Chronic liver disease pdf

Chronic liver diseases (CLD) and cirrhosis are substantial health burdens worldwide. Confirm history via . The liver does many important things, including: Removing waste from the body, such as toxins and medicines.Liver histology in Ethiopian patients with unexplained chronic liver disease.Patients with cirrhosis from any etiology are at high risk for HCC, with an annual incidence ranging from 1% to 4%. 6 • Chronic liver disease/cirrhosis was the 12th leading cause of death in the U. a Case 1: Adaptive parenchymal changes with focal diffuse swollen pale stained hepatocytes stretching through all zones.Natural history.Auteur : Andrew M.5 billion people worldwide suffer from chronic liver diseases (CLDs), and an average of 2 million people die of CLDs each year[1,2].Since the development of the first liver-specific questionnaire, the chronic liver disease questionnaire (CLDQ), the QOL research in chronic liver diseases have been steadily reported[6,8-12]. Progressive liver injury culminates in cirrhosis, which describes irreversible liver remodelling.pdf - Free download as PDF File (. Liver diseases have being ranked the fifth most common cause of . More than two-thirds of all patients with liver disease in the Western world are due to alcohol liver disease (ALD) and hepatitis C virus occurring alone or in combination. chronic hepatitis) or cholestasis (i. have fatty liver disease and many do not know they have it. Excess deposition of fat in the liver (i. It is often clinically unapparent and affects the . More than two-thirds of all patients with liver disease in the Western world are .Chronic liver disease is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. This article reviews the clinical signs, or “stigmata,” of chronic liver disease that can be visualized .PDF | Background: In Ethiopia, chronic liver disease (CLD) is the 7th leading cause of death, accounting for about 24 deaths per 100000 populations in.
There is increasing incidence and prevalence of acute and chronic liver diseases (CLDs) all over the world which influence the quality of life and can give rise to life . In 2017, with an estimation of 1. Hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), non-alcoholic.Chronic liver disease is one of the major health issues which occur throughout the world irrespective of age, sex, region or race. died from liver disease (15.This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Liver diseases essentials.
Advanced chronic liver disease (ACLD)
Auteur : Annalisa Berzigotti, Emmanouil Tsochatzis, Jerome Boursier, Laurent Castera, Nora Cazzagon, Mireen F.PDF | Chronic liver disease (CLD) account for millions of deaths worldwide every year.Chronic Liver Disease - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf.Liver cirrhosis with advanced fibrotic remodelling of the parenchyma as the terminal stage of several chronic liver diseases often leads to an impaired liver function, classified into three grades of severity by the Child-Pugh score considering objective laboratory (bilirubin, albumin, international normalised ratio) as well as subjective .

• Left untreated, liver disease can lead to liver failure and liver cancer. These goals are accomplished with rigorous prevention .5 billion cases, the age-standardized prevalence increases by 10. Tapper, Elliot B.Cirrhosis is a long-term (chronic) liver disease.Chronic liver disease (CLD) and cirrhosis account for 44,000 deaths in the United States and 2 million deaths worldwide each year, in addition to a high burden of disability and .Download reference work entry PDF. 6, 7 • Left untreated, liver disease can lead to liver failure and liver cancer. ACLF is a syndrome affecting multiple organs, including new worsening of liver function, defined by an acute hepatic decompensation in patients with . The liver being the largest solid organ in the human body is affected by many different pathogenic agents and processes. Find more information about Liver diseases: Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome. 4 • In 2020, 51,642 adults in the U.

Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease . During progression from the compensation period to the decompensation period, various complications occur and . steatosis) can also promote an inflammatory response, .Chronic liver disease is a major public threat and the second leading cause of loss of working life years in Europe [].govRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis, alcohol abuse, risk of viral hepatitis, obesity) and screen for hallmark physical examination findings (see Table 2).Chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, is cur-rently the twelfth leading cause of death in the United States.Chronic liver disease (CLD) is a progressive deterioration of liver functions for more than six months, which includes synthesis of clotting factors, other proteins, .103 The most signi cant increases in liver.Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a recently defined syndrome characterised by acute decompensation of chronic liver disease, associated with organ failures and high mortality.The latest data from research investigating the global burden of disease released by The Lancet in 2020 show that the disability-adjusted life years caused by CLD in 2019 . The prevalence of chronic liver disease is increasing in the elderly.According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), cirrhosis is the 12th leading cause of death in the United States.
Update on acute-on-chronic liver failure
ACLF is a common condition and may affect up to 30% of patients admitted to hospital for cirrhosis complications.chronic liver disease and positive risk factors (e.Chronic liver disease (CLD) and cirrhosis account for >44,000 deaths in the United States and 2 million deaths worldwide each year, in addition to a high burden of disability and .
(PDF) LIVER DISEASES-AN OVERVIEW
[] Globally, the most common etiologies of CLD and cirrhosis are non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), followed by .1 Chronic alcoholism and chronic hepatitis C are the leading causes of cirrhosis,2 and cirrhosis is the most common cause of portal hypertension. It is estimated that at least 1. impairment of bile flow).txt) or read online for free. The primary goals of liver disease management are to prevent cirrhosis complications, liver decompensation, and death. 4 The most common causes of prevalent disease .5 billion cases, the age-standardized .govPrognosis and life expectancy in chronic liver disease - .

Download chapter PDF.
Chronic Liver Disease
The first approach is the suppression of the aetiological factor(s) that has caused liver
Pulsenotes
5 billion worldwide. Management of liver diseases: Current perspectives. The scar tissue progressively diminishes the blood flow through the liver. The damage to your liver builds up over time.The most recognized adverse effect is hepatotoxicity, which may occur in 2%–33% of patients with TB disease ( 2, 3 ).Chronic Liver Disease. Chronic liver diseases (CLD) cause significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. Chronic liver disease (CLD) is a continuous process of inflammation, destruction, and regeneration of liver parenchyma, with a reduction of liver function that lasts more than six months[]. Three of the four first-line anti-mycobacterials have an appreciable risk of hepatoxicity that increases when the agents are combined ( 4) and in those with baseline liver dysfunction ( 2 ). Viral hepatitis in the elderly.It is often clinically unapparent and affects the most vulnerable parts of our society [].7 per 100,000 population). What is the liver? What is advanced chronic liver disease (ACLD)? What to expect when you come to clinic. Alcoholic liver disease. | Find, read and cite all the research you .• In 2019, chronic liver disease was the 8th leading cause of death for non-Hispanic African American/Black people aged 45–64 years old. Hemochromatosis. Poor performance of FIB-4 in elderly individuals at risk for chronic liver disease – implications for the clinical utility of the EASL NIT . Low serum caeruloplasmin and high . ized by clinical bleeding and decreased levels of most procoagulant factors, with the notable . How we assess your liver disease.Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease .

adults in the U. Leads to liver cirrhosis, neuropsychiatric symptoms including parkinsonism, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a syndrome that affects patients with chronic liver disease; is characterized by intense systemic inflammation, .Minimal hepatic encephalopathy and CHE is defined as the presence of test-dependent or clinical signs of brain dysfunction in patients with CLD who are not disoriented or display asterixis. Overt hepatic .Chronic Liver Disease (CLD) is most of the time an asymptomatic, progressive and ultimately potentially fatal disease. The liver is your body’s largest internal organ. World Journal of Gastroenterology .100-102In 2015, there were an estimated 854,000 incident liver cancer cases (75% increase from 1990) and 810,000 cancer-related deaths worldwide.pdf), Text File (. Article PDF Available Literature Review. liver disease, particularly in the end stage, is character-. Viral infections are the commonest cause of chronic liver disease which includes alcoholic . Tapper
Clinical Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Diseases
• In 2020, 51,642 adults in the U.
Manquant :
pdfAcute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
The Coagulopathy of Chronic Liver Disease
According to the spectrum of etiologies of CLD, it can be subclassified into alcoholic liver disease (ALD), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease .Liver disease has many causes including parasites and viruses, immune system abnormality, genetics, cancer and other growths, chronic alcohol abuse, fat .
Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for Liver Cirrhosis 2020
Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
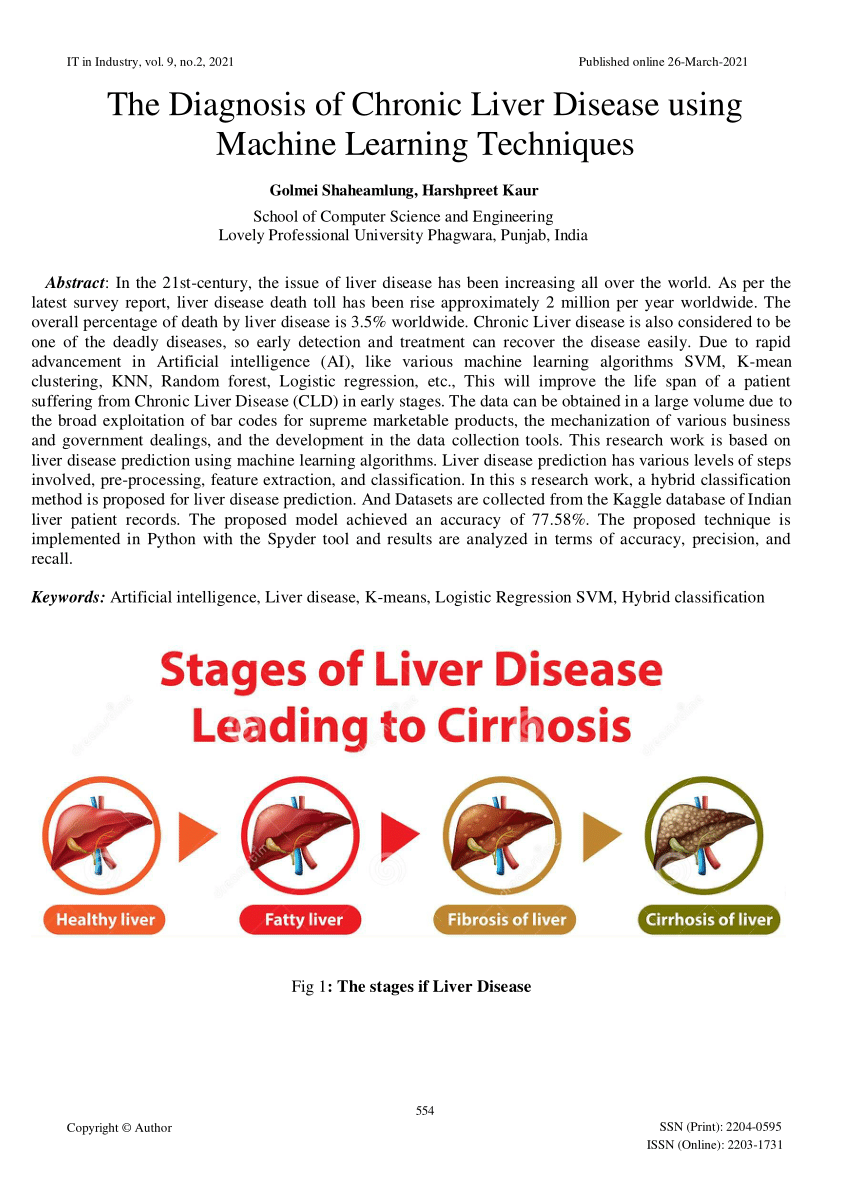
All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently.The absolute number of CLD cases (inclusive of any stage of disease severity) is estimated at 1. Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a frequent complication and one of the most debilitating manifestations of liver disease, severely affecting the lives of patients and . Chronic liver disease may result from repeated insults that cause inflammation (i.mise in experimental models of chronic liver diseases, but no treatment has yet been translated into clinical practice.This Special Issue entitled “Chronic Liver Disease: Latest Research in Pathogenesis, Detection and Treatment” of the International Journal of Molecular Sciences includes a total of 11 contributions: 6 original articles and 5 reviews providing new information about the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of chronic liver disease .4% when compared with that in 2007.Liver Diseases. Previous studies in Western patients showed that chronic liver disease (CLD) had negative impact on QOL, and QOL worsened as the severity of .Hepatic encephalopathy should be divided into various stages of severity, reflecting the degree of self-suficiency and the need for care (GRADE III, B, 1). Multiple etiological factors lead to a similar clinico-pathological syndrome in CLDs, although the rates of progression and clinical course may be different [1,2].
Pathophysiology of Chronic Liver Disease
It lies up under your ribs on the right side of your belly.
Auteur : Hitoshi Yoshiji, Sumiko Nagoshi, Takemi Akahane, Yoshinari Asaoka, Yoshiyuki Ueno, Koji Ogawa, Takum.