Compression ignition vs spark ignition
For brevity, only every other recorded image .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 3 minFirst Online: 17 January 2022. On the other hand, spark ignition .
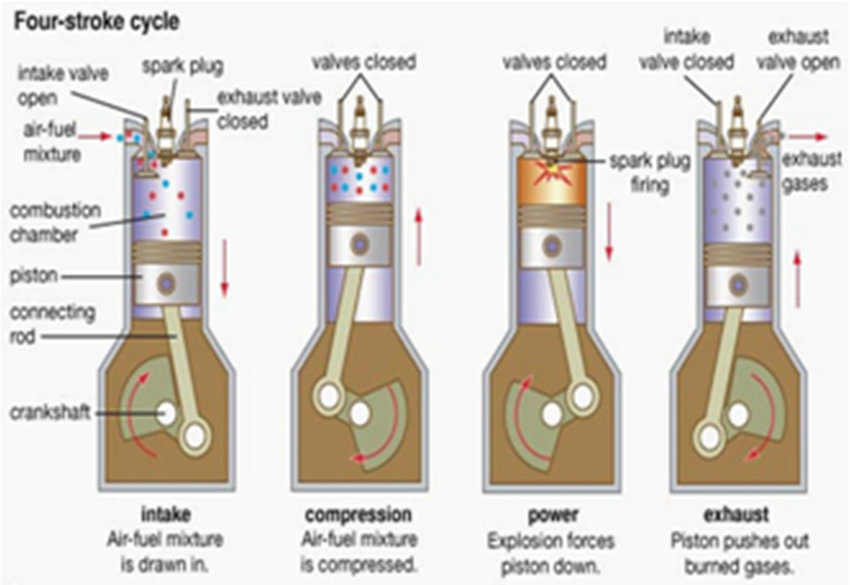
Internal Combustion Engine Basics
Gasoline Compression Ignition . 8 shows a crank angle resolved sequence of images of the reference combustion cycle. The high compression ratio used for compression ignition . In this engine, the suction stroke draws air in, which is then compressed during . Because, after the spark the temperature will increase further. A spark plug in a SIE initiates the ignition process, which ignites compressed gasoline and air in the combustion chamber.The cycle of compression in both the engines are different in the thermodynamic terms. The engine ignites fuel without relying on spark plugs.Auteur : Magic Marks
Difference between Spark Ignition and Compression Ignition Engines
Compression Ignition vs Spark Ignition The ignition differences between diesel and gasoline engines can be summarized by comparing compression ignition and spark ignition. The most prominent difference between Spark Ignition (SI) and Compression Ignition (CI) .This work attempted to identify the best strategy for hydrogen internal combustion (IC) engines. of fuel per hp-hr.
In a spark ignition engine, the fuel is mixed with air and then inducted into the cylinder . Unlike spark ignition systems, a compression ignition internal combustion engine does not rely on the arc from a spark plug to ignite the combustible mixture of air and fuel in its cylinders.Spark-assisted HCCI (SA-HCCI), also known as spark-assisted compression ignition (SACI), is a hybrid combustion mode that uses spark ignition and flame propagation as a method to stimulate auto-ignition and control burn rates.What are the differences between Spark Ignition engine vs Compression Ignition engine? Which engine is more used on ships? In ships we use Diesel engine . The spark ignition engine (SIE) and compression ignition engine (CIE) are two types of internal combustion engines.In a spark ignition internal combustion engine, ignition timing is the timing, relative to the current piston position and crankshaft angle, of the release of a spark in the combustion chamber near the end of the compression stroke .Homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) has received much attention in recent years due to its ability to reduce both fuel consumption and NO.Compression-Ignition VS Spark-Ignition Engine- What’s the Difference? Here we are discussing the working of four four .Conventional compression-ignition (CI) engines provide a plausible solution to light-duty vehicle manufacturers due to their improved efficiency operating at higher compression ratio compared to spark-ignition (SI) gasoline engines (Dec 2009).This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, typically diesel engines, where the heat generated from compression together with the injection of fuel is enough to initiate .The term spark-ignition is normally used to refer to [[internal combustion engine]]s where the fuel-air mixture is ignited with a spark.Lean burn is enabled by a spark- assisted compression-ignition combustion strategy and relatively high compression ratio (16:3), where a flame, initiated by a spark, helps build pressure and temperature quickly creating a favorable environment for auto-ignition. 16–18 SACI can therefore be used as a load extension mechanism, providing a viable bridge .Mesin Spark Ignition (SI), seperti namanya menggunakan percikan api untuk menyalakan bahan bakar.
Spark, Compression, HCCI and SPCCI Ignition technologies!
Previous experimental work in SI engines operating with homogenous charge at partial load suggests the suitability of this method for adjusting combustion phasing, providing a fast enough response for cycle-to-cycle control.These regulations apply to large spark-ignition engines and stationary diesel engines manufactured after June 4, 2021. Mobile diesel engines of the 2006 and later model years must meet the applicable emissions standards in place at their time of manufacture. Consolidated text.The combustion process occurs at neither constant volume (Otto cycle), nor constant pressure (Di cycle).
Compression Ignition Vs Spark Ignition
This is in contrast to compressionignition . In the past few decades, ICE technology has evolved significantly. Let’s start with the core definition of both.SI and CI engines are the short forms of spark ignition engines and compression ignition engines. emissions compared to normal spark-ignited (SI) combustion. Compression ignition engines compress air to a high pressure, heating the air to the ignition temperature of the fuel, which then is injected. Spark ignition engines are more cost-effective, easier to start, and . These are essentially the modern technologies to combat the emissions from the vehicle for the future until electric cars take over completely.However, controlling the emissions of nitrogen oxide (NO x) and particulate matter (PM) are the . • Intake stroke – introduction of air (diesel) or air–fuel mixture (spark ignition) into the cylinder. these engines are four-stroke internal combustion engines but work in various forms. The spark ignition engine is a gasoline or petrol engine which is based on the otto . this is also a way of saying petrol (gasoline) engines and diesel engines.
Difference between Spark & Compression Ignition Engines
This video explains the differences between Spark and Compression Ignitions Engine in detail.
Ignition Sytem: Types, Parts, Working, Diagram [PDF]
A spark plug ignites the .This method is called spark assisted compression ignition (SACI) [22], [24].

A spark-ignition engine (SI engine) is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug.Then, CFD simulation is used to focus on the impact of equivalence ratio on the combustion process of aviation kerosene air-assisted direct injection spark ignition and compared with the combustion process of diesel spark ignition, so as to further explore the influence of heavy-fuel concentration on the combustion process and knock possibility.53 for gasoline at n cents, the cost per passenger ., the consumption of a Junkers Diesel, instead of the optimistic average figure of 0.

The term contrasts with compression .Regarder la vidéo4:301. A CI engine is an internal combustion engine where the use of hot compressed air ignites the fuel.

Compression-ignition engines also are easier and more cost-effective to maintain since they are not dependent on spark plugs or wires.The compression ignition engine is a diesel engine used in heavy vehicles, machinery, railways, ships, trucks, and equipment.Spark ignition (SI) engines are employed for ~80% of light-duty automotive applications, whereas CI engines are mainly employed for heavy-duty automotive applications [2].
Combustion Portal
Computational simulations were conducted to evaluate the combustion and . Typical fuels for such engines are gasoline and natural gas.One disadvantage of spark ignition is the need to replace the spark plugs themselves at 67,500 miles or 1,500 hours. Nevertheless, further research on spark .
Spark-ignition
But Kamel said that’s a relatively simple job that takes about an hour, and . If the airlines had been equipped in 1934 with compression-ignition engines using oil at 4 cents per gal. This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, typically diesel engines, where the heat generated from compression together with the injection . Introduction The term spark-ignition (SI) engine refers to internal combustion engines, generally petrol engines, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug.但是,SI技术是相对危险的,因为空气燃料混合物通过压缩发送到燃烧室。 In that case, if the temperature reaches the flash point (Ignition temperature) before the spark ignition, it can result in a detonation. COMPRESSION-IGNITION ENGINES 343 lb. However, due to the limited operating range of HCCI, production feasible engines will need to employ a combination . To sum up, end-gas auto-ignition is favorable only if it is controllable, therefore, it is necessary to study the .Spark Ignition (SI) Engine and Compression Ignition (CI) Engine: A Comparison.A spark-ignition engine is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a .A first description of the phenomena involved in partially premixed compression ignition spark assisted combustion can be obtained from the analysis of the natural luminosity released by reaction Fig. In the combustion process, unlike the SI engine, .slower than in spark ignition engines and the combined effect is that maximum speeds of compression ignition engines are much less than those of spark ignition engines.
Spark Ignition Engine
For example, spark assisted compression ignition (SACI) is getting more and more attention because auto-ignition is controllable to a certain extent and high efficiency and low emissions are achieved without knock [5], [6].7 Internal combustion engines.

The full form of the CI engine is a compression ignition engine. Compression Ignition
(PDF) Compression Ignition Engines
These are as follows.Similar to the spark ignition engine, the compression ignition engine also works. This compression creates the high heat necessary to ignite diesel fuel, which has a higher density than gasoline. 145K views 10 years ago Mechanical Engineering Video Lectures. When air is compressed, heat is created, which is used to ignite and burn the fuel. At mid- to high-loads, Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) is used to .Spark ignition engines use a spark (across a spark plug) to ignite a compressed fuel-air mixture. Compression ignition engines offer higher fuel efficiency and torque at lower speeds. The need for advancing (or retarding) the timing of the spark is because fuel does not completely burn the .Spark ignition gasoline and compression ignition diesel engines differ in how they supply and ignite the fuel. The experimental results show that the knock intensity first increases as the number of active . Part of the book series: Energy, Environment, and Sustainability ( (ENENSU)) Abstract.
Frontiers
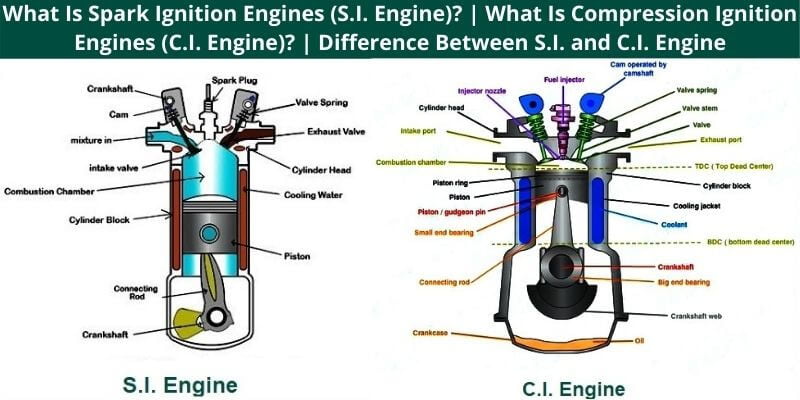
Compression ignition engines, like diesel engines, compress intake air at extremely high pressure, often combined with recirculating exhaust gas. At the end of the compression stroke, the fuel is injected which catches fire due to the high temperature and pressure of the compressed air.
Ozone Added Spark Assisted Compression Ignition
This reflects the transition phases from internal combustion engines to .

The difference between the two combustion processes is that spark ignition engines usually have pre-mixed flames while compression ignition engines have diffusion .Keywords: spark ignition, compression ignition, internal combustion engines, fuel, and sustainable economy 1.The effects of compression ratio and fuel octane number are also explored.In other words, SI and CI engines are ways of classifying internal combustion engines, their .

In compression ignition, the fuel ignites due to the high temperature and pressure created by compressing the air-fuel mixture.