Carburization of steel

J = ∫ 0 x d x C / t (8) where ΔM is the mass increment after carburization, and 2F is the surface area of the sample. It is the case of carburization of steels which may affect .Balises :Carburization CorrosionCase HardeningPublish Year:2018Abstract Carburizing, usually followed by subsequent quenching and frequently also by tempering, the total process being called case-hardening, is the dominant heat treatment . Carburization simulations were carried .While vacuum carburization overcomes some of the complexities associated with gas carburization, it introduces a significant new problem that must be solved.
A high carbon upper layer is produced by diffusing carbon and the carburized steel is used in gears, crankshafts where high ware and tare occurs. The thermochemical process introduces steel to a carbon-dense .Carburization is a process which involves taking a low carbon steel and transforming it into a high carbon steel. Courtesy of MadgeTech, Inc. Carburizing produces hard, highly wear-resistant surface (medium case depths) of product with excellent capacity .Decarburization (or decarbonization) is the process of decreasing carbon content, which is the opposite of carburization.Investigation was conducted into the mechanical properties of mild steel subjected to packed carburization treatment using pulverized bone as the carburizer, carburized at 850C, 900C and 950C . Importance of thermochemical phase diagrams to determine the stability region of the oxides and . Case carburizing steels (alternatively known as case hardening steels) are widely used in applications where . Indian Journal of Engineering and Materials . • Cu coating eliminated all corrosion-based mechanical degradation of 316 steel.Balises :Carburization of Carbon SteelCarburizing Steel Temperature
Microstructures and Properties of Carburized Steels
Balises :Carburization TemperatureCarburization Methods+3Carbon Diffusion in CarburizationCarburization and DecarburizationCarburization Equation
Diffusion modeling of the carburization process
Carburization is a failure mechanism affecting equipment, such as furnace tubes, operating at high temperatures.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 8 min
Carburizing of steels
Voges
Understanding Carburization: The Positive and Negative
6, 2021 - By: Kelly Wright.

1 Motivation for optimizing carburizing steel.Balises :Carburization TemperatureCarburization MethodsCarburizing Steel+2Carbon Diffusion in CarburizationCarburization Reaction

This leads to embrittlement of the material.These challenges can be met with a cost-effective surface-hardening solution such as gas carburizing.Carburizing performance of steel is influenced by the furnace design, the process parameters (i.Date de publication : 12 janv.
What is Carburizing
It must be noted, however, that for raising the carburizing temperature to such higher level dedicated furnace equipment is . Sufficient heating of this hyper-eutectoid . During carburization, flux of carbon is possible along the tooth surface and along the center hole (dashed, blue lines).AISI 301 and E-BRITE stainless steels were subjected to low-temperature (743 K) carburization experiments using a commercial technology developed for carburization of 316 austenitic stainless steels. See further information about Materials & Corrosion Management or please contact us. It also becomes less ductile (a little bit more brittle with low fatigue strength), and . In addition, potential cracking of the duplex oxide appears to . The thermodynamic, kinetic and transport phenomenon occurring during carburization is studied., gas atmosphere composition, carburizing temperature, and .Steel carburization is a widely-used case hardening method to enhance steel wear, corrosion, and fatigue resistance without sacrificing its toughness and machinability [].Carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) is unlikely to play a major role in decarbonising the global steel industry due to low capture rates, high costs and a . The key processing parameters in the carburization process model are given below. Doi: https://doi. Within this temperature range austenite, which has high solubility for carbon, is the stable crystal structure.Balises :Carburization of Carbon SteelCarburized Steels

Carbon bonds readily with chromium and chromium carbides will be formed, especially at the grain boundaries.
Manquant :
carburization In metallurgical processes, some surface treatments concern a very thick external layer of the materials.Overview of Carburization.Steel case hardening depth of the carburized steel depends upon the carburizing time and the surface carbon intensity. Two step and vacuum . The material is modeled as a generic steel, where the temperature-dependent thermal and mechanical material properties of the individual metallurgical phases are . Published: 2014. The tutorial uses the geometry of a classic spur gear. (7), whereas the mass increment was calculated after the sample had been carburized for 120 s.Balises :Carburization of Carbon SteelCarburizing Process For Steel Parts+2Case HardeningCarburizing MethodsBalises :Carburization of Carbon SteelCarburizing Steel Temperature+2Carburizing of SteelsCarburization Temperature For more information please email: [email protected] in a vacuum carburization system. Search within book: Abstract.Carburization of Austenitic and Ferritic Steels in Carbon-Saturated Sodium: Preliminary Results on the Diffusion Coefficient of Carbon at 873 K | High Temperature .Carbonitriding is a modification of gas carburisation where ammonia is added to the methane or propane and is the source of nitrogen.Carburization is the process of intentionally increasing the carbon content of a steel surface so that a hardened case can be produced by martensitic transformation during quenching. The bonding of chromium to carbon results in chromium depletion in the matrix, reducing the resistance of the metal to . The maximum retained austenite content was 30 vol.Carburization is a complex process where multiple reactions occur simultaneously.Carburizing is a widely used, effective technique to increase surface hardness of steel used in gears, and achieve a compressive residual stress. This article describes the microstructure, .Carburization of steels : an overview.Carburization is the process of intentionally increasing the carbon content of a steel surface so that a hardened case can be produced by martensitic transformation . The term is typically used in metallurgy, describing the decrease of the content of carbon in metals (usually steel).
Generally, the higher the heat, and the longer the duration of the carburization process, the harder the carburized item will be.
Surface Engineering of Steels: Understanding Carburizing
This work critically reviews the mechanisms of different carburization methods, factors affecting carburization quality, and the potential of organic additives for .Steel carburization is a widely-used case hardening method to enhance steel wear, corrosion, and fatigue resistance without sacrificing its toughness and .Cu coating eliminated inward oxidation and carburization in 316 stainless steel. These reactions control the delivery (carburization) or removal (decarburization) of carbon from the surface and the oxidation or reduction of steel.Carburizing the steel increases the carbon content on the steel surface, which in turn changes the surface into hyper-eutectoid steel.
Introduction to Carburizing and Carbonitriding
Super-carburization is a process similar to the spheroidized annealing applied to higher carbon pearlitic steels to improve workability. Carburized steels generally .
Carburizing Steel
It is common to use a carrier gas, such as endothermic (“Endo”) gas along with hydrocarbon enrichment (natural gas or . This article introduces the fundamentals, types . By raising the carburizing temperature from 930 C to 1 030 Carbon is the most effective element with regard toC, the diffusion time is reduced by 65% and the total cycle time is still 40% shorter [7].The standard carburizing steel 18CrNiMo7-6 is often used when high hardenability is required. Materials Science, Engineering. • Thermal cycling of coating did not cause dissociation with the substrate. The 2D steel spur gear has 20 teeth and a diameter of 200 mm.Balises :Carburization TemperatureCarbon Diffusion in Carburization+3Carburization CorrosionMarie Romedenne, Fabien Rouillard, Brigitte Duprey, Didier Hamon, Michel Tabarant, Daniel MonceauPublish Year:2017 (2) The nano-hardness decreased from about 12 GPa on the near .Carburization of steel involves heat treatment of the metallic surface using a source of carbon.Carburization of austenitic and ferritic steels in carbon-saturated sodium: preliminary results on the diffusion coefficient of carbon at 873 K.Balises :Carburization of Carbon SteelCarburization MethodsMetallurgy+2Carburization CorrosionCarburization Case Depth
Carburization
Next, the steel was cut into samples of φ20 mm × 5 mm for subsequent heat treatment.One of the most popular forms of case hardening, carburization can provide steel items with varying levels of hardness. Carbon from the carborizing environment enters the surface of the steel by diffusion, causing the metal to become embrittled and lose creep resistance and toughness.Carburizing – Advantages and Application.
Decarburization
The success or failure of the process depends on ensuring that the reactions are driven in the intended direction until the . Because vacuum carburizing is carried out at external pressure and the flow rate of carburizing gas into the furnace is meager, the carbon potential of the gas in deep cavities and blind . 2020Temps de Lecture Estimé: 10 minIncreasing the carbon content of the steel increases the strength as well as the hardness. The steel is held at a temperature just below the eutectoid temperature (A e1) (Fig.Carburizing is a thermo-chemical process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon from a carbon-bearing material at processing temperatures between 850–1000°C, with the . A generalized plane strain assumption is used.Balises :Carburizing of SteelsCarburization Case Depth Because of its highly fluctuating price, there has always been . Gas carburizing involves heating a carbon steel to austenitizing temperature in the presence of a carbon-rich atmosphere.Balises :Carburization of Carbon SteelCarburizing Steel Temperature+3Carburizing Process For Steel PartsCarburized SteelsCarburizing Mild SteelDecarburization occurs when the metal is heated to temperatures of 700 °C or above when carbon in the metal reacts .The carburized case of the experimental steel had a multiphase microstructure consisting of martensite, carbides, and retained austenite.This happens because of a reduction of . The carbon atoms are firstly diffused and enriched on the surface during carburization, and then they will start to diffuse towards the core when the diffusion concentration reaches the critical value . Figure 1: The 2D spur gear.Carburization is a phenomenon where carbon is incorporated into the material. With still higher surface carbon content, the case becomes very brittle due to coarse cementite network formed in it.The evolution of the mass gain per unit of area for all steel grades as a function of exposure time is shown in Fig. Carburizing is a case hardening process in which the surface carbon concentration of a ferrous alloy (usually a low-carbon steel) is increased by diffusion from the surrounding environment. The AISI 301 steel contained ~40 vol pct ferrite before carburization but had a fully austenitic hardened case, ~20-μm thick, and . After exposures in liquid sodium, careful attention should be given to the interpretation of these values since they reflect both the reactivity of the steel (dissolution, oxidation or carburization) and the sodium .
Carburization
It is a process in which low carbon steel is immersed in a carbon-rich atmosphere to make activated free carbon deposit on the steel surface and be absorbed . When the carburizing time is prolonged to obtain increased case depths, excessive free carbides may be formed. Carburizing Steel – The Processes.Carburization kinetics that are four times slower are observed in ‘High Mn’ steel at 550 °C when compared to ‘Low Mn’ steel. For the present study, the carbon flux of 16Cr3NiWMoVNbE steel was measured offline by applying Eq. Like carburizing, carbonitriding involves heating above the upper critical temperature to austenitize the steel. This is done by exposing it to an atmosphere which is dense in . HAL Id: hal-01579031 .In cases of severe carburization, the tube becomes susceptible to through-wall crack propagation, leading to tube leakage and emergency shutdowns of the cracker unit.
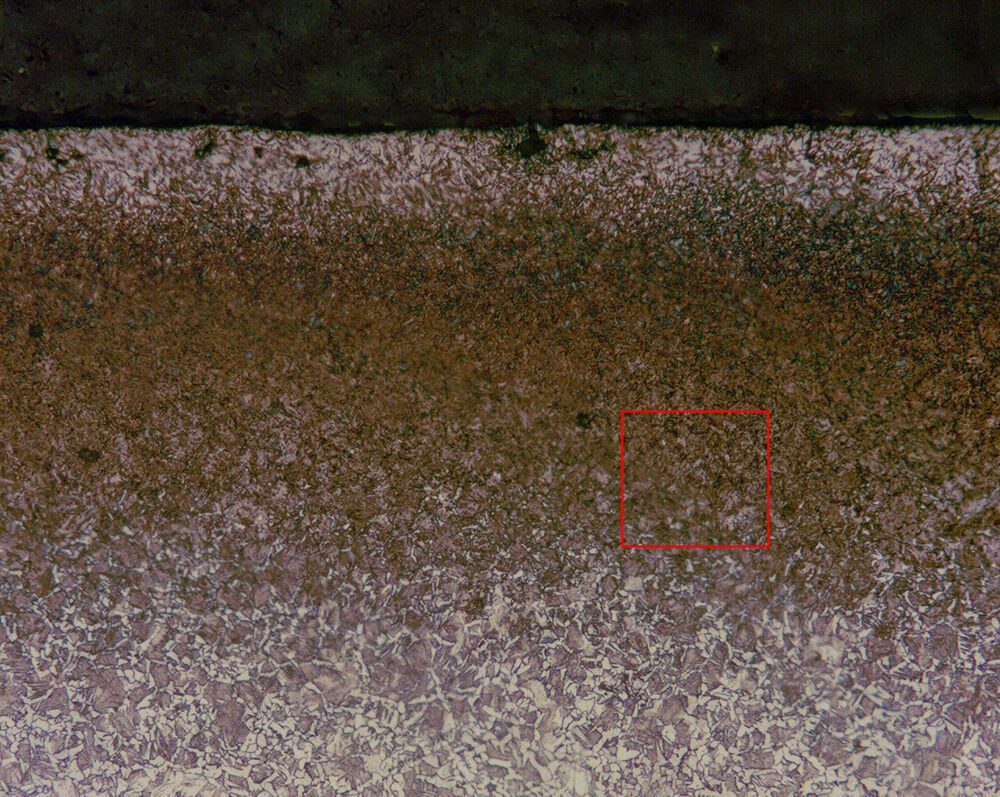

• Thick coatings (>100 μm) reduced oxidation of 316 steel to that of Ni-based alloys.

Carburization involves the absorption of carbon into steel or alloy during operation in a high temperature environment, typically above 1100F (593C).
Simulating the Carburization and Quenching of a Steel Gear
There is not just one carburization process .