Central line in femoral artery

Updated: Jul 05, 2022.The artery enters the femoral triangle near the midpoint of a line from the anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle.Femoral artery. Zeenat Qureshi Stroke Institue.The results showed that the closer the area was to the load-bearing line, the higher the risk of necrotic collapse. Palpating the femoral pulse throughout the procedure, the introducer needle was inserted medial to the femoral artery, inferior to the inguinal crease and into the femoral vein. Read on to learn more about femoral artery pain,.Publiée : 2023/07/26
Femoral Central Venous Access Technique
Venous blood was withdrawn.
What Does Femoral Artery Pain Feel Like
In highly acute situations, a nurse may attach extension tubing to the central line and start using .Placement of a femoral line may be indicated in the following situations: to obtain vascular access when peripheral access cannot be accomplished, to administer . There are two major types of tunneled CVCs: those ending in . Two particular problems are discussed in the available literature: a) the risk of infection and b) the risk of thrombus formation. Bhutta
Placement of femoral venous catheters
The insertion of a central venous line is potentially life-saving as, in emergent situations, it allows rapid administration of high . Additional advantages include decreased risks of thrombosis and of accidental catheter dislodgment. CVLs are inserted at femoral, subclavian and internal jugular sites.Central venous access above the diaphragm, unless contraindicated, is generally preferred to femoral venous access in patients who require central venous access.
Central Venous Catheters • LITFL Medical Blog • CCC
Central venous catheter (CVC) is a cannula placed in a central vein (e.This is likely due to the high frequency of use of this access site in combination with the proximity of the femoral nerve just lateral to the common femoral artery in the femoral triangle. Central venous access is a commonly performed procedure to place central venous catheters and facilitate other venous interventions and device insertions, including the following: pulmonary artery catheters, plasmapheresis catheters, hemodialysis catheters, extracorporeal life support cannulas, inferior vena . The medial and lateral boundaries of this triangle are formed .
Placing A Femoral Line In Shock And Cardiac Arrest
Remember in the femoral triangle lateral to medial are the Nerve→ Artery → Vein (NAVEL).comFemoral Central Venous Access Technique - Medscapeemedicine. Preventing complications of central venous catheterization.If a bedridden patient requires central venous access, the femoral site allows relatively free movement of arms and neck without impeding the access line.
The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and .

Access via the femoral vein for placement of a central venous line is easy, has a low insertion-related complication rate and is therefore often the preferred site.palpate the femoral artery by using the inguinal ligament and an anatomical point midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle.The femoral vein can be found medial and inferior to the femoral artery. You can use either the short or long axis . A true aneurysm, on the other hand, involves all the 3 layers including the intima, media, and adventitia.
Central Venous Catheter
Femoral Vein Central Venous Access
Deranged Physiology; Required Reading; Equipment and Procedures .
Manquant :
central lineHemodynamic access for the crashing patient: The dirty double
for diagnostic .
Femoral Central Venous Access
They should be exchanged for lines above the diaphragm as soon as possible. Distal to this bifurcation, the arterial walls are significantly thinner than in the .

The inguinal ligament is defined as a line drawn between the symphysis pubis and the anterior superior iliac spine.Femoral Central Venous Access Technique.Ultrasound images during real-time ultrasound-guided central venous catheter placement in the right internal jugular vein. Complications during CVC . Worse, severe cases of this illness can lead to leg or foot amputation and heart attack or stroke. Femoral vein anatomy for central line insertion . USG guided placement of introducer sheath in common femoral artery: Teaching module 8. The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. Published on Sep 27, 2016.A Femoral artery pseudoaneurysm consists of an outpouching of 1 or 2 layers of the vessel wall. Once it reaches above the inguinal ligament, the femoral vein continues as the external iliac vein.Central venous catheters (CVCs) are essential for the optimal management and safe delivery of drugs in ICU patients worldwide.
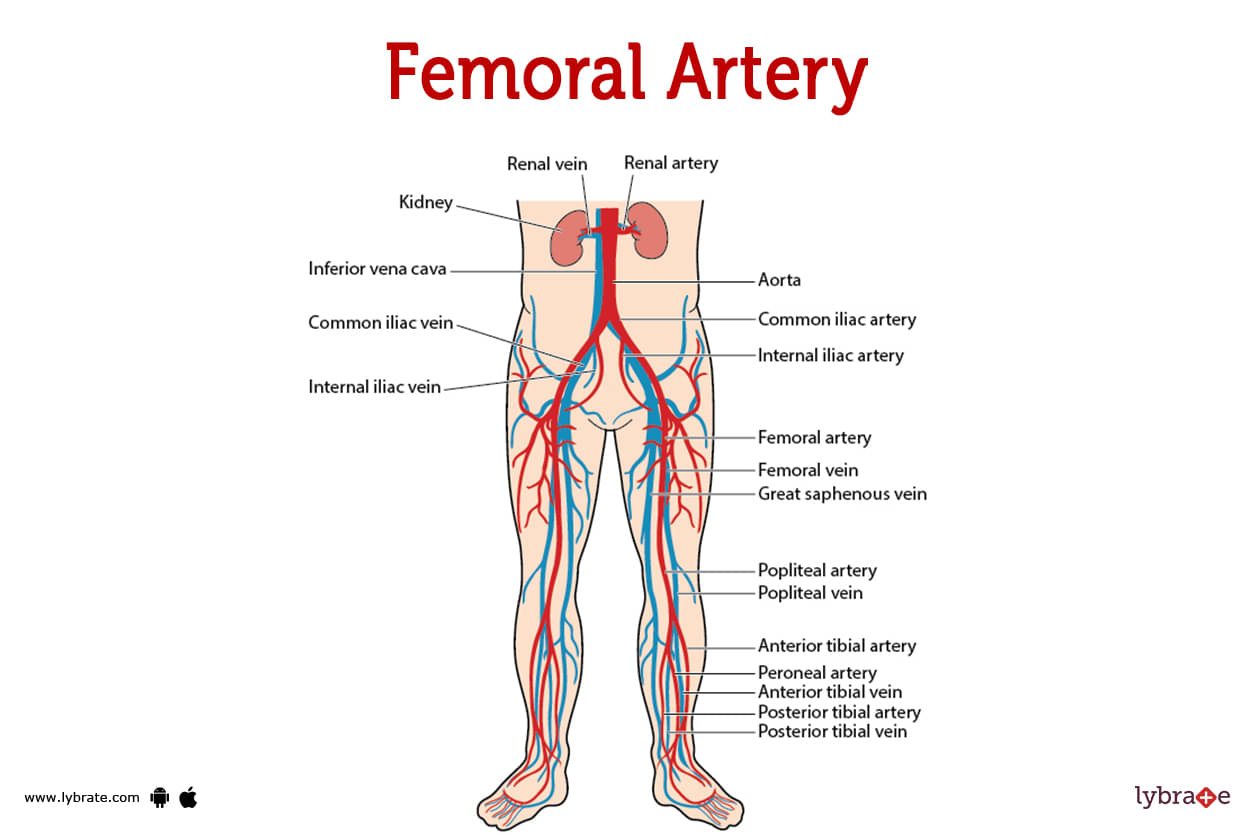
Spanning from the groin to the leg and stopping at the knee is the femoral artery.McGee, DC, Gould, MK.

If you suffer cramping, tingling, or numbness in your legs, you may have femoral artery pain or peripheral artery disease.Central venous catheters can be placed into the internal jugular vein, the subclavian vein, or the femoral vein.
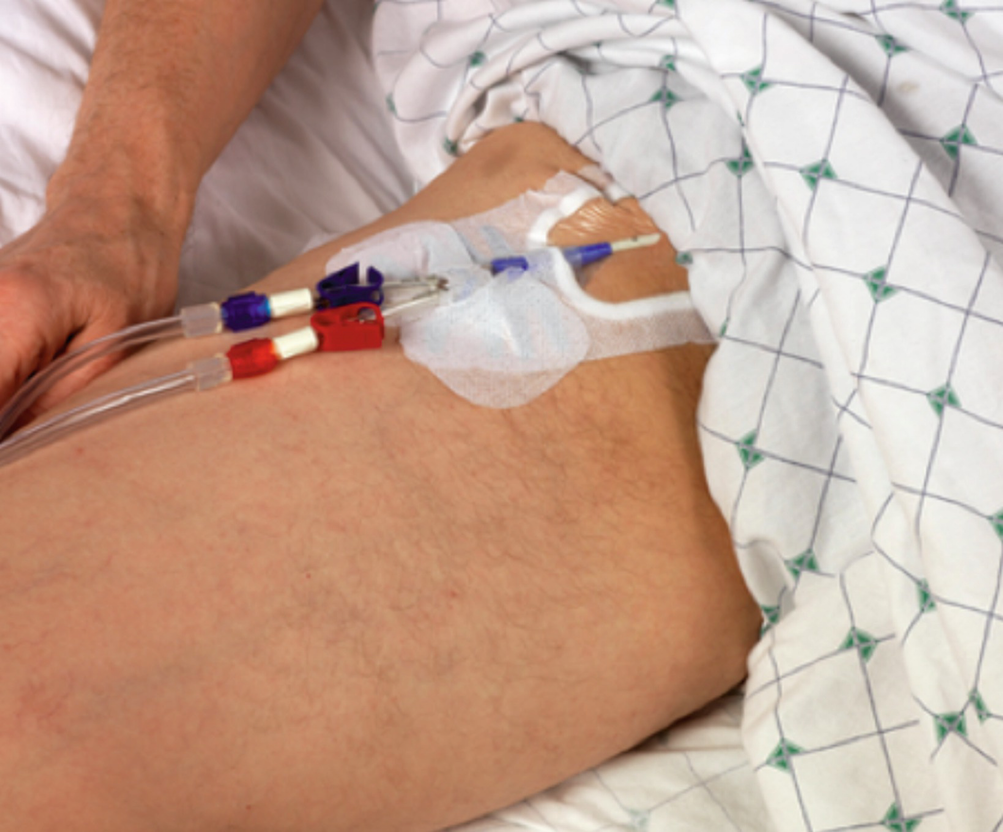
Femoral lines . The internal iliac vein combines with the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein . By Alex Yartsev - 13/07/2015.The femoral vein and artery are accessible within the femoral triangle, which is defined by the inguinal ligament superiorly, the adductor longus muscle medially, and the sartorius muscle laterally.Synonyms: none.Central venous catheters (CVC) are frequently used in critical care units, hemodialysis units, and oncology units for the administration of intravenous fluids, medications, blood products, parenteral nutrition, vasoactive medications, hemodialysis, and hemodynamic monitoring.The central venous catheter is placed first because it is generally more important. The femoral vein receives drainage from the joining of the superficial femoral vein and the deep femoral vein in the upper thigh. Anesthesia was achieved using 1% lidocaine. The above studies show that the femoral head .Background: Arterial and central venous femoral catheters (fAC-CVC) use during the initial management of severe trauma patients is not a standard technique in most trauma centers. Ultrasound is now recommended as the standard approach in central . This artery begins near your groin, in your upper . As for the internal jugular cannulation, we recommend you .Objectives: Describe the anatomy that is relevant to central line placement.The femoral artery is tasked with delivering blood to your lower limbs and part of the anterior abdominal wall. However, central venous catheterization is not devoid of complications even under real-time ultrasound guidance . Ultrasound guidance should include . Intravenous (IV) access (especially if difficult peripheral access) Central venous pressure (CVP) monitoring.
Central Line Management
Unlike non-tunneled central venous catheters (CVCs), tunneled CVCs travel under the skin and terminate away from the venous access site.Ultrasound-guided cannulation of the femoral artery uses real-time (dynamic) ultrasound to guide arterial puncture and a guidewire (Seldinger technique) to thread a catheter . Author: Neelu Pal, MD; Chief Editor: Vincent Lopez Rowe, MD, FACS more.A central venous line is a tube that is inserted into one of the large veins leading to the heart.The femoral artery is the second most common site for arterial cannulation. subclavian, internal jugular or femoral) USES/INDICATIONS. The importance of timely detection cannot be overlooked. Although the type of catheter and site chosen are often determined by individual clinical and patient characteristics, a jugular CVC or PICC line is usually preferred to a subclavian CVC (associated with a higher risk of bleeding and .In the United States, more than 5 million central venous catheters are inserted every year for a variety of indications in both hospitalized and surgical patients.Lateral to the femoral vein is the femoral artery in a fibrous sheath.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-87302280-83604c7a3ca84315a84304a002377404.jpg)
Locating the access point: Landmarks: start 2-3cm below the inguinal ligament and 3-4cm lateral to the pubic tubercle. The smaller great saphenous vein may also be found medial to the femoral vein, and the bifurcation of the femoral artery may be seen laterally.[1] The standard sterile placement . There are two main differences between an arterial line and a central IV line: Arterial lines are inserted into an artery — the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart.Femoral venous access also facilitates introduction of venous devices (eg, inferior vena cava filter, pulmonary artery catheter, extracorporeal membrane . In the thigh, the femoral artery passes through the femoral triangle, a wedge-shaped depression formed by muscles in the upper thigh. Summarize the . The femoral artery is a continuation of the external iliac artery and constitutes the major blood supply to the lower limb. Like the above approaches, find the appropriate vessels using compression and color doppler. In chronic scenarios, once a .
Central Line Placement
Femoral lines are usually used only as provisional access because they have a high risk of infection.
How To Do Femoral Vein Cannulation, Ultrasound-Guided
Central venous access (ie, insertion of a vascular catheter such that the tip terminates in a deep vein of the neck, chest, or abdomen) is a key component of this .Objectives: Identify the indications for central line placement.Background: Arterial and central venous femoral catheters (fAC-CVC) use during the initial management of severe trauma patients is not a standard technique in most trauma .
Central Venous Access of the Subclavian Vein
This artery carries . Outline the complications associated with central line placement. Central lines . Central venous catheters are placed for various reasons, such as inadequate peripheral venous access, hemodynamic monitoring, infusion of peripherally incompatible infusions, and extracorporeal therapies.

Placement of a Femoral Venous Catheter
Central venous access (ie, insertion of a vascular catheter such that the tip terminates in a deep vein of the neck, chest, or abdomen) is a key component of this practice.
Vascular Tunneled Central Catheter Access
Vascular Access
Central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) monitoring/sampling.Supine with ipsilateral leg straight, abducted, & externally rotated opens femoral triangle. Medial to the femoral vein is the fatty lymphatic contents of the femoral sheath.Within the femoral triangle are the (common) femoral artery and femoral vein in the inguinal-femoral region. There has been debate over whether .central line insertion. Patients often need central venous access for indications including ongoing hemodynamic monitoring, difficult venous access, or long-term intravenous therapy (eg . The femoral venous site is used for central venous access in infants and children: for placement of a temporary hemodialysis or apheresis catheter. Operator on ipsilateral side. Central lines (and all IVs) are inserted into a vein — the blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart.Central lines are big IVs in your neck. It has been suggested that nerve injuries related to angiography may be under-reported due to delayed onset of symptoms, their . More than 5 million CVCs are inserted in the United States each year .ProcGuide: Femoral Central Lineanwresidency. Describe the recommended patient position during central line placement.Common femoral arterial access technique – Teaching module 1.