Cavernous transformation portal vein
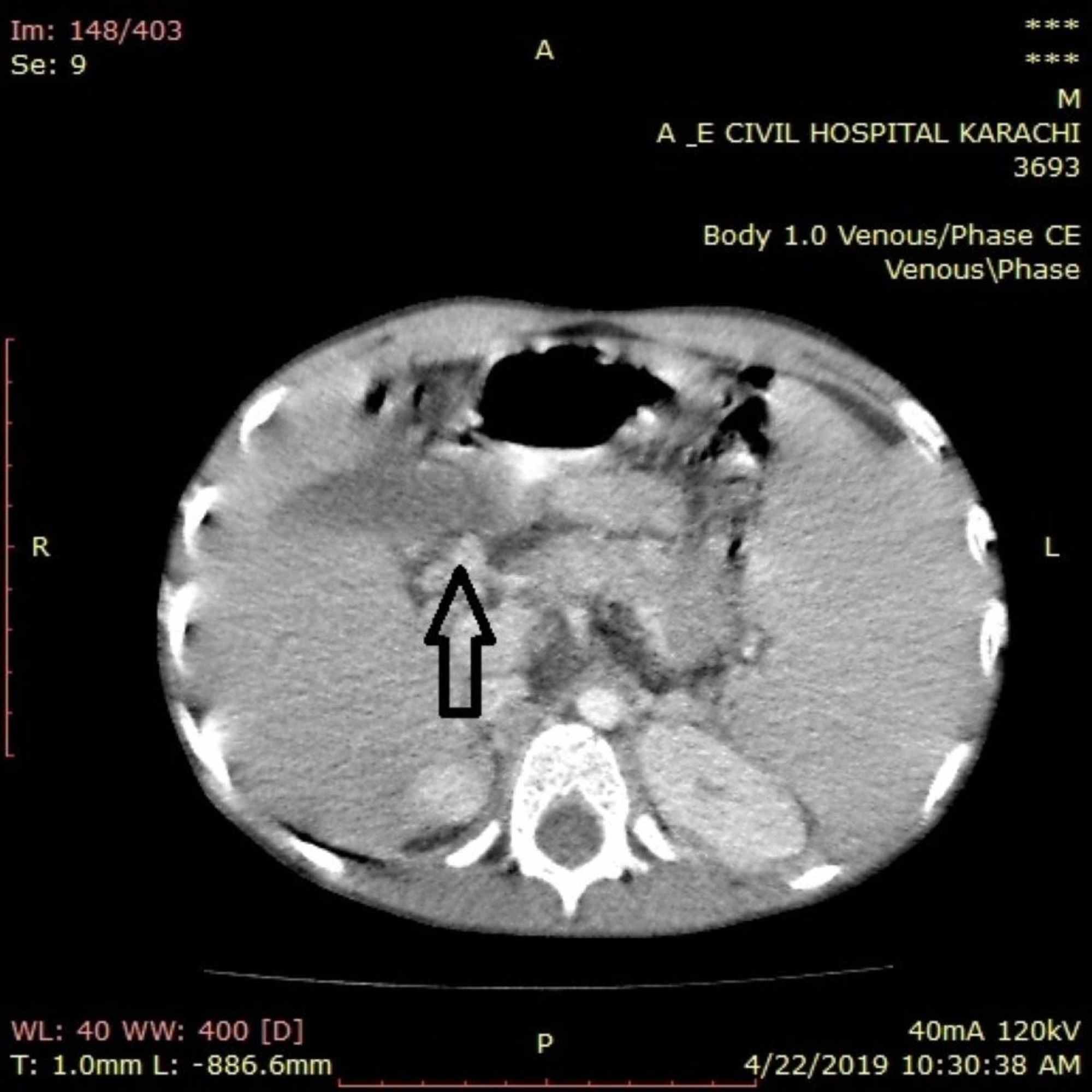
The purpose of this work was to study the hemodynamic consequences of cavernous transformation of .This includes the identification of the superior mesenteric vein or one of its branches as well as the portal vein.Noncirrhotic Portal Vein Cavernous Transformation: To TIPS, or Not to TIPS, That Is the Question - Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology. We wished to study .Purpose Cavernous transformation of the portal vein can be missed on color Doppler exam or arterial phase cross-sectional imaging due to their slow flow and delayed enhancement.In addition, recent anecdotal .門脈の海綿状変化(cavernous transformation of portal vein)の画像所見は? 門脈の海綿状変化は肝外門脈閉塞症の特徴的な所見です。 門脈本幹は造影されずにその代わりに、その 周囲(肝十二指腸間 .Inninepatients, flow within unaffected intrahepatic branches oftheportal veinwas reversed anddirected toward thecavernous transformationCavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV), a consequence of long-standing PVT, is a rare entity secondary to various etiologies and diverse clinical presentations [ 1 ]. Authors SreyRam Kuy 1 , Anahita Dua 2 , Joseph Rieland 3 , David C Cronin 2nd .
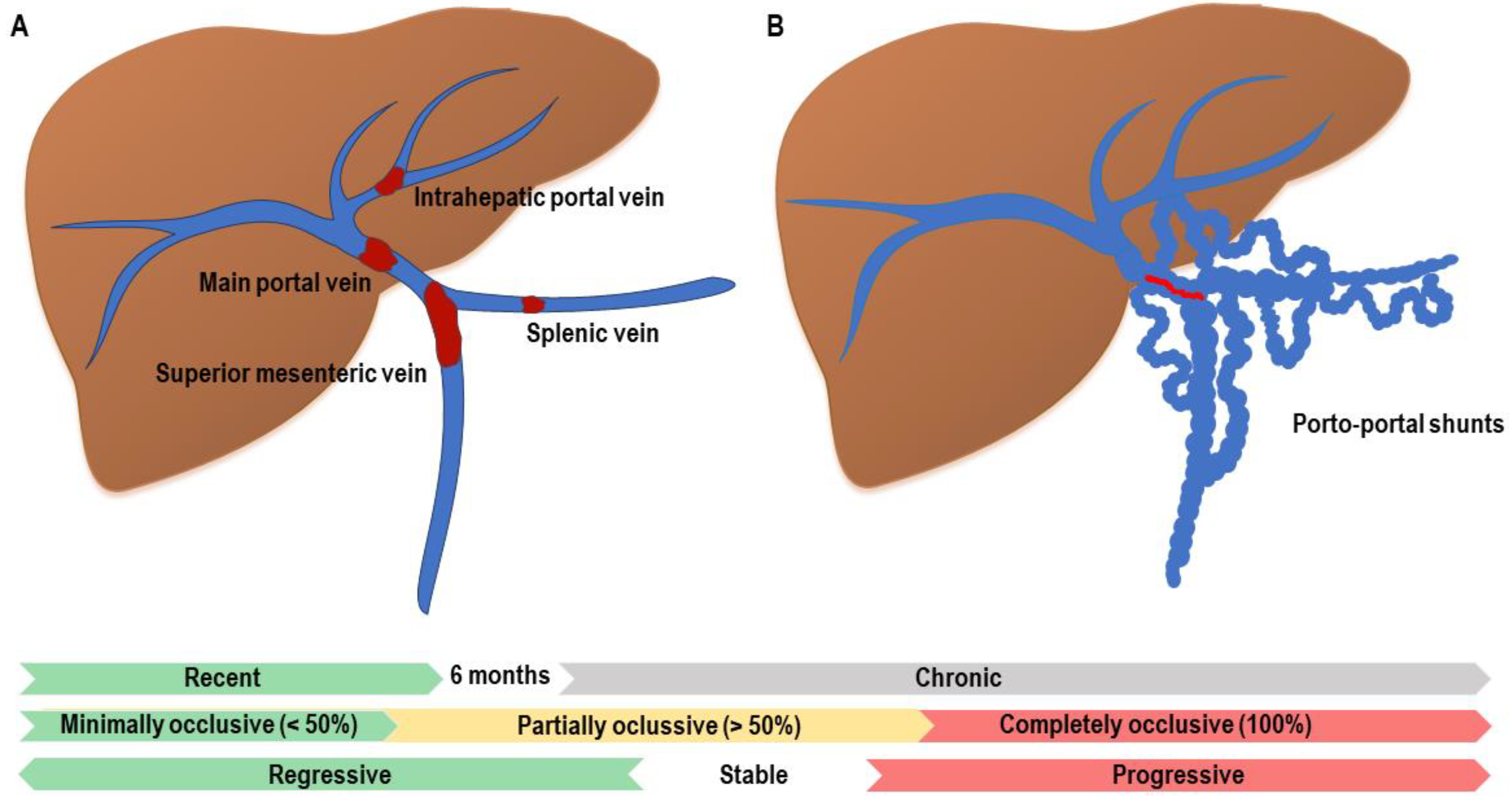
As the PVT becomes a chronic condition, the thrombosed portal vein turns into some sort of fibrous cord that sometimes leads to cavernous transformation with the formation collaterals in the hepatic hilum. Departments of Pathology and Medicine, University and Western Infirmary, Glasgow. Materials and methods: In this retrospective study, clinical data from patients with noncirrhotic CTPV who underwent .
Portal Vein Obstruction: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology
Cavernous transformation .35 The location of these cavernomas results in cholestasis in 50-90% of the .Cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV) in cirrhotic patients with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction (EHPVO) was a relatively rare disease and had no consensus on the treatment. It was ever taken as a relatively rare disease due to its scant literature, . Our study aimed to explore the value of anticoagulation with warfarin treatment for CTPV cirrhotic patients with EHPVO.

CTPV is more common in children than adults and constitutes the main cause of portal hypertension in the former [1], [2], [3].
Garcia, Ronny Cohen

Methods: 3D DCE-MRA, along with subsequent data processing using three-dimensional reconstruction, . upstream dilatation of the bile ducts. Portal vein thrombophlebitis (pylephlebitis) is most commonly due to Bacteroides fragilis and Escherichia coli.orthemain portal vein, seen in73patients, constituted the cavernous transformation. In57patients, thecavernous transformation extended intotheliven,following thecourseof thenight,theleft,onbothportalveins. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) was not reported to treat CTPV for children younger than 5 years old. Search for more papers by this author.
Cavernous Transformation of Portal Vein Due to Portal Vein
In this study, we investigated clinical complications associated with cavernous transformation in the context of cirrhosis and .Cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV) is a compensatory response that aims to restore hepatic blood flow after portal vein thrombosis []. PVT due to streptococcus constellatus bacteremia is very rare, with gastrointestinal tract being the most common . Related pathology. 2016 Feb;63(2):529. 25 The chronicity of the portal thrombosis makes the classic transjugular access difficult to use for the placement of the TIPS and usually a . 2020 Sep 28;S1590-8658(20)30465-5.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein: patterns of intrahepatic and splanchnic collateral circulation detected with Doppler sonography.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV), also called portal cavernoma, refers to the pathological formation of large numbers of collateral vessels when the portal trunk and/or its branches are completely or partially obstructed.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV) is a sequela of extrahepatic and/or intrahepatic portal vein obstruction caused by a combination of local and risk factors. Portal vein thrombosis is . 1, 2 Splenectomy can result in a 10-fold increased risk of developing PVT. Despite recent advances in systemic chemotherapy, long-term survival and . Cavernous transformation of the portal vein J Vasc Surg.58525 Corpus ID: 269256561; Biliary Complications Post Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in a Child With Portal Vein Cavernous TransformationCavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV) results from long-standing portal vein thrombosis (PVT), which involves the development and dilation of multiple small collateral vessels that develop around the portal vein in the setting of portal hypertension to bypass the occlusion. Gibson, James B.
Cavernous transformation of the portal vein
Cavernous transformation of portal vein (CTPV) is the main cause of portal hypertension and its related variceal bleeding in children.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein can be missed on color Doppler exam or arterial phase cross-sectional imaging due to their slow flow and delayed enhancement. Departments of Pathology and Medicine, University and Western Infirmary, Glasgow . Ramesh Babu CS, Sharma M.Background: In recent years, several techniques have been introduced to allow safe oncologic resections of cancers of the pancreatic head.Auteur : Radhames Ramos, Yoojin Park, Ghulamullah Shazad, Christine A. 3 In patients with an occluded portal vein caused by PVT, collateral circulation is built around the venous thrombus and cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV) .
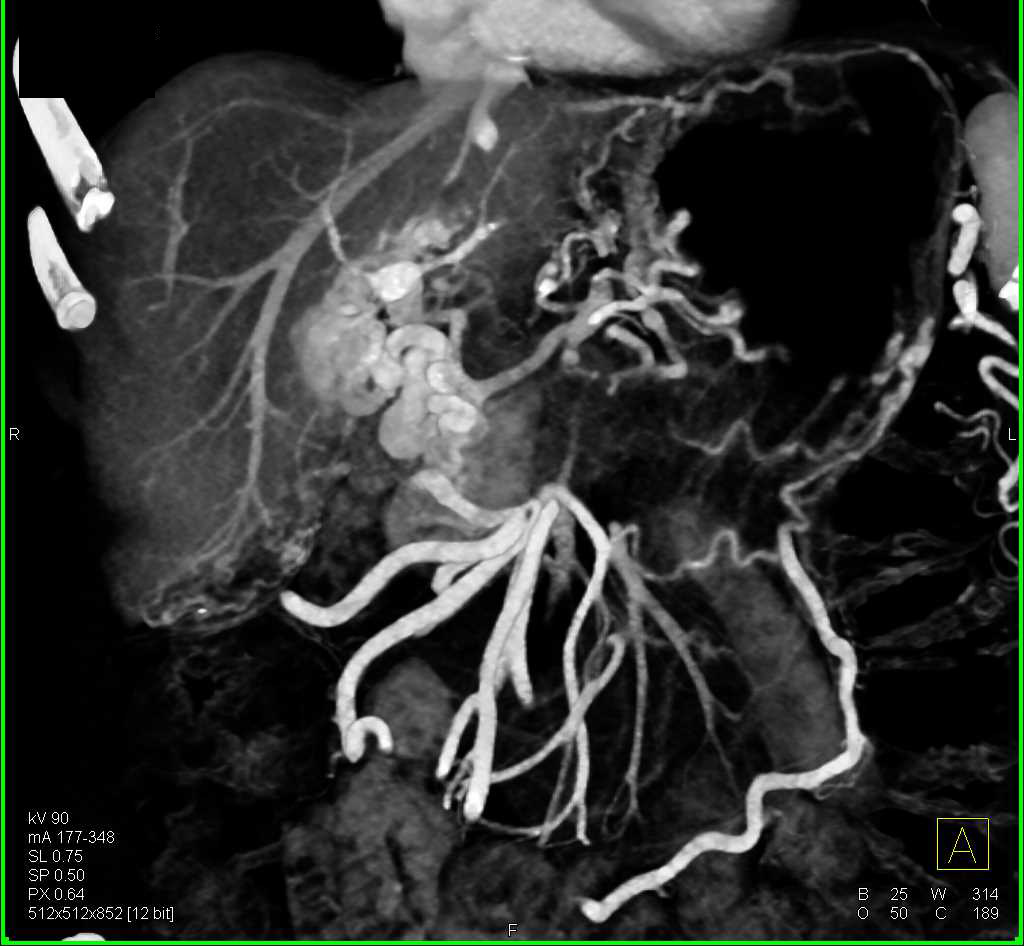
Leg swelling, in this case, is due to para-aortic lymphadenopathy (lymphoma) compressing the inferior .Typical features of cirrhosis and portal hypertension including small irregular liver, marked splenomegaly, ascites and enlarged mesenteric veins.CTPV, also known as portal cavernoma, is the result of portal vein thrombosis that causes the formation of periportal or intrahepatic venous collaterals.Biliary obstruction caused by cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV) is extremely rare.Location and extent of cavernous transformation of the portal vein dictates different visceral side revascularization in Meso-Rex bypass. CTPV is more common in children than adults and constitutes . CTPV is also referred to as a portal cavernoma, due to the spongelike appearance of the portal vein. The etiology, however, remains unknown. The long arrow indicates the splenic vein at the junction with the superior mesenteric vein just below the site of the thrombosis.While a MPA resection with reconstruction is nowadays a standard procedure for tumors with a portal vein (PV) or superior mesenteric vein (SMV) infiltration, a cavernous transformation of the portal vein as a consequence of a complete portal . Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar; 38. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1995;165(5):1151–1155.Selective involution of these veins leads to the formation of the portal vein and rotation of the foregut contributes to the formation of its extra-hepatic course 10.
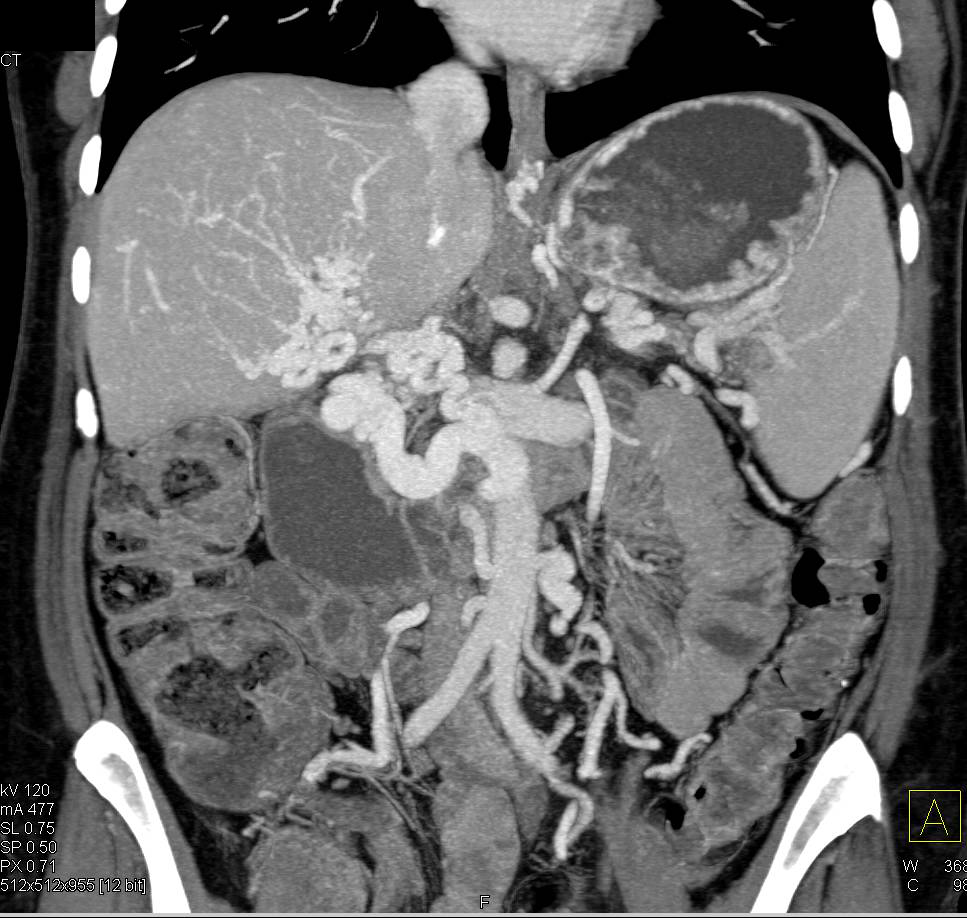
Shows both the cavernous transformation of the portal vein and the dilatation of bile ducts 8. Rui Tang, Guangdong Wu, Qiang Yu, Xuan Tong, Xiangfei Meng, Yucheng Hou, Xin Huang, Abudusalamu Aini, .Cavernous transformation of the portal vein is defined as the formation of venous channels within or around a previously thrombosed portal vein. Keywords: Cavernous transformation of the portal vein; . Methods: From January 2015 . and portal vein. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) offers many advantages over other . Abnormal involution can lead to congenital abnormalities, including a congenital portosystemic shunt. Commentary/Perspective | Volume 34, ISSUE 2, P195-196, February 2023. MRCP features of portal biliopathy in order of frequency are as follows: biliary stenosis.
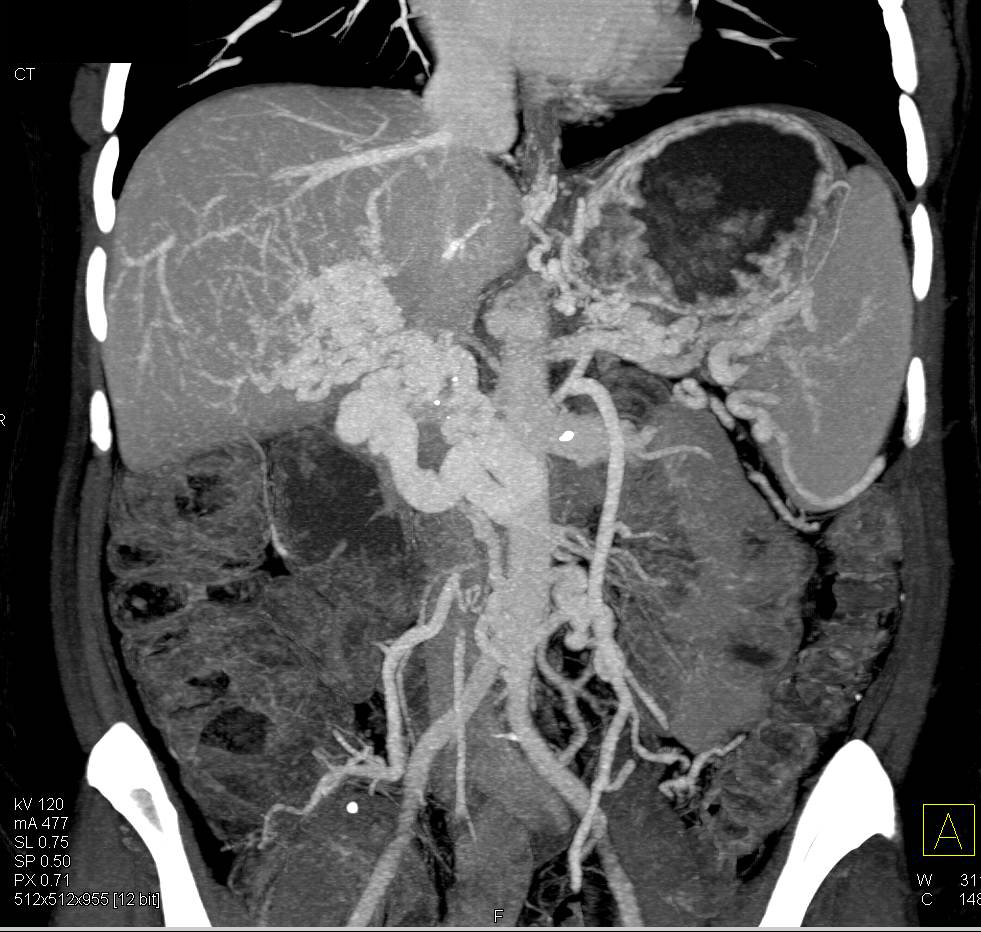
Objective: Cavernous transformation of the portal vein is defined as the formation of venous channels within or around a previously thrombosed portal vein.Portal vein thrombosis with cavernous transformation. Venous bypass graft.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein refers to numerous vascular structures in the region of the portal vein, which enhance during the portal venous phase. Non-cirrhotic portal vein cavernoma (PVC) is a cause of portal hypertension (PH) frequently affecting women of childbearing age.The prevalence of PVT in cirrhosis, reportedly 2–40%, increases with liver disease severity. In cavernous transformation, numerous tortuous collateral vessels form around and bypass the portal vein.Background and aims: Cavernous transformation of the portal vein can occur after portal vein thrombosis (PVT).Cavernous transformation of the portal vein has been shown to occur between 6-12 days from unresolved PVT with bypass of blood through the paracholedochal veins. The purpose of this work was to study the hemodynamic consequences of cavernous transformation of the portal vein in a group of afflicted patients by use of Doppler sonography. In this case report, the patient was a 26-month-old boy who presented with .Cavernous transformation of the portal vein.Obstructive jaundice caused by postsplenectomy cavernous transformation of the portal vein mimicking cholangiocarcinoma Gastrointest Endosc .Cavernous Transformation of the Portal Vein is a rare complication of portal vein thrombosis or thrombophlebitis (PVT).Cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV) is a rare vascular disorder defined as the formation of multiple collateral vessels in the hepatic hilum because of portal vein obstruction. Search for more papers by .Background: To investigate characteristic features of three-dimensional dynamic contrast-enhanced MR angiography (3D DCE-MRA) and validate its clinical significance for the diagnosis of cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV). More aggressive management including long-term anticoagulation in patients with myeloproliferative disorder or .Cavernous transformation of the portal vein, also known as portal cavernoma, is thought to be a sequela of portal vein thrombosis (PVT). 2020 Sep;92(3):786-787. The short arrow points to a serpiginous mass consistent with periportal collaterals, the so-called cavernous transformation of the portal vein.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV), also known as portal cavernoma, is a sequelae of thrombosis in the portal vein causing its occlusion and portal hypertension. angulation of the CBD.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein is a long-term sequele of portal vein thrombosis in which the etiology determines the outcome. Note also, the enlarged thrombosed portal vein with multiple venous collaterals in the porta hepatis indicative of so-called cavernous transformation. Abernethy malformation. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) offers many advantages over other imaging techniques and can be used to successfully detect cavernous . Pancreatic cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in the Western world and still has a rising incidence [1].Hematemesis secondary to cavernous transformation of the portal vein in a patient with Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome Dig Liver Dis . wavy appearance of the bile ducts 3.

Purpose: To compare the clinical outcomes of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation versus portal vein stent placement (PVS) in patients with noncirrhotic cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV). Cavernous transformation of the portal vein is frequently associated with prothrombotic disorders and often entails multiple hemodynamic changes, porto-collateral shunt development and . Biliary tract anatomy and its relationship with venous drainage.Cavernous Transformation of the Portal Vein (CTPV) is a rare and incurable complication of portal vein thrombosis (PVT) that should be considered as one of the differential diagnoses of a hepatic mass.







