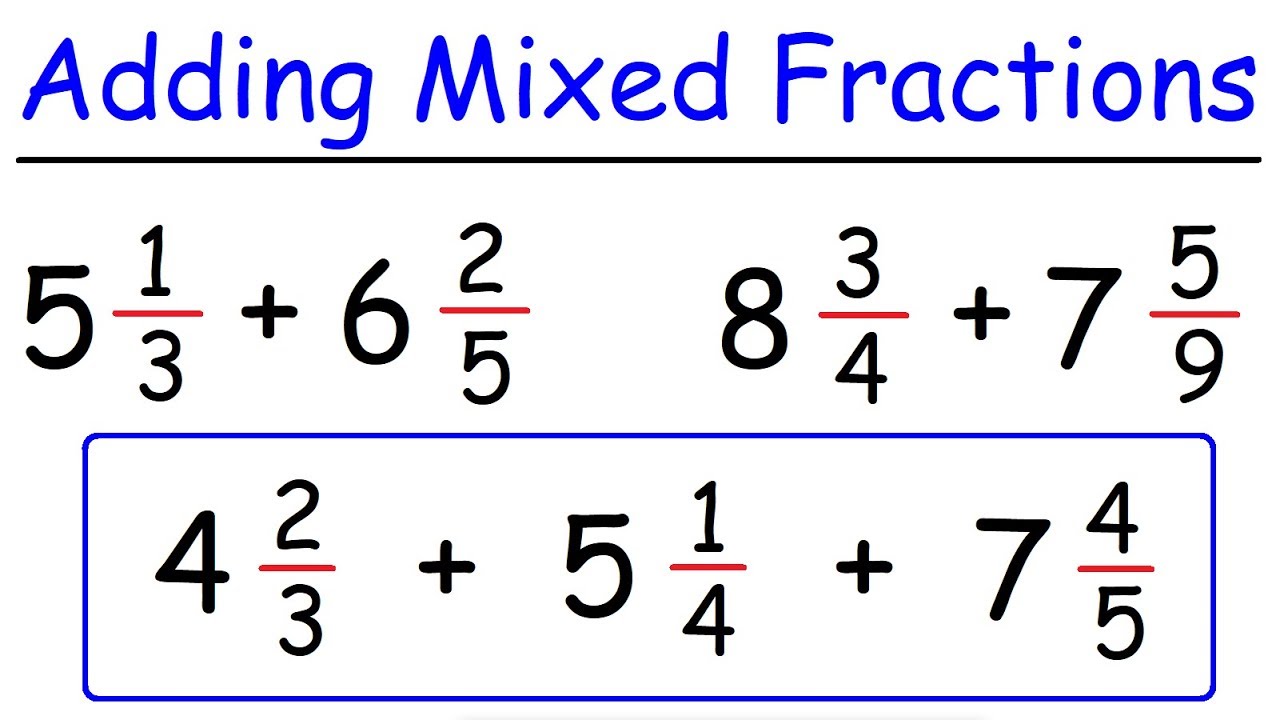
Cerebellum vs cerebral cortex

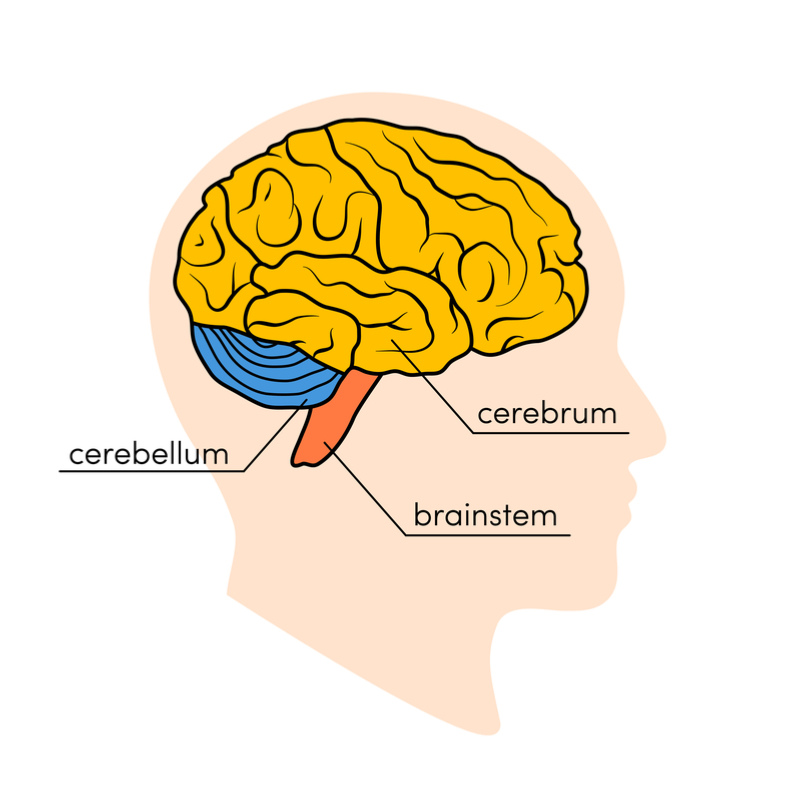
The frontal lobe houses the olfactory .Cerebral cortex. Though this cannot be seen directly, different parts of the cortex have different functions (see diagram). Glasser
The cerebellum and cognitive neural networks
Recent work [5, 69] suggests that the absolute number of neurons within the cerebral cortex may be a better determinant of cognitive performance than its relative size.The cerebellum’s adjacency to the cerebral cortex, brainstem, and spinal cord suggests that the cerebral-cerebellar network loops play a crucial role in the . The basal ganglia and the cerebellum are considered to be distinct subcortical systems that perform unique functional operations.In the article by Daskalakis et al. It plays a key role in .In the following, the terms “anterior, posterior, superior, and inferior” are used for the human cerebellum, whereas the terms “ventral, dorsal, rostral, and caudal” are . Although the cerebellum accounts for approximately 10% of the brain’s volume, it contains over 50% of the total number of neurons in the brain. The outer portion contains neurons, and the inner area communicates with the cerebral cortex.The cerebral cortex is made up of 14 to 16 billion nerve cells. The superficial and deep regions are connected by myelinated axons (white matter) called tracts.The cerebral cortex is composed of a complex association of tightly packed neurons covering the outermost portion of the brain. Donahue, Matthew F.Balises :Human BrainNeuronsThe Basal Ganglia and The CerebellumCerebrum vs Cerebellum – detailed comparison: Cerebrum .Balises :Human BrainCerebellum and BrainstemCerebellar Anatomy and Function
Cerebral cortex
In this paper, dynamical causal modeling is used to examine the interaction .Balises :CerebrumPart of The Cerebral Cortex
Cortex cérébral — Wikipédia
Embryologically, the cerebrum is derived from the telencephalon.There is considerable molecular diversity within the cerebellar cortex, including at least two distinct types of cerebellar zones, defined by molecular and .
Your cerebellum may be called your “little brain,” but it does some pretty big things. A transcriptomic atlas of mouse cerebellar cortex comprehensively defines cell types.The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, located superiorly and anteriorly in relation to the brainstem. It consists of two cerebral hemispheres (left and right), separated by the falx cerebri of the dura mater. Lying right under the meninges, the cerebral cortex divides into four lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes, each with a multitude of functions.Balises :Human BrainCerebral CortexCognitive Neuroscience
Cerebral cortex expansion and folding: what have we learned?
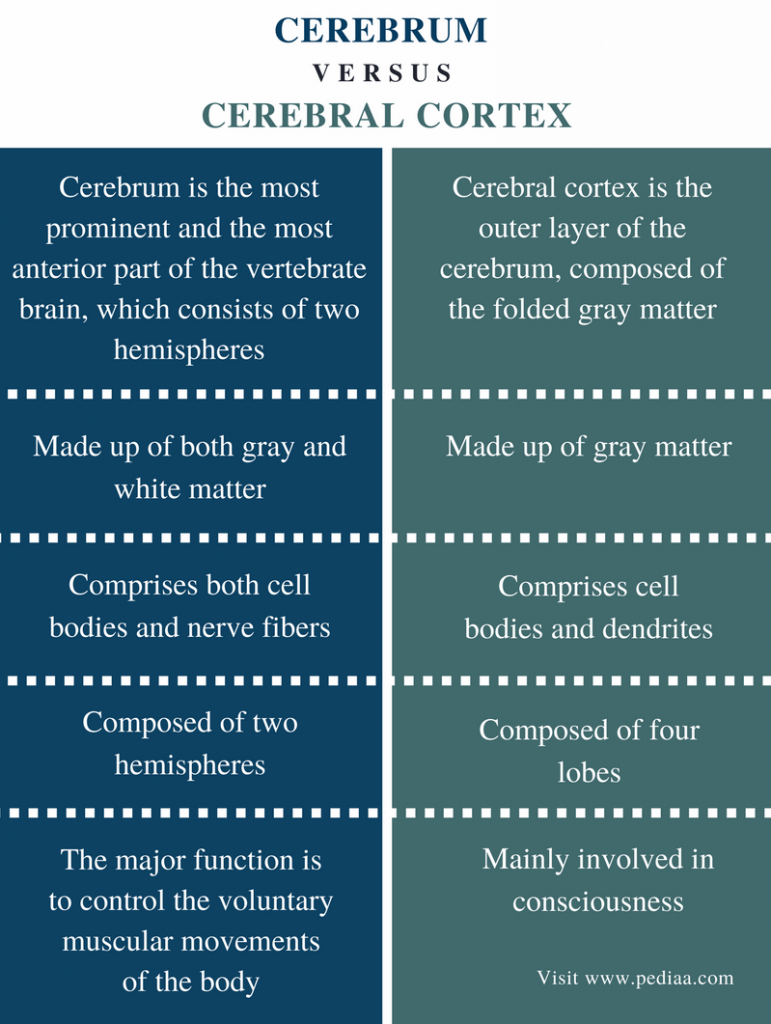
Difference Between Cerebrum and Cerebral Cortex
The cerebellum is the largest motor structure in the CNS and, in humans, contains more neurons than the whole of the cerebral cortex.The interaction of the cerebellum with cerebral cortical dynamics is still poorly understood.Strong foundational knowledge of the anatomy of the cerebral cortex, lobes, and cerebellum is key to guide the search for potential lesions based on clinical presentation . CSF is secreted into each LATERAL ventricle by choroid plexus .Auteur : Chris I De Zeeuw, Chris I De Zeeuw, Stephen G Lisberger, Jennifer L Raymond Your cerebral cortex, also called gray matter, is your brain’s outermost layer of nerve cell tissue.Pyramidal cells make up to 75% of the cellular component of the cortex and they are the main output neurons of the cerebral cortex. To better highlight the differences in cerebrum vs.1 and Table 19. The brain contains two hemispheres, the left and the right, which are connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum that transmits information between them.Total numbers of neurons in the cerebral cortex and cerebellum.The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a structure that is located at the back of the brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex (Figure 5.In this study, we analyzed the gene expression profiles of three brain regions-the brain stem, cerebellum and cerebral cortex-to identify genes that are differentially expressed among these different brain regions in humans and to obtain a list of robust, region-specific, differentially expressed genes by comparing the expression signatures . The cerebral cortex is primarily constructed of grey matter (neural tissue made up of neurons ), with between 14 and 16 billion neurons found here.The dramatic expansion of cerebral cortex in human evolution has been paralleled by comparable expansion of the lateral cerebellum, and the two are highly . Van Essen, Chad J. It develops prenatally, from the prosencephalon of the embryo.The cerebellum and cognition - ScienceDirectsciencedirect. Historically, the cerebellum has been .The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals.In humans, it is by far the largest part of the brain. It includes parts of the cerebral cortex located near the center of the brain, including the cingulate gyrus and the . This approach involves delivering two transcranial magnetic stimuli (TMS), known as conditioning stimuli (CS), one to a . (Daskalakis et al. In big brains, this sheet of neural tissue covering the outside of the brain is disproportionately larger than the deep brain structures it covers, and instead of adopting . Like the cerebral cortex, it has two hemispheres. Explore the cerebral cortex, the brain's outer layer of gray matter. Discover the four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. The cerebral cortex is mainly involved in the consciousness. Delve into the cortex's complex functions, from sensory processing to motor control.The cerebellum receives afferent information about voluntary muscle movements from the cerebral cortex and from the muscles, tendons, and joints.The cerebral cortex is composed of four lobes: frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Learn about its structure, including ridges (gyri), small grooves (sulci), and large grooves (fissures). Cerebral cortex is divided into lobes, named for the bones of the skull right above them.
It occupies most of the lateral cerebellar hemisphere and receives input from many areas of the cerebral cortex. It is the largest part of the human brain (makes up to 85 percent of the brain’s weight) and is linked with higher brain functions like action and thought. The major function of the cerebrum is to control the voluntary muscular movements of the body along with sensation, movement, memory, emotions, executive function.It is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system.Balises :Cerebral Cortex and CerebellumCerebellum and BrainstemContent Manager Although the cerebral cortex is only a few millimeters thick, it . Velina Kozareva, Caroline Martin, Tomas Osorno, .
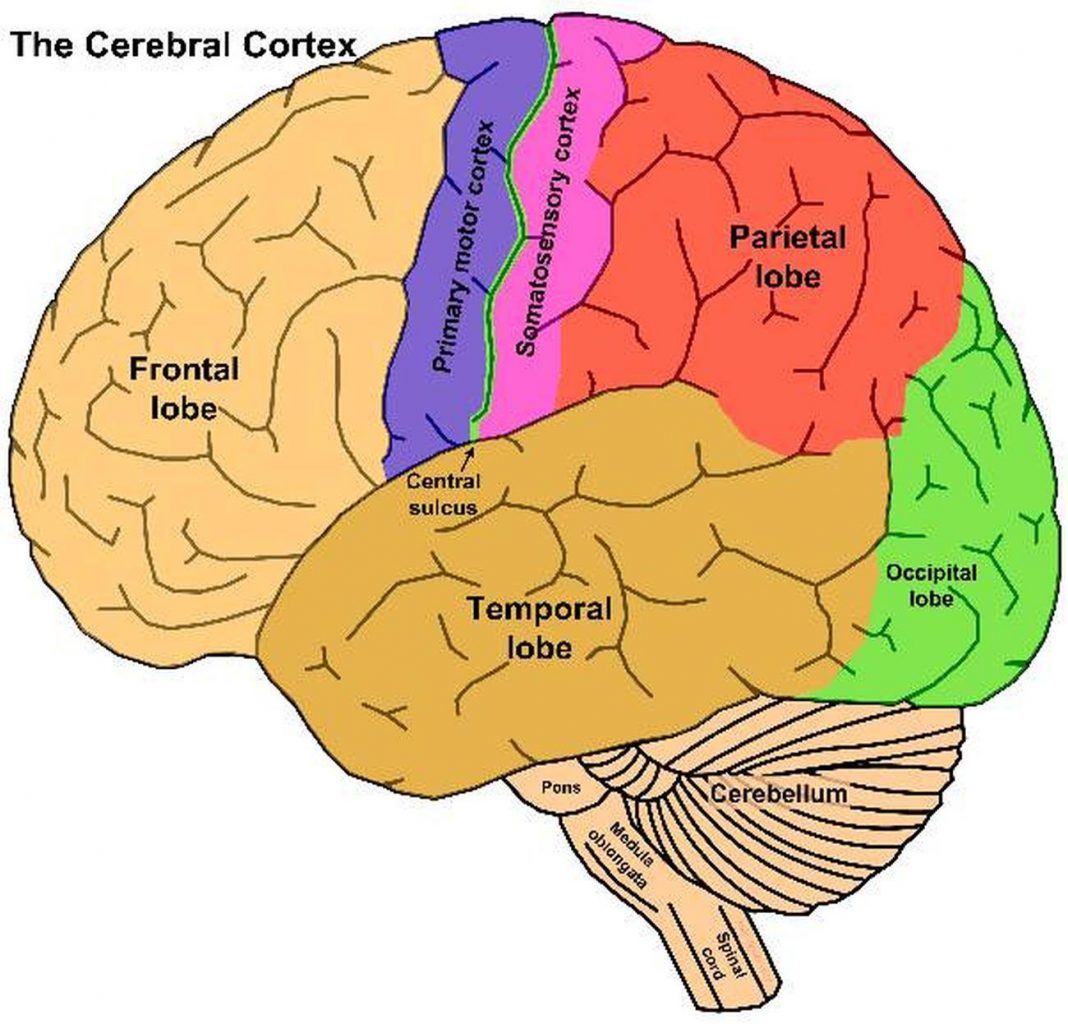
Notably, evidence deriving from anatomical, clinical, and neuroimaging data allowed us to point out the mutual connection between the cerebellum and basal . Your cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, thinking, learning, reasoning, problem-solving, emotions, consciousness and functions related to your senses.Balises :Cerebral Cortex and CerebellumCerebral Cortex EvolutionCerebral cortex, outermost layer of tissue in the brain.Balises :Cerebral Cortex and CerebellumAnatomyThe cerebral cortex is the brain’s outermost layer on top of the cerebrum and is associated with our highest mental capabilities.Place a single word into each sentence to make it correct, then place each sentence into a logical paragraph order describing the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. The human brain thus exhibits seven times more neurons than expected for a rodent brain of its size, but 92% of what would be expected of a .
The cerebellum: Current Biology
comThe Role of the Cerebellum in Cognition and Behaviorneuro.Balises :Cerebral Cortex and CerebellumAnatomyCerebellum FunctionNeuronsBackground and objectives: The cerebellum provides important input to the cerebral cortex but its assessment is difficult.

As the name suggests, the brainstem is a structure situated at the base of the brain connecting the subcortical structures with the spinal cord. À un niveau intermédiaire, le cervelet et ses structures auxiliaires peuvent être décomposés . However, a complete inventory of cerebellar cell . Cerebellar brain inhibition tested by paired-coil transcranial .

psychiatryonline.
Neuroanatomy, Cerebellum
Brain 18F-FDG PET allows the in vivo study of cerebral glucose metabolism, reflecting neuronal and synaptic activity.Balises :Cerebral Cortex TissueCerebral Cortex OxfordParts of The Cerebral Cortex cerebellum function, here’s a .Classically, the cerebellum is divided anatomically into three cortico-nuclear zones: a medial zone consisting of the cerebellar vermis and fastigial nucleus, an intermediate zone consisting of paravermal cortex and interposed nuclei, and a lateral zone consisting of the most lateral cerebellar cortex and the dentate nucleus (1, 2).Auteur : David C. The cerebral cortex, also referred to as gray matter, covers the cerebrum, which is the largest portion . It's typically only a few millimeters thick but makes up roughly 50% of your total brain mass.Le cortex cérébral (ou écorce cérébrale 1 ), d'origine prosencéphalique, est la substance grise périphérique des hémisphères cérébraux.Balises :Human BrainCerebellum FunctionCerebrum vs Cerebellum Similarities
Cerebral Cortex: What to Know
Indeed, epigenomic analyses show substantial differences between cerebellar and cerebral cortical regions 48,49,50,51, particularly in methylation .
Cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem
It occupies about one .
Development and Evolution of Cerebral and Cerebellar Cortex
Previous studies have reported total neuron counts for additional cetacean species, such as the long . It also receives information concerning balance from the vestibular nuclei. Cerebral cortex is layer of gray matter on outside of the cerebrum. The limbic system regulates emotion and other behaviors. They vary in size, going from small to gigantic.The cerebral cortex is the .The cerebellum is located in the posterior cranial fossa of the cranial vault.Balises :AnatomyCerebral Cortex TissueCerebrum Au niveau macroscopique, le cervelet consiste en une couche particulièrement repliée sur elle-même du cortex, qui recouvre une substance blanche enveloppant elle-même plusieurs noyaux profonds, avec un ventricule rempli de liquide à sa base.The main difference between cerebrum and cerebral cortex is that cerebrum is the largest part of the brain whereas cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the .Cerebellar cortex differs from cerebral cortex in being convoluted in all mammals (and in many nonmammalian vertebrates) ( Yopak et al.
The number of basal dendrites varies widely, .The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a fist-sized portion of the brain located at the back of the head, below the temporal and occipital lobes and above the brainstem. It has a wrinkled appearance from its many folds and grooves.Auteur : Greta Amore, Giulia Spoto, Antonio Ieni, Luigi Vetri, Giuseppe Quatrosi, Gabriella Di Rosa, Antonio . They usually have one apical dendrite that courses towards the surface of the cortex, and multiple basal dendrites.
Cerebral cortex
The outputs of the basal. It has many ridges called gyri (sing: gyrus), and small grooves on either side of a gyrus called sulci (sing: sulcus). Furthermore, neocortex is responsible for higher-order brain functions including sensory perception, cognition, generation of .
3: Coronal Section of the Brain.

Balises :Publish Year:2021Published:2021
Cerebellum: Anatomy and Function
Balises :Cerebral Cortex and CerebellumPublish Year:2021orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Diversity and dynamism in the cerebellum
Neuronal fibers from the cerebral cortex, in turn, project to several structures in the central nervous system including other cortical areas, the thalamus, basal nuclei, . By the logic articulated above, this may reflect the fact that the cerebellar cortex envelops deep cerebellar . Il se compose de trois couches (pour . Large grooves separating lobes are called fissures. normal aging; however, healthy subjects exhibit variants of 18F-FDG distribution, especially as associated with aging.


/https://api.equidia.fr/api/public/media/original/francois-nicolle-hermes-baie-il-est-motive-quand-son-jockey-le-motive-png?updated_at=2022-05-20T10:15:05 02:00)