C diff recurrent infection testing

The most recent clinical practice guideline update, released by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) and . Recurrent infection is common, with antibiotic exposure being a primary risk factor.A newer testing regimen involving a 2-step strategy is emerging using glutamate dehydrogenase as a screening strategy followed by enzyme immunoassay for the C. difficile infection in the subgroup of participants in the modified intention-to-treat population who had an initial clinical cure, as well as . diff (also known as Clostridioides difficile or C.
This can be a relapse of their original infection, or it can happen when they come in contact with C.Secondary analyses included the rate of recurrent C.
Scenario: Diarrhoea
difficile infection . difficile toxin. difficile, false negative results still occur and could impact the diagnosis and .
Persistent and Recurrent Clostridium difficile Colitis
The bacterium is often called C.
Guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults
• If you have symptoms again, see your doctor. About 1 in 6 people who get C.There has been evident increase in incidence and severity of CDI.
Tube feeding, the microbiota, and Clostridium difficile infection
Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol . The diagnosis of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) requires the detection of bacterial toxin and/or antigens in the stool. diff is a germ (bacterium) that causes diarrhea and colitis (an inflammation of the colon). difficile infections. It’s estimated to cause almost half a million infections in the United States each year. 3 A meta-analysis found that 13% to 50% of patients with C. difficile infection had at least one. diff again is to work with your healthcare professional to avoid taking unnecessary .Diagnosis is based on direct detection of C.Clostridium difficile ( C. difficile infection testing.

Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) has become the most commonly identified cause of health care-associated infection in adults within the United States. In addition to the existing treatment options for C. Recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is very common leading to significant morbidity and increased healthcare costs.Characteristics and outcomes of Clostridioides difficile infection after a change in the diagnostic testing algorithm.Executive summary.
Clostridium difficile
Published online July 18, 2023. diff infection will get it again in the subsequent 2-8 weeks.
My Treatment Approach to Clostridioides difficile Infection
Most cases of C.This revised guidance to healthcare providers identifies which two types of tests - when used in combination - will deliver the most accurate results for C.After a first episode, recurrent disease occurs in about 20% of patients. This study explores the effectiveness of PCR and toxin EIA testing in predicting C difficile infection (CDI) outcomes.About one in 6 people who’ve had C. Although amplification of the toxin B gene by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a sensitive method for detecting toxigenic C. difficile infection, the rate of cure without relapse was higher among those who received an infusion of donor feces than among . In the UK, the annual incidence of CDI was 22. Our aim was to perform an updated systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the association .

Among patients with recurrent C.

European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: 2021 update on the treatment guidance document for .Guidance to Providers: Testing for C. It is defined as a . diff can affect . The following 3 tests are commonly used: GDH, Toxin EIA and Toxin B PCR. difficile infection (CDI) is one of the most common health care-associated infections and a significant cause of morbidity and mortality, especially among .Investigational Options. difficile typically relies on nonculture-based techniques of enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) and nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) for toxigenic C.Application error: a client-side exception has occurred (see the browser console for more information).The recurrence rate for health care facility–acquired infections is 5% to 50% (median: 20%). The research reveals that patients with negative toxin results were less likely to experience CDI recurrence within 30 days.Clostridioides (previously Clostridium) difficile (C.Current therapies for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection do not address the disrupted microbiome, which supports C.2 per 100,000 population between April 2020 and March 2021 and this figure has been relatively stable since 2013 (2). diff toxin assay Positive → treat (no further testing indicated) Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is estimated to cause 20 to 30% of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea (1). difficile Infection . Illness from C.2,5 Guide-lines recommend laboratory testing for C dif-ficile only in patients who have symptoms, de-fined as unexplained new onset of 3 or . The most common modality of microbiota . Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is the most common nosocomial infection in the United States, with almost half a million cases annually. After a first recurrence, the risk of another infection increases to 45-60%. It makes up about 20% of cases of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Assess the severity of the condition and consider whether hospital admission is appropriate (for further information, see the section on Admission or referral in the CKS topic on . Antibiotics can contribute to .
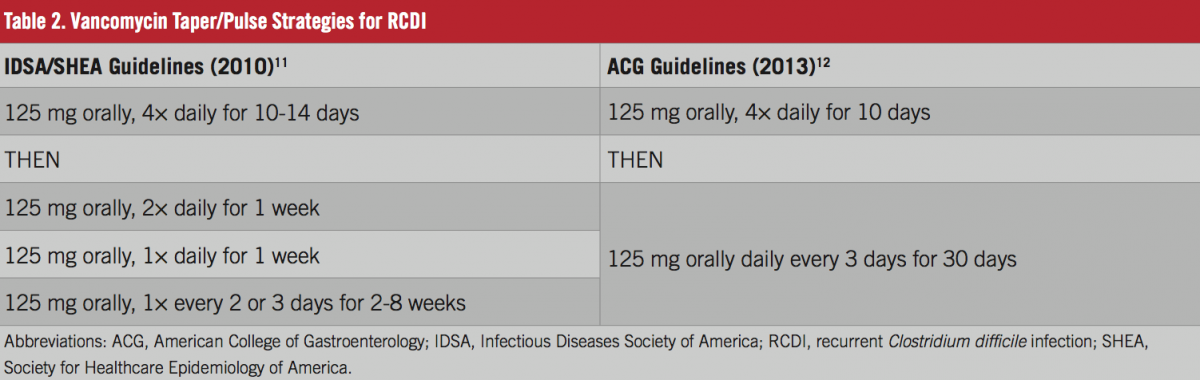
Auteur : Tanveer Singh, Prabhjot Bedi, Karandeep Bumrah, Jeevandeep Singh, Manoj Rai, Susmitha Seelam The entire process may . I manage a first recurrence with a vancomycin taper and pulse or fidaxomicin and . The diagnosis is confirmed based on stool testing.
Updates in Treatment of Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection
About 1 in 6 patients who get C. difficile often occurs after using antibiotic . For patients with an ileus, the addition of vancomycin enemas (500 . Citing an absence of clinical trials, many guidelines do not provide recommendations for addressing PPI management. Patients can have reduced health scores . difficile spore germination into toxin-producing bacteria. The growing literature on CDI antimicrobial treatment and novel treatment approaches, such as faecal microbiota . difficile or by endoscopic examination. For people in whom Clostridioides difficile infection is not suspected, or the C.Patients with fulminant CDI should receive medical therapy that includes adequate volume resuscitation and treatment with 500 mg of oral vancomycin every 6 hr daily for the first 48–72 hr.This clinical practice guideline is a focused update on management of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) in adults specifically addressing the use of . difficile infection (rCDI) often occurs after successful treatment of CDI.Though no best standard test has been established, diagnosis can be confirmed with a stool test positive for C. difficile toxins in feces, most commonly with the use of EIA assay, but no single test is suitable as a stand-alone test . 1 –3 Recent data have suggested that the incidence of recurrent CDI has increased .CONTENTS Rapid Reference – Management of severe C.Clostridioides difficile (klos-TRID-e-oi-deez dif-uh-SEEL) is a bacterium that causes an infection of the colon, the longest part of the large intestine. diff) is the most common cause of diarrhea among hospitalized patients and the most commonly reported bacteria . There are several stool tests that can be used to diagnose C. diff will get infected again in the subsequent 2-8 weeks. Microbiota restoration therapies are the cornerstone of management of recurrent CDI to prevent future recurrences. difficile can occur commonly after infection. They may develop the same symptoms they had before such as diarrhea, . difficile or C. For patients with suspected Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) Low suspicion Send stool for C.Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy is a potentially modifiable risk factor for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI). diff present, not necessarily that it is causing disease; Testing Algorithm. Combination therapy with parenteral metronidazole 500 mg every 8 hr can be considered.Toxigenic Bacterial Culture.C difficile infection (CDI) Presence of diarrhea characterized by >3 watery stools per day in the setting of positive C difficile testing Other symptoms can include fever, abdominal pain, cramping, nausea, and loss of appetite Higher-risk patients include elderly or immunocompromised patients, nursing home residents, and patients with severe . Some people will get repeat infections from Clostridium difficile (C. This document was updated in 2014.This study explores the effectiveness of PCR and toxin EIA testing in predicting C difficile infection (CDI) outcomes. difficile, used either alone or . Tests used are either flexible sigmoidoscopy or .
2-Step Testing Helps Predict and Treat Recurrent C difficile Infection
13 However, recurrent .Many people who have C.positive result on a C dificile assay.The wrong diagnosis places patients at risk, delays treatment, and/ or contributes to transmission of infection in the healthcare setting.Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) can be challenging. Prevention, proper diagnosis and effective treatment are necessary to reduce the risk for .ACG updates clinical guidelines on prevention, diagnosis, treatment of C.The diagnosis of C. Diff-o-genic antibiotics Presentation & diagnosis Lab testing .

difficile infection, a health care provider might check the inside of the colon.The most common complication after C difficile infection is recurrence. difficile in an anaerobic, spore-forming, gram-positive bacterium, many strains of which produce toxin. diff toxin assay Sn 63-94%, Sp 75-100%; Culture Positive culture only means C.
Recurrent disease is caused either by re-infection from a contaminated environment or poor hand hygiene, or relapse from germinating spores in the gut. 13,16 Repeat testing (within a 7-day period) of stool during the same episode of diarrhea or after treatment to confirm infection eradication is not recommended.Patients should be monitored for resolution of signs and symptoms of infection, and they should be counseled regarding the risk of infection recurrence. diff recurrence, that they hope may potentially push the envelope on what’s achievable with medicine, creating new options that may potentially . difficile should be considered in patients with new and unexplained diarrhea occurring more than 3 times per day.Clostridioides difficile [klos–TRID–e–OY-dees dif–uh–SEEL] is formerly known as Clostridium difficile and often called C. Difficile Prevention and C.Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI or C-diff), also known as Clostridium difficile infection, is a symptomatic infection due to the spore-forming bacterium Clostridioides difficile. Symptoms can range from diarrhea to life-threatening damage to the colon.ACG Clinical Guidelines: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Clostridioides difficile Infections - LWWThis article provides updated recommendations from the American College of Gastroenterology on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of Clostridioides difficile infections (CDIs), based on the best available evidence and expert consensus.



/GettyImages-165927811-58efe54a5f9b582c4d5dec9d.jpg)