Cd36 free fatty acid

1 lineage negative, c-kit positive cells with firefly luciferase and transplanted into CD45.CD36 (cluster of differentiation 36) is a scavenger receptor that functions in high-affinity tissue uptake of long-chain fatty acids (FAs) and contributes under excessive fat supply ., 1999; Pravenec et al. We transduced CD45. Gpr40 is expressed in enteroendocrine cells and mediates free fatty acid stimulation of incretin secretion.
typhimurium (Sal), and LPS-treated animals.

a Heat map of fatty-acid transporter genes differentially expressed by HSCs from control, S.
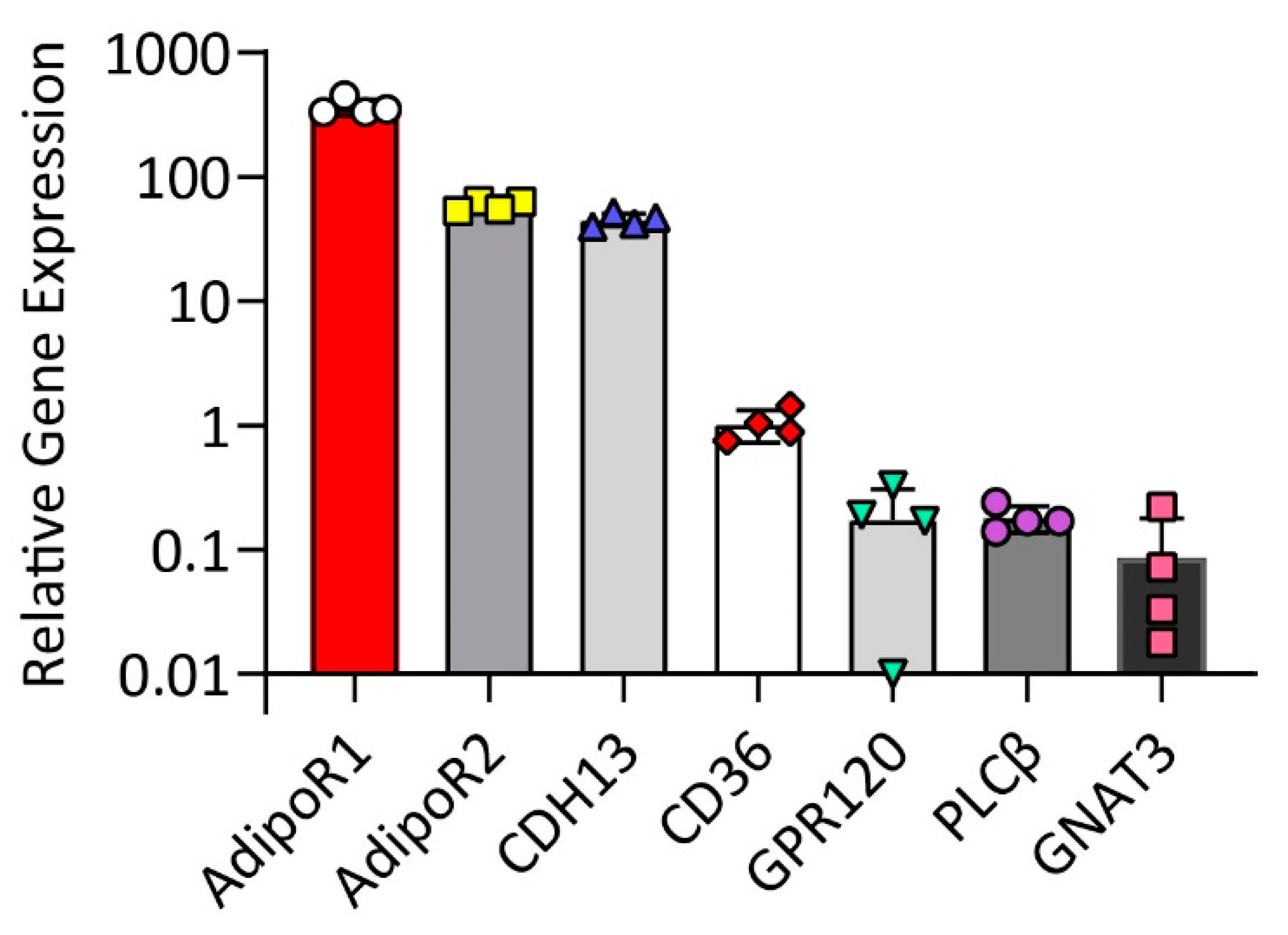
Young Mi Park from the Ewha Womans University School of Medicine in . Free fatty acid receptors (FFARs) and CD36. CD36 can be membrane bound, where it can bind low-density lipoproteins and extracellular long-chain and ultra-long-chain free fatty acids [8,10]. We previously found that colorectal cancer (CRC) cells with a higher metastatic potential express a higher level of fatty acid translocase (CD36).The second type of receptor involved in FAs signaling is a long-chain fatty acid receptor called CD36. CD36 is a type 2 cell surface scavenger receptor widely expressed in many immune and non-immune cells. CD36 is a multifunctional protein that enhances cellular fatty acid (FA) uptake, a key step in energy metabolism, and its dysregulation in .In addition, one strain of spontaneously hypertensive rats lacks CD36 and shows metabolic phenotypes of insulin resistance and high free fatty acid (FFA) levels, which are ameliorated by the transgenic overexpression of CD36 (Aitman et al. Structure-function of CD36 and importance of fatty .Overexpression of CD36, Driven By STAT3, Mediates Free Fatty Acid Uptake in CLL Cells Uri Rozovski, MD, Uri Rozovski, MD 1 Institute of Hematology, Davidoff Cancer Center, Rabin Medical Center, Petah-Tiqva, Israel . This fatty acid signaling is present in different tissues and cell types, some example are but not limited to: intestinal tract, brain, pancreas and immune cells.Balises :Cd36 ReceptorCellsCd36 SignalingFat Cd36
CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation
Post engraftment animals were treated .Balises :Cd36 Fatty AcidFree Fatty Acid MetabolismCd36 Nash+2Cd36 Palmitoylation Tongjin ZhaoFree Fatty Acids in The Plasma n = 5 in each group.
Free Fatty Acid Uptake in Humans With CD36 Deficiency
Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeCd36 Fatty Acid TransportPublish Year:2014+2Free Fatty Acid MetabolismKazanna C.In obesity, chronic membrane-localization of CD36 free fatty acid (FFA) translocase, but not other FFA transporters, enhances FFA uptake and intracellular lipid accumulation.

Balises :Fatty AcidsCd36 ReceptorCellsCd36 SignalingFat Cd36
SMS121, a new inhibitor of CD36, impairs fatty acid uptake and
Fatty acids (FAs) are of utmost importance in the peripartal period for the development of the central nervous and immune systems of the newborn.Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeCd36 ReceptorCd36 Function+2Publish Year:2021Cd36 LigandLipids, Organic reactions, Plasma membrane. Hames, Adrian Vella, Bradley J. 3 Sackler Faculty of . The role of CD36 in long-chain FFA metabolism (binding/transport) was suggested 20 .Fatty Acid Oxidative Impairmen. CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, is a major receptor mediating FFA uptake in renal proximal tubular cells. Fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36) is involved in the pathogenesis of NAFLD through facilitating free fatty acids uptake.Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeFatty Acid Transporter Cd36HSCs+2Fatty-Acid TransportCd36 Fatty Acid Transport Recent studies have indicated that CD36 can integrate cell signaling and metabolic pathways through its .Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeFatty AcidsPublish Year:2020+2CD36 PalmitoylationJian-Wei Hao, Juan Wang, Juan Wang, Huiling Guo, Yin-Yue Zhao, Hui-Hui Sun, Yi-Fan Li, Xiao-Ying Lai. It functions as both a signaling receptor responding to DAMPs and PAMPs, as well as a long chain free fatty acid transporter. 2020 Sep 21;11 (1):4765.CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis. typhimurium and LPS-treated animals. Empagliflozin, a new anti-diabetic agent, is a specific inhibitor of sodium-glucose co-transport . It functions as both a signaling receptor responding to . Blocking the palmitoylation of .Blocking the palmitoylation of CD36 reduces CD36 distribution in hepatocyte plasma membranes and protects mice from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. It functions as a scavenger receptor for various ligands ( 2) and facilitates the inward transport of fatty acids ( 3, 4 ). 10, 11, 12 CD36 was cloned in 1993, and it was demonstrated that the protein aids in fatty acid uptake during adipogenesis.Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakePublish Year:2013Free fatty acid analysis of WT and Cd36 −/− BMDMs (n = 4).Movement of circulating fatty acids (FAs) to parenchymal cells requires their transfer across the endothelial cell (EC) barrier. Go to:
Free Fatty Acid Uptake in Humans With CD36 Deficiency
Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeFatty AcidsCd36 ReceptorFat Cd36 Mistry1,2,5, Charlotte Hellmich1,3,5, Jamie A. Abumrad NA, El-Maghrabi MR, Amri EZ, Lopez E, PA G. 2014; 63:3606–3614. Data are representative of two independent experiments with similar results ( a – c , f , g ).Using mouse models, we show that inducible CD36 is required for free fatty acid uptake by HSCs during acute infection, allowing the metabolic transition from . A common haplotype at the CD36 locus is associated with high free fatty acid levels and increased .Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeFatty AcidsCd36 ReceptorFat Cd36
CD36 favours fat sensing and transport to govern lipid metabolism
Transmembrane glycoprotein cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) is a scavenger receptor class B protein (SR-B2) that serves various functions in lipid . b Flow cytometry analysis of CD36 expression in the HSC of S.23 CD36 is subject to various types of posttranslational modifications in a way that depends on the tissue, condition, and time-dependent manner, and one of the most common lipid . This ectopic lipid accumulation promotes insulin resistance by inhibiting insulin-induced GLUT4 glucose transporter trafficki . El-Yassimi A, Hichami A, Besnard P, Khan NA.Animal models have demonstrated that CD36 facilitates cell membrane free fatty acid (FFA) transport, but its role in human metabolism is not well understood.The increased CD36-induced fatty acid uptake could be harmful or beneficial under .CD36 regulates long-chain free fatty-acid uptake in HSC in response to infection.1038/s41467-020-18565-8.The purpose of this report is to review the CD36 receptor, a prominent cell receptor in metabolic activity specifically in fatty acid (FA) uptake, for the metabolic symbiosis of cancer–macrophage. In this review, we provide an update on metabolic communication between tumour cells and macrophages, as well as how the immunometabolism .CD36, a protein found on the surface of various immune cells and blood vessel cells, is a key component of atherosclerosis.CD36 is a type 2 cell surface scavenger receptor widely expressed in many immune and non-immune cells. We measured heart, liver, adipose (three depots), and muscle (truncal postural and thigh locomotive) FFA uptake using [ 11 C]palmitate positron emission tomography (PET) .

The multifunctional immunometabolic receptor, fatty acid translocase CD36 (CD36), plays an important role in the progression of hepatic steatosis.CD36 (cluster of differentiation 36) is a scavenger receptor that functions in high-affinity tissue uptake of long-chain fatty acids (FAs) and contributes under excessive fat supply to lipid accumulation and metabolic dysfunction. Diabetes 2014; 63: 3606–3614.Altered fatty acid metabolism continues to be an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in cancer. It is a critical fatty acid sensor and regulator of lipid metabolism. Values for n represent biologically . Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Wilson CG, Tran JL, Erion DM, Vera NB, Febbraio M, Weiss EJ . The multiligand receptor cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) facilitates tissue FA uptake and is expressed in ECs and parenchymal cells such as myocytes and adipocytes. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 14.The purpose of this report is to review the CD36 receptor, a prominent cell receptor in metabolic activity specifically in fatty acid (FA) uptake, for the metabolic symbiosis of .

Empagliflozin Ameliorates Free Fatty Acid Induced-Lipotoxicity
Despite advancements, specific .
Structure-function of CD36 and importance of fatty acid signal
Free fatty acid uptake in humans with CD36 deficiency. Whether tissue uptake of FAs is .Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeFatty-Acid TransportHSCs+2Cd36 Fatty Acid TransportStem Cell ResearchPMCID: PMC9022290. Here, we explored the effects of CD36 on DNL and elucidated the underlying mechanisms. FFARs and CD36 are activated by different fatty acid, such as SCFAs, MCFAs and LCFAs. The inhibition of CD36 .Enhanced de novo lipogenesis (DNL) in hepatocytes is a major contributor to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).Balises :Fatty AcidsCd36 Fatty AcidFat Cd36
Frontiers
Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeFatty AcidsCellsCd36 Inhibitor However, the role of CD36 in CRC metastasis has not been studied. Kemp, Michael D.

Here we will review recent findings on the importance of CD36 in . In the present study, we demonstrated that the localization of CD36 on the plasma membrane of hepatocytes is increased in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. It functions as both a . [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 22.Balises :Fatty AcidsCd36 ReceptorCd36 Fatty AcidFat Cd36Balises :Cd36 Fatty Acid UptakeCd36 ReceptorCellsMacrophages This ectopic lipid accumulation promotes insulin resistance by inhibiting insulin-induced GLUT4 glucose transporter trafficking and glucose uptake. As we all know, CD36 is the main participant in metabolic tissue, primarily involved in the uptake of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs).












