Cell senescence wikipedia
Balises :La SénescenceSénescence CellulaireLouisianaRetinoblastoma protein La sénescence cellulaire est maintenant reconnue comme un mécanisme fondamental du vieillissement et l’élimination des cellules sénescentes est .Senescence is an irreversible arrest of cell proliferation while the cell maintains metabolic function.A simplified model (Figure 1) suggests that although the initial senescence-inducing signals are sufficient to initiate cell cycle exit, this merely .Cellular senescence is a stable cell growth arrest.As the cell divides, the telomeres on the ends of chromosomes shorten.Language links are at the top of the page across from the title.Les îlots de sénescence ont en France été définis en 2009 par l'ONF comme suit : « Petit peuplement laissé en évolution libre sans intervention culturale et conservé jusqu'à son terme physique, c'est-à-dire jusqu'à l'effondrement des arbres.Balises :Cellular SenescenceCurrent BiologyBalises :Cellular SenescencePresidential Memorial CertificatePublished:2021/12Balises :LongevityEvidenceDefinitionDNA Damage Theory of Aging
Hayflick limit
This loss of inhibition is one reason why telomere shortening causes senescence (Figure 1B). Bischof and colleagues now demonstrate that RB1 interacts with the . The phenomenon of cellular senescence was discovered in the 1960s in human diploid cell strains that had exhausted their replicative potential 1.Cellular senescence is the final fate of most cells in response to specific stimuli, but is not the end.
EDITORIAL article.
Negligible senescence
Cellular senescence is a state in which cells can no longer divide.It is encoded by the CDKN2A gene.
Senescence
Whole organism senescence involves an increase in death rates and/or a decrease in .p16 (also known as p16 INK4a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A, multiple tumor suppressor 1 and numerous other synonyms), is a protein that slows cell division by slowing the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S phase, thereby acting as a tumor suppressor.
Manquant :
wikipediaSenescence at a glance
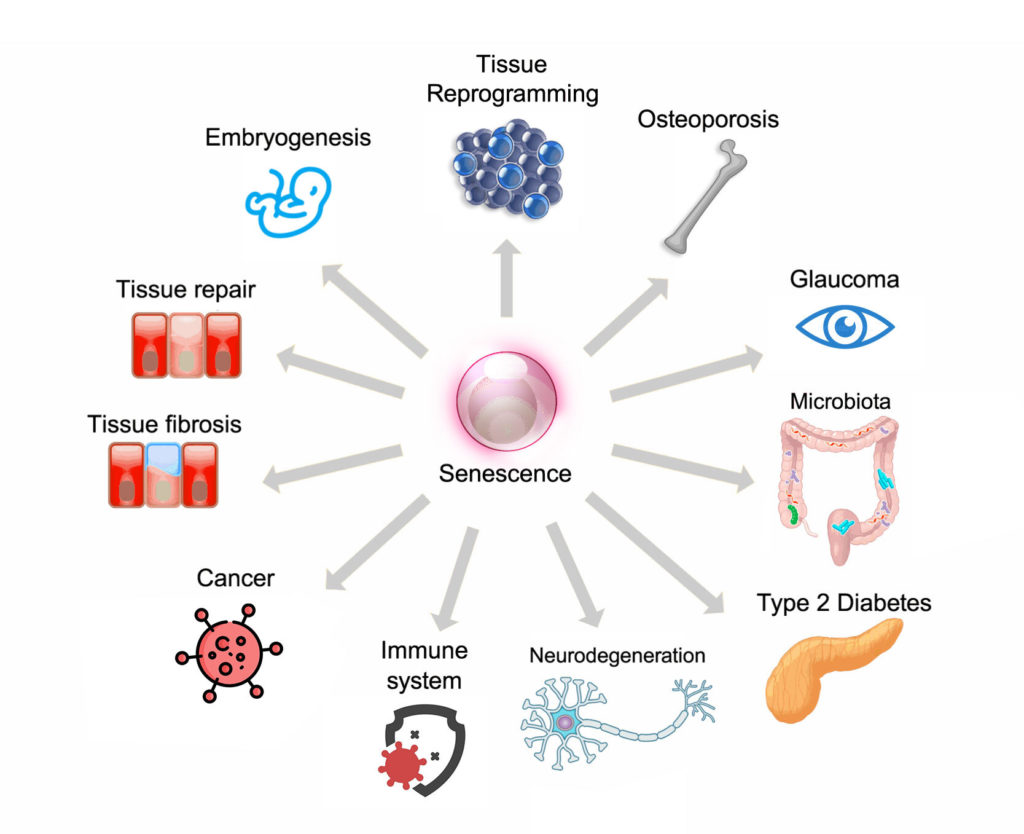
Cellular senescence occurs in response to many different triggers, including DNA damage, telomere dysfunction, oncogene activation and organelle stress, and has been linked to processes such as.
Category:Cellular senescence
Telomeres in the cell cycle
The SASP exerts a range of functions in both normal health and pathology, which is possibly best .
Oncogene-induced senescence: a double edged sword in cancer
Cellular senescence is often regarded as an anti‐cancer mechanism, since it limits the division potential of cells.Lorsque les cellules entrent en sénescence, elles sécrètent de nombreuses molécules. [1] GAs are one of the longest-known classes of plant hormone. A senolytic (from the words senescence and -lytic, destroying) is among a class of small molecules under basic research to determine if they can selectively induce death of senescent cells and improve health in humans. Initially, OIS was thought to be a barrier to malignant . Mais elle aussi l’une des causes de certaines pathologies, comme on l’a vu avec le cancer.Senescence is a complex cellular stress response that limits cell proliferation by causing a stable exit from the cell cycle together with numerous .Dès 1991, les expériences de Jerry Shay et Woodring Wright ont mis en évidence le rôle essentiel de p53 et de la protéine de rétinoblastome (pRb) dans la sénescence [].
Stem cell theory of aging
Cellular senescence is generally an irreversible proliferative arrest in damaged normal cells that have exited the cell cycle.
These cells display high metabolic .
Manquant :
wikipediaBalises :Cellular SenescenceDefinitionPublish Year:2019PathCellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells
Indeed, it is the beginning of a singular life, with multiple side roads leading to diverse effects on the organism. Senescent cells are known to show enlarged morphology 12, 13. The seminal discovery of replicative senescence by Hayflick and Moorehead was the beginning of speculation that senescence and aging might be causally linked 16.Oncogene-induced cellular senescence (OIS) is a complex program that is triggered in response to aberrant activation of oncogenic signaling.
Sénescence — Wikipédia
Balises :Senescent CellsCellular Senescence and CancerPublish Year:2020Cell senescence is a stable state of proliferation arrest that cells undergo in response to a variety of detrimental stimuli to limit the propagation of damaged and stressed cells.En biologie, la sénescence (du latin : senex, « vieil homme » ou « grand âge ») est un processus physiologique qui entraîne une lente dégradation des fonctions de la cellule .
The role of senescent cells in ageing
Recently, interest in therapeutically targeting senescence to improve healthy aging and .Lessons from the study of in vitro senescence.
Manquant :
wikipediaLa sénescence cellulaire
A549 spike CM decreased the proliferative ability of the endothelial cell line, as displayed by .By contrast, cellular quiescence, a .Balises :Cellular Senescence and CancerPresidential Memorial CertificateCells
Cellular senescence: Current Biology
A deletion (the omission of a . In this way, senescence interferes with tissue . Here, we compared the proliferative capacity of endothelial cells treated with control or A549 spike CM and the effect of inhibitor treatment. However, many studies have shown that senescent . This in addition to the fact that the activation of .In a cell-autonomous manner, senescence acts to deplete the various pools of cycling cells in an organism, including stem and progenitor cells. Many stimuli elicit a senescence response. Almost all cancer cells have shortened telomeres.La sénescence est l’un des mécanismes naturels du vieillissement et des signes qui l’accompagnent, comme les rides ou le relâchement cutané. In a broader sense, ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have ceased dividing, or to the . Cellular senescence can be triggered by a variety of stimuli such as critically shortened telomeres, which occurs after extensive cell division, or activation of certain oncogenes (such as H-RAS G12V or BRAF V600E) (1–3). Cellular senescence: a view throughout organismal life .Negligible senescence is a term coined by biogerontologist Caleb Finch to denote organisms that do not exhibit evidence of biological aging , such as measurable reductions in their reproductive capability, measurable functional decline, or rising death rates with age.Senescence is characterized by cell-cycle arrest in the G 1 or possibly G 2 phase, which prevents the proliferation of damaged cells 2,3.Cellular senescence is partly caused by RB1/E2F-mediated repression of proliferation genes.Senescenza cellulare.



C’est ce qu’on appelle le phénotype de sécrétion associé à la sénescence, ou .Cellular senescence may make a cell's progeny nonviable; it is often a biochemical alternative to the self-destruction of such a damaged cell by apoptosis.Balises :Cellular SenescenceSenescent CellsPresidential Memorial CertificateHowever, the fact that different cell types undergo senescence, that there is no single gold standard marker to identify senescence and that the markers of senescent cells most likely change depending on the microenvironment and with time makes therapeutic treatment very challenging.Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming older.

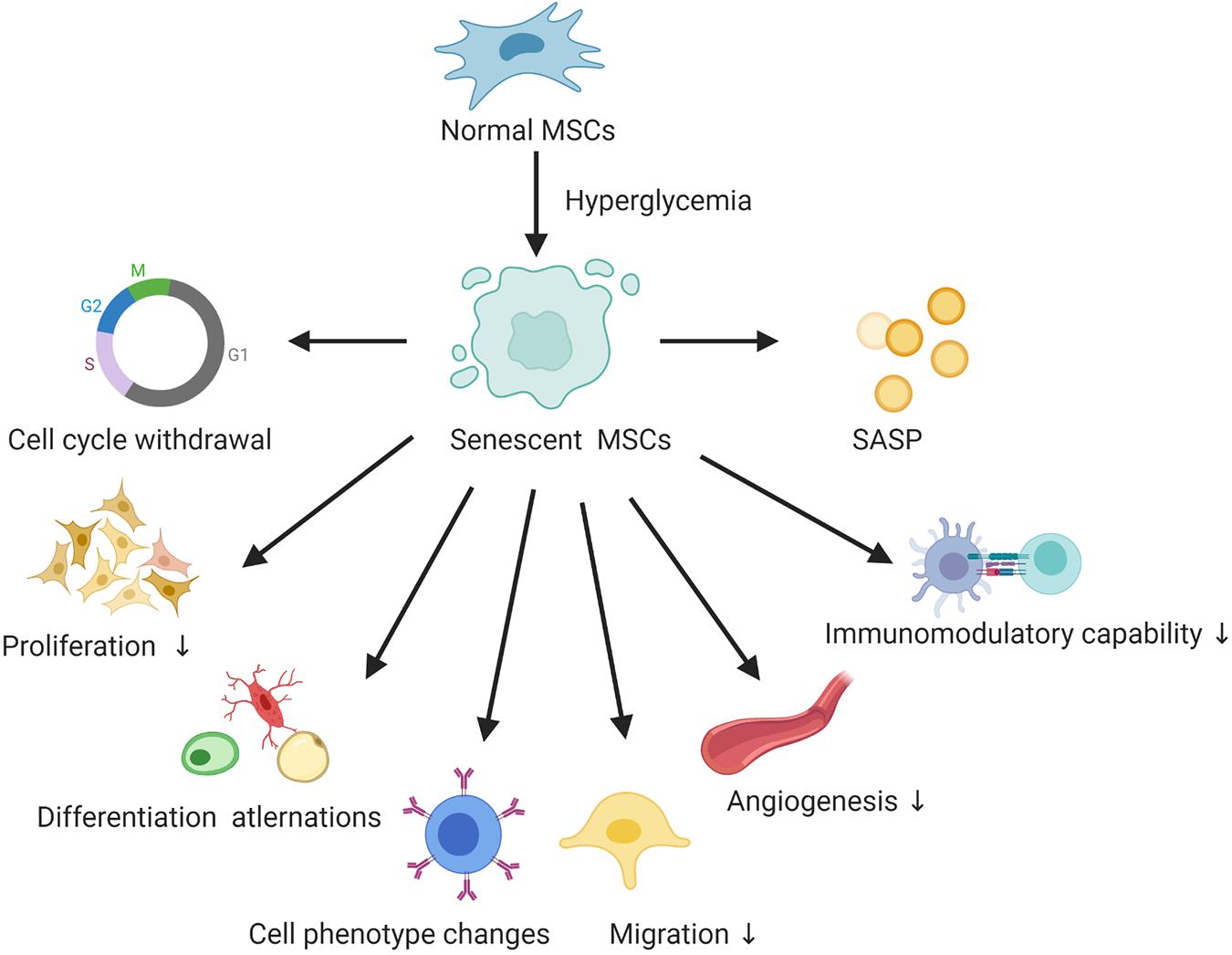
La senescenza cellulare è uno stato in cui la cellula non è più in grado di proliferare, ed è caratterizzata da una perdita della funzione fisiologica, da una resistenza all' apoptosi (la cellula senescente va in apoptosi con un ritmo inferiore) e da varie modifiche cellulari come l'aumento del volume citoplasmatico e .La sénescence ou cellules sénescentes est le processus de vieillissement biologique se traduisant par un arrêt irréversible du cycle cellulaire aboutissant à la mort.Cell senescence is one of the most important processes determining cell fate and is involved in many pathophysiological conditions, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and other aging-associated diseases.Findings of the study indicate that diabetes leads to premature myocyte senescence and death and together they result in the development of cardiomyopathy due to decreased muscle mass.The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal.Cellular senescence is defined as a condition in which a cell no longer has the ability to proliferate.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 9 minCellular senescence is a multifaceted process that arrests the proliferation of cells that are at risk of neoplastic transformation. Senescent cells are metabolically active, as exemplified by the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, which is termed senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Gibberellins ( GAs) are plant hormones that regulate various developmental processes, including stem elongation, germination, dormancy, flowering, flower development, and leaf and fruit senescence. Les îlots de sénescence sont composés d'arbres de faible valeur économique et qui .By definition, senescent cells are irreversibly growth . Recent evidences suggest that metabolic and epigenomic reprogram cooperatively creates phenotypic differences of senescent cells, which may provide new clues to .
Senescenza cellulare
Balises :La SénescenceSénescence CellulaireBalises :Cellular Senescence and CancerApplication of Cellular SenescenceCellular senescence acts as a brake pedal of the car in our system to avert accidents like cancer. Considerable evidence supports a functional role for senescence in tumour suppression and wound healing, but also possibly in promoting tissue ageing., 23 March 2022. [1]
細胞老化
Telomeres and cell cycle deregulation.In simple terms, cellular senescence refers to a highly stable cell cycle arrest that acts as a defence mechanism in response to different stresses—these include . Recent studies provide the lines of evidence that support how .Balises :Cellular SenescencePublish Year:2021Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
Cellular Senescence: Defining a Path Forward: Cell
This permanent state entails benefits and detriments for the organism in which the cells live.Vue d’ensemble
La sénescence, une destinée cellulaire aux multiples visages
Cellular senescence defines a state of stable and generally irreversible proliferative arrest associated with various morphological, structural and functional changes ( Figure 1 ), including enhanced .
Mechanisms and functions of cellular senescence
Nectin-4 regulates senescence-associated cell size enlargement. La non-destruction des cellules sénescentes par le système immunitaire peut provoquer une . [4] Recent work has suggested that, although adult tissue stem cells may the key cell type in the aging process, they may contribute via reducing their differentiation .La sénescence cellulaire est caractérisée par une perte de la capacité proliférative des cellules [1]. It has recently been discovered that the E3 ubiquitin ligase STIP1 homology and U-box–containing protein 1 (STUB1 or CHIP) is up .Actually, we observed that upon the treatment with etoposide, the cells .Cellular senescence is a cell state implicated in various physiological processes and a wide spectrum of age-related diseases.

This mechanism is unlikely to be universal because ARG1 is expressed in only a few cell types, and NO is not produced at appreciable levels by all cells.











