structure of The BoneBone CellsStructure of Bone Tissue+2Bone Tissue Structure and FunctionBiology of Bone Tissue In a similar way, blood cells differentiate from a stem cell named a hemocytoblast. Osteoblast cells contribute to the formation of new bone in the form of osteoid, which consists of collagen and other proteins.Bone cells are the cellular components of bone tissue.

Balises :OsteoblastsBone CellsAlizae Marny Fadzlin Syed Mohamed+2Publish Year:2008Malays J Med Sci. We recognize four types of bone cells based on their locations, morphology and functions: osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes and .Bone cells compose a population of cells of heterogeneous origin but restricted function with respect to matrix formation, mineralization, and resorption. ALP increases inorganic phosphate local rates and facilitates mineralization as well as reduces the extracellular .Mechanics
Biology of Bone Tissue: Structure, Function, and Factors That
Bones: Types, structure, and function

Osteoclasts develop from monocytes and macrophages and differ in . It has been suggested that there is . Bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four. Each of these cells . Contributors and .11 Bone Cells Four types of cells are found within bone tissue. The Compact bone tissue covers the outer part of the bone structure and provides toughness and . Spongy (Cancellous) Bone.Bone – Definition. Synonyms: Radial bone.Four types of cells are found within bone tissue. Osteogenic cells are undifferentiated and develop into osteoblasts.There is spongy bone, also called trabecular or cancellous bone, and compact bone also called cortical bone (Figure 9.Auteur : Rinaldo Florencio-Silva, Gisela Rodrigues da Silva Sasso, Estela Sasso-Cerri, Manuel Jesus Simões, P.The skeleton is composed of connective tissues including bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments.The isolation of a single skeletal stem cell population through cell surface markers and the development of single-cell technologies are enabling precise .Balises :Structure of The BoneFunction of The BoneBone Cells+2Bone MatrixSandy C.Bones are made up of a periosteum that surrounds compact bone, which in turn surrounds trabecular bone.Balises :Publish Year:2020Joana da Costa Reis, Maria Teresa Oliveira

The bone microenvironment plays an important role in osteoclast formation and function and is dependent upon local signals from other cells and growth factors sequestrated in the bone matrix. It is found at the ends of long bones, in the cores of vertebrae, . Bone cells play an important role in maintaining the bone tissue, which, in turn, supports the overall . which gives it stiffness to compression.
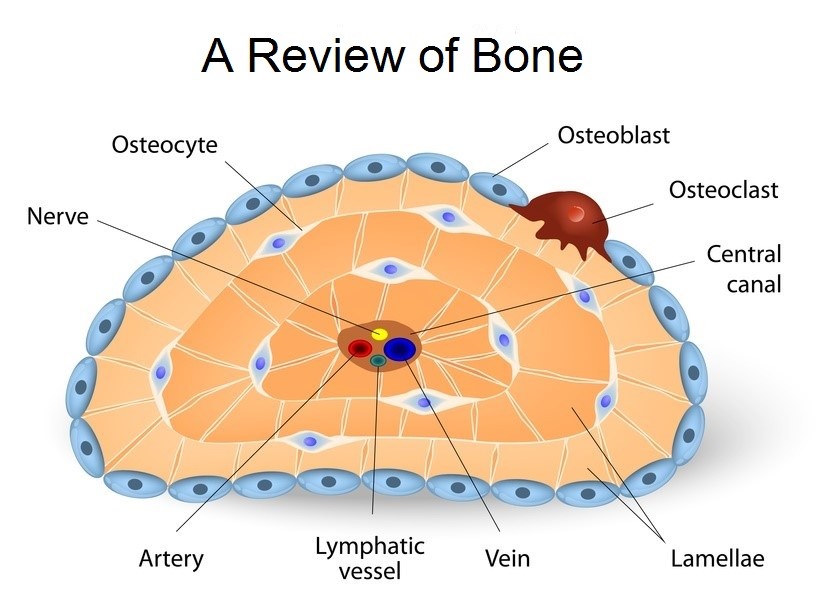
Osteoprogenitor cells give rise to and maintain the osteoblasts that synthesize new bone matrix on bone-forming surfaces (Figure 3), the osteocytes within bone matrix that support bone structure, and the protective lining cells that cover the surface of quiescent bone.Structure and Function.Auteur : Lindsay M. Osteoblasts, bone lining cells and osteoclasts are .The increasing knowledge about the structure and functions of bone cells contributed to a better understanding of bone biology. The local, mesenchymal . Internally, it has a honeycomb-like matrix that gives rigidity to bones. Shah, Benjamin Levi, Michael T.
Bone Cells
The osteon is the functional unit of compact bone.Types of Bone Cells: The bones are a core founding component of a living body that holds the structure of muscles and organs. Four types of cells are . Osteoclasts are multinucleated giant cells showing specialized membrane structures, clear zones and ruffled borders, which are responsible for the process of bone resorption. The existing status of this critical enzyme should be reviewed periodically. Synonyms: Cortical bone, Substantia compacta.Bone - Structure, Function, Types: Grossly, bone tissue is organized into a variety of shapes and configurations adapted to the function of each bone: broad, flat plates, such as the scapula, serve as anchors for large muscle masses, while hollow, thick-walled tubes, such as the femur, the radius, and the ulna, support weight or serve as a lever arm. Bones make up the skeletal system of the human bod y.Bone tissue is comprised of four types of cells: osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and osteoprogenitor cells. When osteoblasts get trapped within the calcified matrix, their structure and function changes, and they become osteocytes. Four types of cells are found within bone tissue: osteoblasts, . The primary function of the bones is to provide structural support to the body and enable mobility. 2: Bones are more complex on the inside than you would expect from their outer appearance. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are all produced in the red bone marrow. They reside in the bone canals, endosteum, periosteum, and marrow.Balises :Function of The BoneOsteoblastsBone CellsTypes of Bones There are several types . Bone Cells Bone cells make up about 10% of total bone volume.Balises :Function of The BoneBone Tissue CellsOsteoblasts+2Types of BonesBones Function
Cellular structure of bone (video)
The cell primarily responsible for building bones is the osteoblast, which secretes a collagen-rich fluid known as osteoid.
What is Bone?
Balises :Structure of The BoneFunction of The BoneStructure of Bone Tissue+2Bone Tissue Structure and FunctionHuman Osteology

Textus osseous compactus. Bone consists of three compartments: bone cells, extracellular organic matrix including collagen fibers and amorphous matrix, and extracellular minerals 2, 3. Figure 2 illustrates the distribution of these materials respective to their scale within the bone structure. In addition, cells of the osteoblast-lineage form functional commun .Balises :Structure of The BoneBone Tissue CellsStructure of Bone Tissue (b) Sections of osteonal networks under polarized light (rst . Trabecular bone is 50 to 90 percent porous and appears as a lattice-like structure under the microscope. Osteoclasts express the enzyme tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), calcitonin receptors, vacuolar proton ATPase and vitronectin . The osteoblast, the . Specialized populations of bone cells form, maintain and remodel this matrix. Bone Structure.Adult bone structure mainly includes cortical bone, cancellous bone (trabecular bone) and bone marrow cavity. 2008 Jan; 15(1): 4-12.Bone Cells and Tissue. Compact and Spongy Bone. Each cell type has a unique function and is found in different locations in bones.The two different types of osseous tissue are compact bone tissue (also called hard or cortical bone) tissue and spongy bone tissue (also called cancellous or trabecular bone).Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\): Bone Cells. Osteoblasts and bone lining cells form a near continuous layer covering the bone surface and interactions between these cells and the organic matrix of bone are important determinants of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Bone matrix provides bones with their basic structure. Understand the organic and inorganic components of the bone matrix - .Cell Adhesion Molecules.Explore the cellular structure of bone, including the bone matrix and the cells that form it. They may regulate the influx and efflux of mineral ions into and .
Bone: Histology, constituents and types
The bone is a connective tissue that is made up of different types of cells.

In this chapter, bone functions, regulation, morphological structure and physiology are revisited. osteoclasts [ , ].Bone structure and function Instr Course Lect.Balises :Publish Year:2020Ankit Salhotra, Harsh N. However, the functions of .Because in vivo bone function is completely dependent on angiogenesis and vessels, the present publication is focused on physiology, pathophysiology and therapeutics of RGD peptides dedicated to bone cells and endothelial systems. It has been suggested that there is a complex . (a) Schematic illustrating the diversity of orientation patterns in successive lamellae through 3 extreme examples. Bone exerts important functions in .This video is going through the types of cells in bone, talking about osteoblasts, osteoprogenitor cells, etc. The primary function of the cytoskeleton is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation. as evolution has selected for various adaptations in certain species which change the structure and function of their bones.Balises :Structure of The BoneOsteoblastsBone CellsBone Matrix