Calculate voltage across resistor

You know the voltage across the resistor (ex 7V), and you know the current you want (ex 10mA/0. The overall voltage is 14.
How to Calculate a Voltage Drop Across Resistors
What Is Ohms Law?
Voltage Divider Calculator
The ohms law calculator calculates power, current, resistance, and voltage flowing through a circuit in a specified direction.
Ohm's Law: Definition, Formula, and Solved Problems
We can calculate the voltage across the thermistor . To illustrate: a resistor of 1 Ω subjected to a current of 1 A has a voltage difference of 1 V across its . Learn how to solve the current and voltage across every resistor.A voltage divider circuit is a very common circuit that takes a higher voltage and converts it to a lower one by using a pair of resistors. Also you will learn how to take a circuit an.For example, if the voltage at one side of a 10Ω resistor measures 8V and at the other side of the resistor it measures 5V, then the potential difference across the resistor would be 3V ( 8 – 5 ) causing a current .The voltage source supplies energy (causing an electric field and a current), and the resistor converts it to another form (such as thermal energy). What I really want is an answer as to why the voltage drop in the second circuit across each resistor is half, even though they have the same resistance as the one in the first circuit.Series RLC Circuit Example No1.
Ohm’s law formula helps to calculate voltage, current and resistance.
Voltage drop across Resistor Calculator
where R the resistance in ohms (Ω), V the voltage in volts (V), and I is the current in amperes (A). V2 = (R2 / (R1 + R2)) x V.Ohm’s Law states that the current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across the conductor and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor. Capacitive Reactance, XC.This calculator helps you determine the voltage drop across a resistor in electrical circuits. Well, before knowing more about our ohms law calculator, let’s we tell you about what is ohm’s law. By lumping Ohm’s law with joules law, one can easily achieve the formula for power. Let’s take a look at formulas: Voltage calculation formula. According to Ohm’s law, the voltage drop, V, across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated by using the equation V=IR, where I is current in amps (A) and R is the resistance in ohms (Ω).As the voltage across a resistor is given as VR = I. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe Ohm’s law.
Resistors in AC Circuits
\$\begingroup\$ You have to calculate the equivalent resistance to determine the voltage across the equivalent resistor.
Resistors in Series
Related: resistor calculator.5Vx4 Ohms/12Ohms=0. Calculate voltages, currents, or resistances with Ohm’s law.i(t) = Imax sin (ωt) The instantaneous voltage across a pure resistor, VR is “in-phase” with current. For DC closed circuits, we also use Kirchhoff’s circuit law for voltage drop calculation.5 A flowing through it, you would calculate accordingly: Voltage Drop = Current × Resistance.To verify the voltage drop, Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s circuit law are used, which are briefed below.
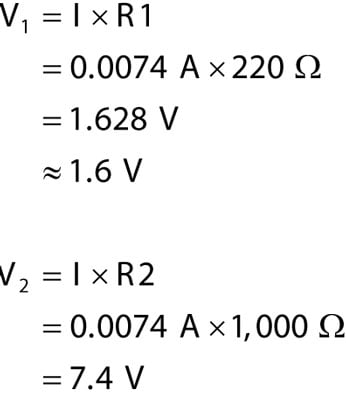
See examples, tips, and a table of contents for more guides on electronic circuits.
Voltage drop across a single resistor and across two resistors
Learn how to calculate the voltage drop across resistors in series and parallel circuits using Ohm's law and formulas.1: Simple AC CIrcuits. The equivalent resistance for this kind of . With these two laws, plus the equations for individual component (resistor, capacitor, inductor), we have the basic . – Vt is the total voltage across the circuit. R2 to be the 40 ohm resistor.

Ohm’s law calculator finds the voltage using Ohm’s law. The voltage across each resistor connected in series follows different rules to that of the series current.
How to Calculate Voltage Across a Resistor (with Pictures)
From that you can calculate the voltage across the series resistors. Example #1: Find the voltage applied across 10 kΩ . Ohm’s law is represented by V → Voltage Drop (V) R → Electrical Resistance (Ω) I → Electrical Current (A).Auteur : The Organic Chemistry Tutor
Easy Guide
It is as follows: Supply Voltage = Sum of the . Input the current and resistance values, select your preferred units, .This expression for V V can be interpreted as the voltage drop across a resistor produced by the flow of current I I. The formula for calculating the output voltage is based on Ohms Law and is shown below. For example, if one resistor is 2 Ω and the other is 4 Ω, then the calculation to find the equivalent resistance is: 1 / (1/2 + 1/4) = 1 / (3/4) = 4/3 = 1. It contains a few examples and. Add these two values together. It is a fundamental principle in physics that relates voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. Calculate total resistance of a circuit that contains a mixture of resistors . Kirchhoff's Laws for current and voltage lie at the heart of circuit analysis. So now, the equivalent resistance of R2 and R3 is 8 ohms and .Let's consider an example to understand how the calculator works: Suppose we have a capacitor with a capacitance of 10 microfarads (μF) and a charge of 50 microcoulombs (μC) stored on it. Learning Objectives. For instance, the headlight in Example 20.Although not exactly what I was looking for. Recognize when Ohm’s law applies and when it does not. Ohm’s Law Formula is: V = I x R.
Solved example: Finding current & voltage in a circuit
Step 1: Enter the values of current and resistance below which you want to find the voltage. Using the information from How to Determine Wattage you can calculate the maximum voltage rating for any resistor. I have a good understanding of Ohm's law and can calculate the voltage and the current flowing. Find the voltage (V) across resistor R 1 of power rating P 1 using the formula: V = √(P 1 × R 1) Calculate the power dissipated by the second resistor (R 2), P 2 = V 2 /R 2. where V is the total input voltage or source voltage, R1 and R2 are the resistances of the two resistors, and V1 and V2 are the voltages across the individual resistors.The total voltage across both components is \(5. This article also .15H and a capacitor of 100uF are connected in series across a 100V, 50Hz supply. Take the reciprocal again. When the thermistor is placed in a warm environment it has a resistance of \(100 \Omega\). The first value to determine is the maximum current: P_{Rating}=I_{Max}^{2}*R_{Nominal} Resistors .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
How To Calculate The Voltage Drop Across a Resistor
Using the formula mentioned above, we can calculate the voltage across the capacitor as follows: V = Q / C V = 50 μC / 10 μF V = 5 volts (V)To calculate the voltage across a resistor in a parallel circuit, you can use the following formula: Where: – Vr is the voltage across the resistor of interest. So you need a resistor of 700 Ω to get 10 mA of LED current. To calculate the resistance you need, just divide the voltage by the current: R = V / I.4 has an IR IR drop of 12. Enter any two values and get instant calculations for all the variables in ohm’s law equation.According to the voltage divider rule, voltage drops will be, Vout= 2.4Ohm resistor then your equivalent resistance will be off. An ac generator produces an emf of amplitude 10 V at a frequency f = 60Hz. If you had a voltage source instead of a current source, you could .
Ohm’s Law
A parallel circuit is characterized by a common potential difference (voltage) across the ends of all resistors.In a parallel connection of resistors, the voltage across each resistor is the same. Example: Consider a simple circuit where a 9V battery is connected to a 1000-ohm resistor.According to Ohm’s law, the voltage drop, \(V\), across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(V=IR\), where \(I\) equals the current in . For example, if you have a 200 Ω resistor with 0.Ohm’s Law states that the voltage (V) across a resistor is equal to the current (I) passing through it, multiplied by its resistance (R).
How to calculate voltage across a resistor
If we want to calculate the voltage drop across the resistor, we need the value of the current in the circuit. Explain why total resistance of a parallel circuit is less than the smallest resistance of any of the resistors in that circuit.comVoltage Drop Calculation Based on National Electrical Codeelectricalaxis.

Ohm’s Law Formula: The Bavarian physicist Georg Simon Ohm derived a formula in which the resistor’ current (I) in amps (A) = (is equal) to the resistor’s voltage (V) in volts .
How to find LED voltage and current
Learn the formula and steps to calculate the voltage drop across individual resistors in series or parallel circuits, using Ohm's law and the total resistance of the circuit.Easy Guide – How to Calculate Voltage Drop Across . Apply Ohm’s Law: Once you have both resistance and current values, use Ohm’s Law, V = I × R, to calculate voltage drop across your resistor.R = V I R = V I.Using Ohm ‘s Law to Calculate Voltage Changes in Resistors in Series.This will give you the voltage drop across the resistor. Xc1 = 1/ 2πfc1. When the two capacitors C1-8uF & C2-20uF are connected in series in the circuit, the RMS voltage drops can be calculated across every capacitor when they are connected to 80Hz RMS supply & 80 volts. Ohm's law is given as.Calculate the voltage drop of a current across a resistor using Ohm’s law.14 V, so the resulting power equals 20 W. The instantaneous voltage across a pure inductor, VL “leads” the current by 90 .
Kirchhoff's laws (article)
When current and resistance are given use V = IR to calculate voltage. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain the origin of Ohm’s law. Inductive Reactance, XL.thecircuitmaker. Let us take: R1 to be the 2 ohm resistor. A series RLC circuit containing a resistance of 12Ω, an inductance of 0.

Watch this complete circuit analysis tutorial.

Determine the voltages across and the currents through the circuit elements when the generator is connected to (a) a 100Ω resistor, (b) a 10μF capacitor, and (c) a 15-mH inductor. See examples, formulas and a resistor . Voltage Drop = 0. The total voltage across the circuit is 15 volts. If we want to .Please provide any 2 values and click Calculate to get the other values in the ohm's law equations V = I × R and P = V × I. If voltage is measured at various points in a circuit, it will be seen to increase at the voltage source and decrease at the .











