Carnitine uptake deficiency

Carnitine deficiency occurs in aberrations of carnitine regulation in disorders such as diabetes, sepsis, cardiomyopathy, malnutrition, cirrhosis, endocrine disorders and with aging. It encompasses a broad clinical .Carnitine Deficiency. 1 This transporter protein maintains intracellular carnitine concentrations by transporting carnitine across .CTD stands for “carnitine transporter deficiency. We present two cases of carnitine deficiency in pregnancy.Carnitine uptake defect is caused by a defect in the carnitine transporter in the cell membrane resulting in urinary carnitine wasting, leading to severe systemic and intracellular carnitine deficiency.
Carnitine uptake defect (CUD) is an inherited condition in which the body cannot bring enough carnitine, a substance that helps the body convert energy from fats into the cells.
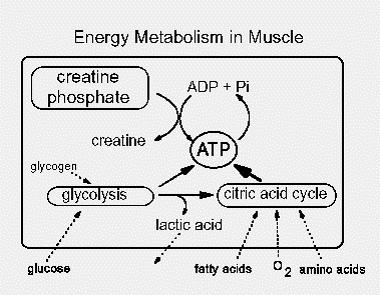
Primary Carnitine Deficiency
Severe neonatal-onset disease .
Carnitine Uptake Deficiency (CUD)
They are caused by enzymes that do not work properly. Deficiency of plasma-membrane carnitine transporter In the Faroe Islands, the prevalence is 1/1,300 and the incidence is 1/720.Primary carnitine deficiency is a condition that prevents the body from using certain fats for energy, particularly during periods without food (fasting).In CUD, carnitine that is present in the diet or synthesized by the liver cannot be transported into cells. In a second case, a mother known with carnitine .Systemic primary carnitine deficiency (CDSP) is a disorder of the carnitine cycle that results in defective fatty acid oxidation.Primary carnitine deficiency is an inherited (genetic) condition that prevents the body from breaking down certain fats and turning them into energy.Results of citrullinemia and carnitine uptake defects screening. Metabolic testing revealed very low free carnitine levels. It can cause a heterogeneous group of disorders.What is carnitine deficiency? Carnitine is a natural substance that the body uses to process fats and produce energy.
Carnitine deficiency
PCD can be detected through tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), but transplacental transport of free carnitine from mothers may .Systemic primary carnitine deficiency (CDSP) is an autosomal recessive disorder of carnitine transportation typically characterized by episodes of .Background: Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) analysis is a powerful tool for newborn screening, and many rare inborn errors of metabolism are currently screened using MS/MS.La carence en carnitine résulte d'un apport insuffisant ou de l'incapacité à synthétiser la carnitine. Find out what to .Primary carnitine deficiency (PCD) caused by pathogenic variants in the solute carrier family 22 member 5 (SLC22A5) gene is a rare autosomal recessive disease that results in defective fatty acid oxidation.
Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Primary Carnitine Deficiency
The blood is tested for more than 25 treatable diseases, including carnitine uptake defect (CUD).Carnitine uptake deficiency.comMaigrir grâce à la L-carnitine ? + Les signes d'un déficitsagessesante.Primary carnitine deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease associated with acute hypoketotic hypoglycaemia, cardiomyopathy and sudden cardiac .Defects in the OCTN2 carnitine transporter results in autosomal recessive primary carnitine deficiency characterized by decreased intracellular carnitine accumulation, .
Systemic Primary Carnitine Deficiency
Carnitine and its derivatives and insulin resistance.

A nine-mo-old boy presented with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, massive hepatomegaly and jaundice. Systemic primary carnitine deficiency (SPCD) exact prevalence is unknown and varies depending on ethnicity. Nutritional supplementation of L-carnitine, the biologically active form of carnitine, is ameliorative for uremic patients, and can improve nerve conduction, . Celle-ci peut être responsable d'un groupe hétérogène de pathologies. People with CTD have problems using fat as energy for the body.
Primary Carnitine Deficiency and Cardiomyopathy
OCTN2 is a protein in your .A founder mutation has led to an extremely high incidence of CTD in the Faroe Islands, often manifesting as sudden death in adults due to previously undetected disease. It is one type of fatty acid oxidation disorder. Age of onset: Infancy, Neonatal.Primary carnitine deficiency (OMIM entry #212140) is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disease caused by pathogenic variations in the SLC22A5 gene, encoding the Organic Cation Transporter Novel 2 (OCTN2) protein.Systemic primary carnitine deficiency (CDSP) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by a defect in plasma membrane uptake of carnitine due to SLC22A5 gene mutations.The carnitine transporter is a protein responsible for transporting carnitine into cells where it is required for importing fatty acids into the mitochondrion. It can cause muscle weakness, heart or .
Systemic primary carnitine deficiency
It can also cause heart or liver problems. CUD is identified in ~ 1 in 60,000 babies born in BC. The study population included 46,699 newborns screened for citrullinemia (A) and 30,237 for carnitine uptake defects (B).Carnitine uptake deficiency (CUD) Systemic carnitine deficiency (SCD) Primary carnitine deficiency.Condition Description: Carnitine Uptake Defect (CUD), a fatty acid oxidation (FAO) disorder, is caused by a defect in the carnitine transporter in the cell membrane.Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase (CACT) is a critical component of the carnitine shuttle, which facilitates the transfer of long-chain fatty acylcarnitines across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Carnitine membrane transporter deficiency or primary carnitine deficiency (PCD) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder of fatty acid oxidation, in which the transport of carnitine into cells is impaired.(A) A total of 314 newborns were enrolled in the second-tier screening due to abnormal (but below the diagnostic cutoff) concentrations of total galactose, . Primary carnitine deficiency has a frequency of about 1:40,000 newborns in Japan [ Koizumi et al.Learn about the blood test for carnitine uptake deficiency (CUD), a condition that affects the body's ability to recycle an important nutrient called carnitine.
Carnitine Deficiency

CACT deficiency causes a defect in mitochondrial long-chain fatty acid β-oxidation, with variable clinical severity. These findings showed that the defect in this form of carnitine deficiency was an inability to establish a concentration gradient across the cell .Carnitine uptake deficiency Carnitine brain transporter deficiency The British Inherited Metabolic Disease Group (BIMDG) has published on its website guidelines for the .Primary carnitine deficiency (OMIM 212140), also known as carnitine uptake defect, carnitine transporter deficiency or systemic carnitine deficiency, is an autosomal recessive disorder of the carnitine cycle . A screen positive result means that more tests are needed to know whether or not a baby has CUD.
Carnitine Uptake Defect (CUD)
Here are the ones for the management of an Acute decompensation in children with a carnitine transporter .Overview
Déficit en carnitine
Carnitine uptake deficiency (CUD) affects the body’s ability to recycle an important nutrient called carnitine. This can cause muscle weakness. In the course of her second pregnancy, maternal carnitine levels showed a deficiency as well. This results in a deficiency of carnitine inside the cells leading to an inability to use fatty acids for energy production. Carnitine deficiency is when not enough (less than . Carnitine is essential for the transfer of long-chain fatty acids from the cytosol to mitochondria for subsequent β-oxidation. If confined to muscles, this disease causes weakness in the hips, shoulders, and upper arms and legs.Carnitine deficiency is a condition where the body can't use carnitine, a natural substance that helps process fats and produce energy.PubMed and Web of Science were searched using the following terms: “primary carnitine deficiency,” “carnitine transport defect,” “carnitine uptake defect,” “SLC22A5 mutation,” “SLC22A5 variant,” “OCTN2 mutation,” and “OCTN2 variant” between 1999 (pathogenic variant was first described) and December 2022 (Nezu et al.Carnitine deficiency results from inadequate intake of or inability to metabolize the amino acid carnitine.Eriksson et al. The latter results in an intramitochondrial defect in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids that impairs energy production and causes the accumulation . Individuals affected by CUD are unable to break down certain fats, which can result in a build-up of unused fatty acids in the body. Symptoms of CDSP in infants can include poor feeding, tiredness, irritability and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) but CDSP can also present .Primary Carnitine Deficiency (PCD) (OMIM #212140)—also referred to as systemic primary carnitine deficiency (CDSP), carnitine transporter defect (CTD), or . Carnitine deficiency results from inadequate intake of or inability to metabolize the amino acid carnitine. Deficiency of plasma-membrane carnitine transporter. Muscle metabolism is impaired, causing myopathy, hypoglycemia, or cardiomyopathy. (1989) showed absence of carrier-dependent uptake of carnitine in fibroblasts from a patient with hereditary carnitine deficiency. Maternal CUD is a condition that occurs when an infant is born to a woman with untreated CUD.Carnitine functions to carry fatty acids obtained through diet to the energy centers in muscle cells (mitochondria). - Failure to thrive. The carnitine uptake defect (CUD), caused by a lack of the primary carnitine transporter (OCTN2), is a rare inherited fatty acid oxidation disorder (FAOD).What is carnitine deficiency? Carnitine deficiency is one of a group of metabolic muscle diseases that interferes with the processing of food (in this case, fats) for energy production. PheneGene Graphics.Carnitine transporter deficiency — Carnitine transporter deficiency (CTD; also called primary systemic carnitine deficiency or carnitine uptake defect) is an . The incidence of PCD has reported to be 1 in 100,000 live births.
Role of carnitine and its derivatives in the development and
Carnitine uptake deficiency Carnitine brain transporter deficiency The British Inherited Metabolic Disease Group (BIMDG) has published on its website guidelines for the emergency management of patients with inherited metabolic disorders. Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common chronic metabolic diseases with an underlying absolute or relative insulin deficiency. Primary carnitine deficiency is when not enough carnitine can get into cells in the body., 1999] and 1:37,000-1:100,000 newborns in Australia [ Wilcken et al. However, the sensitivity of MS/MS screening for several inborn errors, including citrin deficiency (screened by citrulline level) and carnitine uptake defect . In our first case, systematic screening revealed L-carnitine deficiency in the first born of an asymptomatic mother. [5] [8] Carnitine enters mostly by passive diffusion from plasma and via low-affinity transporters, and this modest increase is enough to prevent muscle . Explore symptoms, .The muscle carnitine levels rise slightly (only up to 5% to 10% of controls), due to the abnormal OCTN2 which is unable to increase the uptake of carnitine into the myocyte adequately.
- .Carnitine is a nutrient that helps the body’s cells work normally.frRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Carnitine Uptake Defect (CUD; Primary Carnitine Deficiency)
Primary carnitine deficiency (OMIM 212140) is an autosomal recessive disorder of fatty acid oxidation due to the lack of functional OCTN2 carnitine transporters. Infants typically present with hypoglycemic, hypoketotic encephalopathy. Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Fatty acid oxidation disorders (FAODs) are a group of rare inherited conditions. 29 Secondary systemic carnitine deficiency can be caused by lack of dietary intake usually in strict vegans, prolonged total parenteral nutrition without carnitine supplementation, .

It is caused by an abnormal gene.