Carotid fibromuscular dysplasia treatment

Fibromuscular dysplasia is usually asymptomatic regardless of location.Is there a cure for fibromuscular dysplasia? There’s no cure for FMD. FMD commonly affects the carotid arteries, which run along the neck and supply blood to . The ideal treatment of FMD .
Carotid Artery Fibromuscular Dysplasia
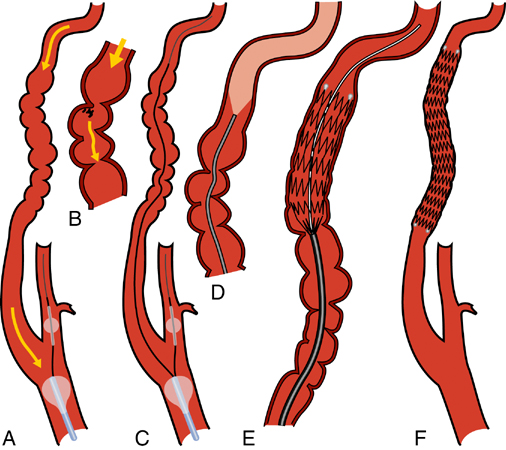
A and B, Medial fibroplasia in the internal carotid (A) and renal .
Fibromuscular Dysplasia Treatment and Therapies
Treatment of fibromuscular dysplasia varies by location.Fibromuscular dysplasia is most common in women between the ages of 40 and 60, but the condition can also occur in children and the elderly. Vascular procedures, . FMD has been found in nearly every arterial bed in the body, although the most commonly affected are the renal and carotid arteries.
A and B, Medial fibroplasia in the internal carotid (A) and renal (B) arteries with the classic string of beads appearance.Reach us by phone or online to request an appointment, find a provider and more. Mayo Clinic doctors evaluate and treat more than 715 people with fibromuscular dysplasia each year. Horner syndrome.Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) of the carotid artery is a non-atherosclerotic and noninflammatory disease that can lead to stenosis and/or aneurysm of medium-sized arteries. The majority (more than 90%) of patients with FMD are women. 1 FMD does not . Because atherosclerosis also blocks arteries, people with fibromuscular dysplasia and risk factors for atherosclerosis (such as high blood . 1,2 Since it was first identified in 1938, FMD has been described in virtually every arterial bed but most commonly affects the renal and extracranial carotid arteries.There is no standard treatment for FMD.Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a non-atherosclerotic, non-inflammatory disease of the blood vessels that causes abnormal growth within the wall of an artery. This article focuses on cerebrovascular . Arteries within the brain and kidneys also can be affected.A carotid web (CaW) is an atypical form of fibromuscular dysplasia characterized by a fibrous, shelf-like intimal flap originating from the posterior wall of the .13%) from 40,887 patients who had undergone carotid artery stenting demonstrated no neurologic or .
Fibromuscular Dysplasia
It may involve angioplasty, bypass surgery (see figure Bypass Surgery in the Leg), or aneurysm repair.What is fibromuscular dysplasia? Sometimes affected arteries look beaded. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. While the true prevalence of this disease remains unknown, studies suggest that more people may be affected than previously reported.
Background and purpose: An atypical form of fibromuscular dysplasia located in the internal carotid-bulb (CaFMD) is thought to be uncommon and is poorly described as a cause of ischemic stroke in the young.Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a non-atherosclerotic, non-inflammatory arteriopathy that results in stenosis, aneurysm, dissection and arterial tortuosity.Fibromuscular dysplasia is rare among patients referred for carotid artery angioplasty. Any treatment to improve blood flow is based on the arteries affected and the progression and severity of the disease.

Outcomes of carotid stenting in patients with fibromuscular dysplasia
There are various types of FMD, with multi-focal fibroplasia . Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) occurs when cluster of cells develops inside the blood vessel walls, causing it to narrow or bulge and restricting blood flow. Depending on what type of FMD you have, you and your doctor will determine your treatment plan.Several key findings in recent years have reshaped our understanding of fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD), an uncommon nonatherosclerotic disease of medium-sized arteries that affects mainly women. FMD most commonly affects middle-aged women; . The different .
Fibromuscular Dysplasia Treatment & Management
75–77 Although diaphragms were mainly reported in the carotid bulb, they have also been described in the ostium and V3 . Treatment varies by location. This study aimed to obtain a better description of CaFMD in Afro-Caribbean population, who could be particularly affected by it.
Invasive treatment for carotid fibromuscular dysplasia
Patients with renal artery FMD and hypertension should undergo primary angioplasty with the goal of curing the hypertension. It most commonly involves the arteries to the kidneys resulting in high blood pressure, aneurysms, and occasionally splitting (dissection) of the .
FAQs about Fibromuscular Dysplasia
1 FMD does not affect the venous system.
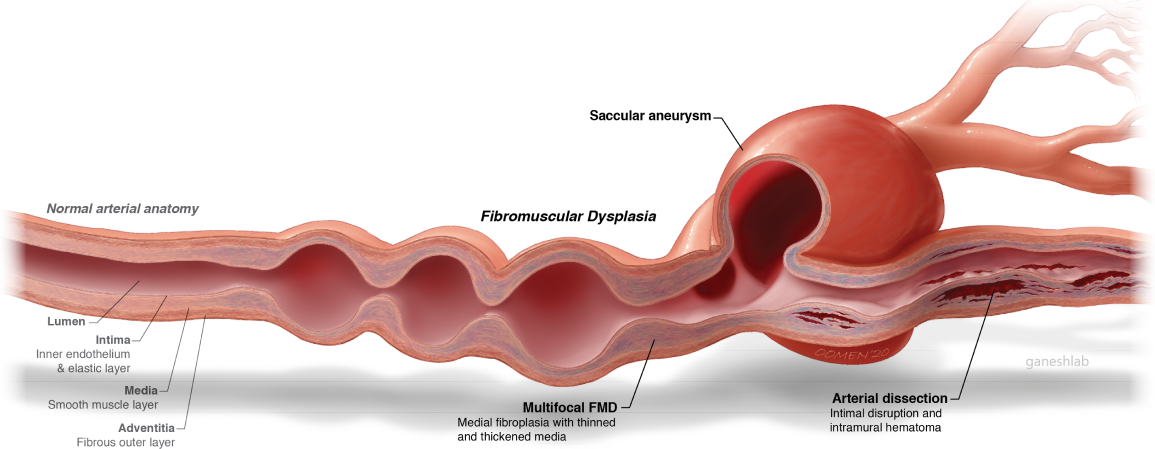
It primarily manifests in the renal and extracranial carotid and vertebral arteries, and is associated with major vascular events such as carotid artery dissection, renal . C and D, The less com-mon intimal fibroplasia, which presents as a focal, bandlike narrowing in the internal
Fibromuscular Dysplasia and Stroke
Management focuses on thorough evaluation and surveillance, lifestyle modification, and treatment of symptoms. Affected blood vessels demonstrate single or multiple areas of narrowing (stenosis).FMD can be asymptomatic but symptoms such as headache, pulsatile tinnitus, or uncontrolled hypertension may lead the cardiologist to the diagnosis [2••].Cervical artery dissection.The epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis of FMD in adults are reviewed here.At the University Hospitals FMD Program, our multidisciplinary team of fibromuscular dysplasia specialists works closely with patients to create treatment plans that are customized to the individual. Partly because of the unknown etiology of FMD, no curative therapy exists.Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a nonatherosclerotic disease of medium‐sized vessels that can present with arterial stenosis, beading, dissection, and aneurysm.You can get a variety of different types of treatments for fibromuscular dysplasia. However, men can also have FMD, and those who do have a higher risk of complications such as aneurysms (bulging) or dissections (tears) in the .Expertise and rankings.This article is a comprehensive document on the diagnosis and management of fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD), which was commissioned by the working group .FMD primarily manifests as beaded (multifocal) or focal lesions in medium or small-sized arteries, though the clinical phenotype of FMD has recently been expanded .Fibromuscular dysplasia is a nonatherosclerotic, noninflammatory vascular disease that most commonly affects the renal and internal carotid arteries . FMD is a rare disease that mainly affects the distal extracranial internal carotid and renal arteries.Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) of the carotid artery is a non-atherosclerotic and noninflammatory disease that can lead to stenosis and/or aneurysm . Symptoms, when they occur, vary by location:Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a non-atherosclerotic, non-inflammatory polyvascular disease that may result in dissection, arterial stenosis, occlusion, and aneurysm [1••].Diagnosis
Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
The carotid arteries, which pass through the neck and supply blood to the brain, are commonly affected. A rare vascular disease, fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) can affect any artery in your body.Fibromuscular dysplasia in the carotid and renal arteries as imaged with angiog-raphy, the gold standard test. Summarize the investigations in a patient suspected of having .Review the treatment of fibromuscular dysplasia. Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is the abnormal development or growth of cells in the walls of the body’s arteries. For many patients, the FMD treatment plan is focused on medical therapy (for blood pressure control and to prevent blood clots) managing .Auteur : Sylvia Z.Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is an idiopathic, noninflammatory, nonatherosclerotic vascular disease of small- to medium-sized arteries.Treatment consists of antiplatelet therapy for asymptomatic individuals and percutaneous balloon angioplasty for patients with indications for intervention.Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a noninflammatory arterial disease that affects the extracranial carotid arteries in young patients.Fibromuscular dysplasia may affect the renal arteries (in 60 to 75% of patients), carotid and intracranial arteries (25 to 30% of patients), intra-abdominal arteries (9% of patients), or external iliac arteries (5% of patients). It differs from . These bulges can cause the blood vessels to appear beaded as multiple growths develop. This can put individuals at risk for artery blockages, stroke, artery dissection (tear in an artery) or aneurysm (artery bulge). This technique is described in detail and provides three distinct advantages over conventional graduated intraluminal dilatation--atraumatic passage of the catheter through the affected vessel with fluoroscopic . A characteristic “string of beads” pattern .FMD most commonly affects the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys (renal arteries) and brain (carotid and vertebral arteries), but it can occur in almost any . Among patients with identified FMD, renal involvement occurs in 60-75%, cerebrovascular involvement in 25-30%, visceral involvement in 9%, and arteries of the limbs in about 5%.An entity named ‘carotid web’ or ‘carotid bulb diaphragm’ has been classified as atypical FMD of the carotid bulb by some authors and has been described predominantly in black/Afro-Caribbean patients. Cardounell, Lorena Gonzalez
Fibromuscular dysplasia
There is no cure for FMD. The disease causes the blood vessel to narrow (stenosis), develop a bulge (aneurysm), and tear (dissection).

In the case of significant FMD stenosis, it may be treated with carotid . It may involve percutaneous transluminal angioplasty alone, percutaneous stent angioplasty, bypass surgery, or .












