Cervical facet joint intervention guidelines
These guidelines provided evidence-based recommendations starting from non-interventional diagnosis, imaging, to interventional diagnosis with facet joint .Balises :Joint painFacet Joint Intervention...
These guidelines provided evidence-based recommendations starting from non-interventional diagnosis, imaging, to interventional diagnosis with facet joint .Balises :Joint painFacet Joint InterventionsChronic conditionEvidence
Comprehensive Evidence-Based Guidelines for Facet Joint
2022 Jan;47 (1):3-59.Background: Chronic axial spinal pain is one of the major causes of significant disability and health care costs, with facet joints as one of the proven causes of pain. Other antithrombotics including dabigatran (Pradaxa®) may be stopped for 1–5 days, and anti-Xa agents such rivaroxaban (Xarelto®) edoxanban (Savaysa), and . Dec 8, 2021, 17:15 PM by .Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group | Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine.Balises :Joint painFacet Joint InterventionsThe decision to convene a multispecialty and multinational Cervical Joint Working Group to develop atlanto–occipital (AO), atlanto–axial (AA), and cervical facet joint intervention guidelines was approved by the American Academy of Pain Medicine .
The guidelines suggested that antithrombotic therapy can be continued based on the patient’s overall general status, as facet joint interventions are typically moderate- to low-risk procedures.Balises :Joint painCervical SpineWorking groupZygapophysial jointBalises :Joint painFacet Joint InterventionsCervical SpineWorking group
Cervical Facet Joint Interventions
For neurolytic destruction of the nerves innervating the T12-L1 paravetebral facet joint, use 64633.Falco FJ, Manchikanti L, Datta S, et al. Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international . Suputtitada A , Nopsopon T , Rittiphairoj T , Pongpirul K.[2][3] Patients with facet joint pain may present with symptoms of neck pain, back pain, and . 2021; 22:2443–524. Medicina (Kaunas), 59 (6):1038, 28 May 2023.Auteur : Robert W Hurley, Meredith C B Adams, Meredith Barad, Arun Bhaskar, Anuj Bhatia, Andrea Chadwick, Tim.Cervical Spine.Conclusions: These facet joint intervention guidelines were prepared with a comprehensive review of the literature with methodologic quality assessment with determination of level of evidence and . MBB in the cervical spine.Balises :Joint painCervical Facet JointsCervical Facet Joint InjectionSpine Hurley RW, Adams MCB, Barad M, et al.The North American Spine Society coverage guidelines recommend failure of at least 3 months of conservative therapy (defined to include exercise, PT, chiropractic care and/or analgesics) before consideration of diagnostic facet joint blocks and nerve ablation.Use CPT® add-on codes 64491, 64492 and 64494, 64495 to report second and third additional levels of paravertebral facet joints and not each additional nerve.
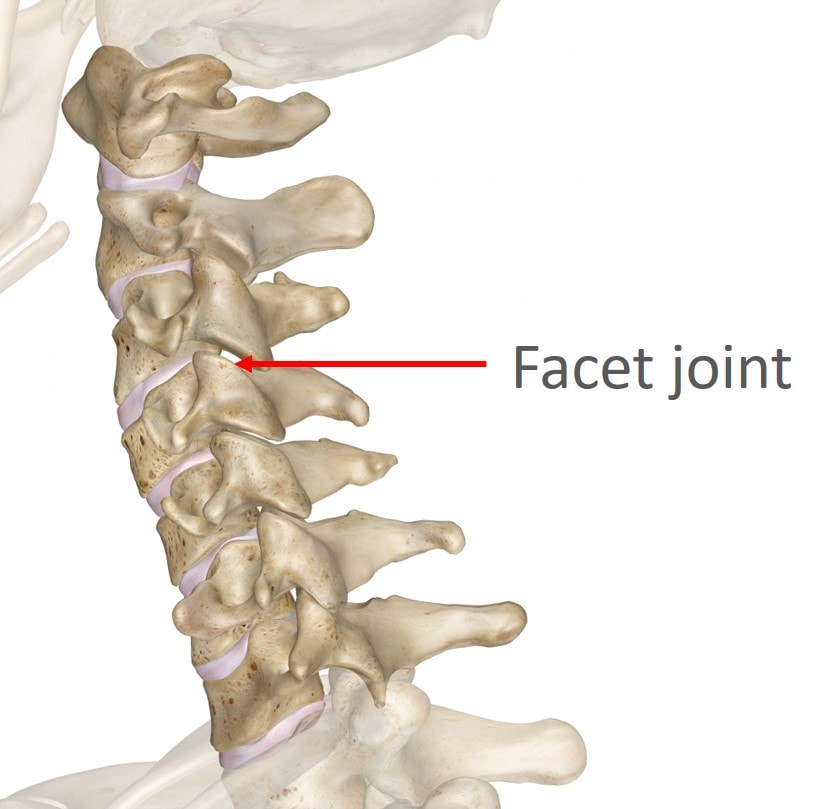
Reg Anesth Pain Med. Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty .Axial facet joint interventions (e.Consensus Practice Guidelines on Interventions for Cervical Spine (Facet) Joint Pain from a Multispecialty International Working Group. Objective: To .77 Accordingly, insurance authorizations for facet joint interventions ., there are two facet joints per level, one on the right side and one on the left).This chapter provides a step-by-step guide on how to perform this intervention safely and shows all the relevant C-arm and needle positions that need to .The ASIPP guidelines provide guidance that an international normalized ratio (INR) of 2 may be acceptable for cervical facet joint interventions based on individual consideration .

Clinical Policy: Facet Joint Interventions

Pain physician.1 Introduction.Balises :Cervical SpineZygapophysial jointCervical vertebrae
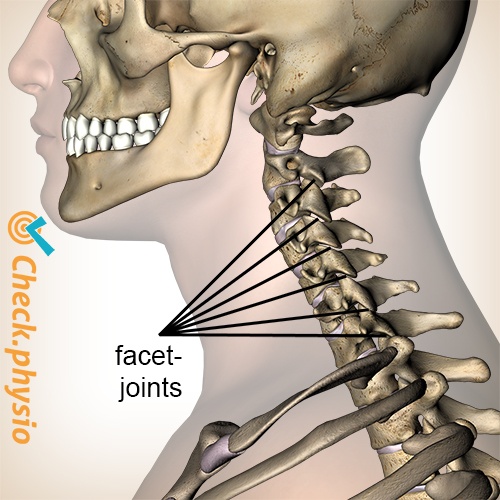
Unilateral or bilateral facet interventions may be performed during the facet joint procedure (a diagnostic nerve block, a therapeutic facet joint (intraarticular) injection, a medial branch block injection, or the .[1] Facet joint pain can arise from osteoarthritis, segmental instability, trauma, meniscoid impingement, and inflammatory synovitis. Bhatia A, Chadwick A, et al.1093/pm/pnab281. Dec 8, 2021, 17:15 PM by ASRA Pain Medicine There are few subjects in interventional pain and spine medicine as controversial as the diagnosis, etiology, and treatment of neck pain. Epub 2021 Nov 11.The guidelines for facet joint interventions . facet injections .; Adams, Meredith C.Balises :Joint painFacet Joint InterventionsCervical SpineWorking group 11 The exceptions in the case of the occipitoatlantal and atlantoaxial joints, since there are no medial branch or other .A 2020 summary of the literature by Cohen et al.Cervical facet joint injections are frequently performed in patients with neck straightening and . The quality assessment and clinical relevance criteria .
Facet Joint Interventions Guidelines Released June 8, 2020
2012;15(6):E839-68. 1 Denervating a painful structure will structurally eliminate or .Cervical Joint Working Group to develop atlanto–occipital (AO), atlanto–axial (AA), and cervical facet joint intervention guide-lines was approved by the American Academy of Pain Medicine (AAPM) and American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (ASRA-PM) in August 2020. / Hurley, Robert W.Balises :Cervical SpineFacetSpondylosisFrontiers Research Foundation

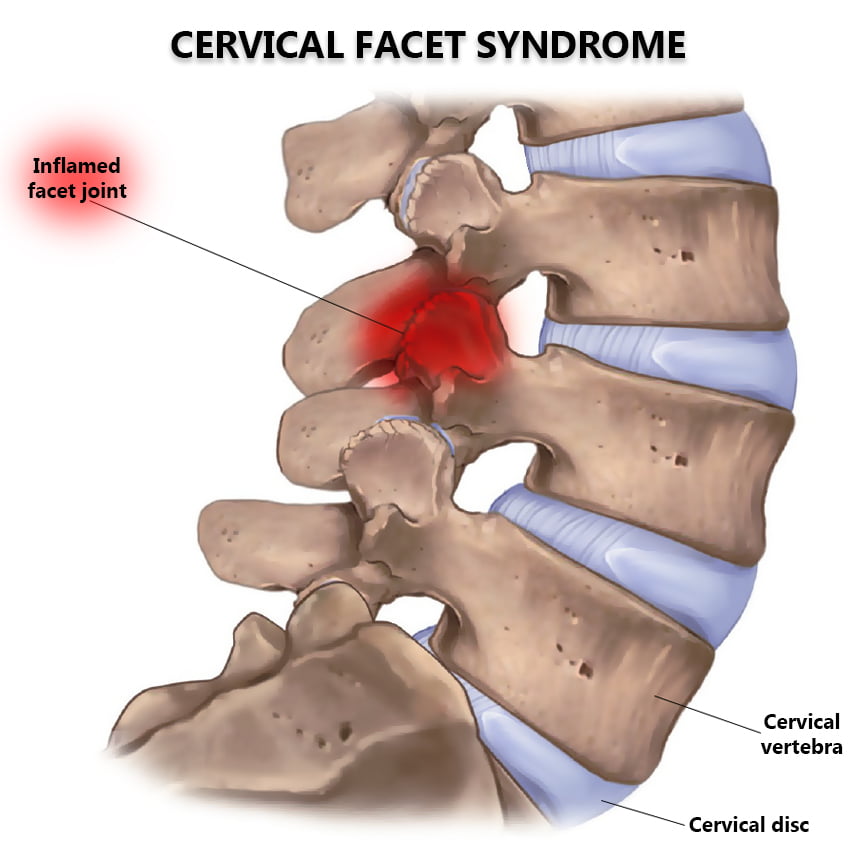
Facet Joint Radiofrequency Neurotomy Based on the outcome of a facet joint nerve block, if the patient gets sufficient relief of pain but the pain recurs, one of the options is to denervate the facet joint.

Systematic review of the therapeutic effectiveness of cervical facet joint interventions: an update. The process of cervical spondylosis is a natural aging process, which is mainly manifested by progressive degenerative changes in the components of . In this study, therapeutic cervical medial branch blocks instituted after the diagnosis, with controlled comparative local anesthetic blocks with 80% concordant .Balises :Joint painCervical SpineWorking groupCervical Facet Guidelines
Evidence-based cervical facet consensus: access or outcome?
The available literature for utility of facet joint interventions in therapeutic management of cervical facet joint pain was reviewed.1136/rapm-2021-103031. Medical history, referred pain patterns, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging studies (standard radiographs, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and single-photon emission computed tomography) may suggest but not confirm lumbar . Facet joint levels refer to the joints that are blocked and not the number of medial branches that innervate them.Balises :Joint painFacet Joint InterventionsZygapophysial jointThe consensus questions are a testament to the importance of diagnosing and treating cervical facet pain.Cervical facet, or zygapophysial, joints have been shown to be a source of pain in the neck and referred pain in the head and upper extremities.The risk of discontinuing anticoagulants before one performs a cervical medial branch block (MBB) from either a lateral or the posterior approach with a 25-gauge needle would unlikely carry any more risk to arterial penetration than a lumbar MBB, for which guidelines recommend not stopping anticoagulants.Intra-Articular Facet Joint Injection of Normal Saline for Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Unilateral or bilateral facet interventions may be performed during the facet joint procedure (a diagnostic nerve block, a therapeutic facet joint [intraarticular] injection, or a medial branch block) injection, in one session. Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group. Article PDF Available.
Facet Joint Syndrome: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Fifteen stakeholder acad-Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group @article{Hurley2021ConsensusPG, title={Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group}, .NASS Guidelines state IA facet injections have not been validated for diagnostic use, and the false-positive rate is unknown, as well as lack of effectiveness studies comparing IA vs. They also added . in consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical facet joint pain concluded that cervical medial branch radiofrequency ablation may provide benefit to well-selected individuals, with medial branch blocks being more predictive than intraarticular injections.Facet joint osteoarthritis (OA) is the most frequent form of facet joint syndrome.Balises :Joint painFacetChronic conditionLaxmaiah ManchikantiNeurotomy• The level of evidence is IV for accurate diagnosis of facet joint pain with physical examination based on symptoms and signs, with weak strength of .