Cooling history of igneous rocks
ISBN 9780674644816.As the rate of cooling increases, crystal size decreases.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Refer to Figure 3.The focus of this chapter will be on igneous rocks, which are the only rocks that form from what was once a molten or liquid state. Determine the cooling history of the .Development of alkali feldspars in igneous rocks can be considered in three stages; magmatic, involving crystal growth from the melt; subsolidus or postmagmatic, involving coherent exsolution and development of regular, strain controlled crypto or . However, if the magma starts to cool faster, only small crystals can form. Texture describes the physical characteristics of the minerals, such as grain size. This rigorous and up-to-date synthesis of current research and thought in igneous petrology explores the .Two different crystal sizes within an igneous rock indicate that the cooling rate of the magma increased. These may be defined as rocks of zero grain size. They have a mineral composition that is intermediate between granite and basalt.The texture of an igneous rock is determined by the cooling history of the magma from which it formed.This temperature gradient helps geologists understand the cooling history of a particular igneous rock.netFeldspars in Igneous Rocks | SpringerLinklink. This page titled 8. Students will be able to directly link how the environment on .Igneous rocks are “fire-born,” meaning that they are formed from the cooling and solidification of molten (melted) rock.The minerals that make up igneous rocks crystallize at a range of different temperatures. Phaneritic texture describes coarse grained rocks. A phaneritic rock can also be referred to as a porphyritic-phaneritic rock if the phaneritic rock contains .
Formation, composition, and classification of igneous rock
comIgneous Rocks - Definition, Characteristics, Types, .
Cooling Processes in Magmatic Systems
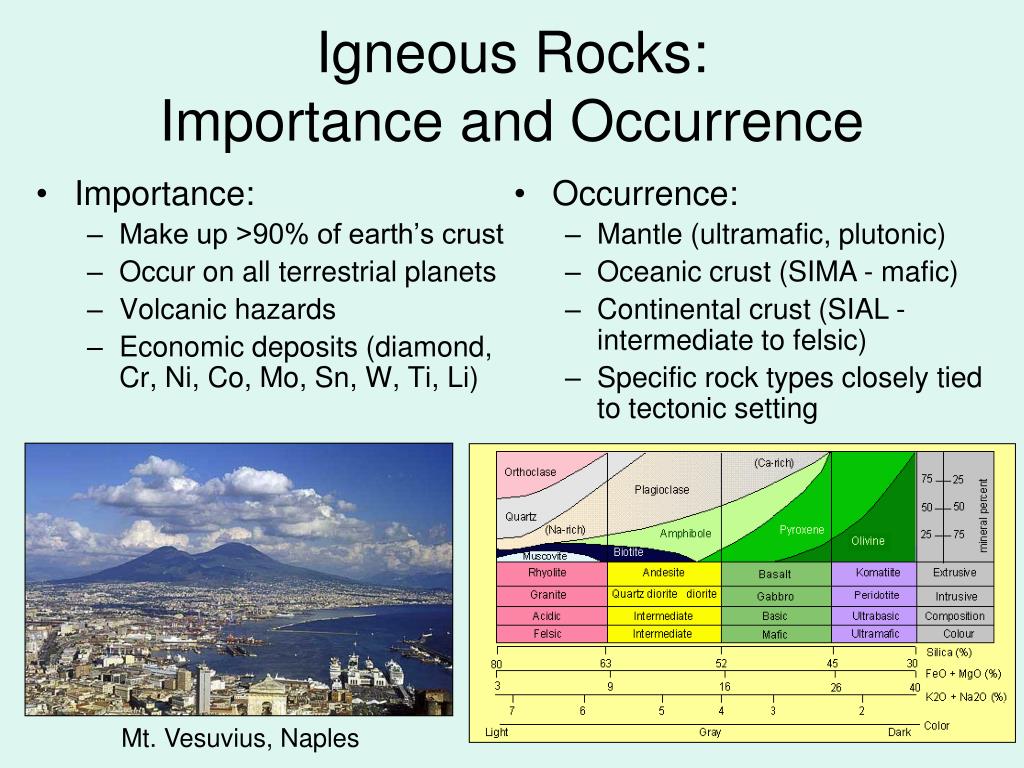
Ultramafic: igneous rocks composed chiefly of . The word igneous derives from ignis, the Latin word for “fire.
Chapter 4
Larger scale features, such as fractures and layering, are considered rock structures in comparison. What does the texture of an igneous rock tell you about its cooling history? Phanertic = Large crystals = slow cooling. Intermediate: igneous rocks rich in minerals such as Na-Ca plagioclase and hornblende.Overview
Igneous Rocks
Andesite: Igneous Rock
The focus of this chapter will be on igneous rocks, which are the only . Composition refers to the rock’s specific mineralogy and chemical composition . Mafic: igneous rocks rich in dark-colored ferromagnesian minerals (augite, hornblende) but with abundant plagioclase feldspar. These rocks, with large crystals (known as .Igneous rocks in which all the minerals are present in practically uncrystallised form or glass due to very rapid cooling are grouped as glasses.Modified date: 08/11/2023.4: Igneous Processes and Volcanoes - Geosciences . How does the rock cycle diagram—in particular, the labeled arrows—support the fact that sedimentary rocks are the most abundant rock type on Earth's surface?, Apply your understanding of igneous rock textures to describe the cooling history of each of the . This rock classification is based on the origin of each of these rock types, or if you prefer, based on the rock-forming process that formed the rock.
The focus of this chapter will be on igneous rocks, which are the only rocks that form from what was once a molten or liquid state.Types of Rocks.Diorite is an intrusive igneous rock of intermediate composition. Porphyritic = Mixed cooling history, slow then fast.The rock cycle is the natural, continuous process that forms, breaks down, and reforms rock through geological, chemical, and physical processes.eduRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Igneous rock
Granite is a classic coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock.Dynamic history.Texture and composition.1 at end of Chapter 3 provides a glossary of common igneous rock texturesStudents will investigate how temperature affects crystallization, and apply their conclusions to igneous rock formation.

It has a durability that compares favorably to granite and trap rock. The different colors are .How Are Igneous Rocks Formed? - WorldAtlasworldatlas.Chapter 3: Igneous Textures The texture of a rock is a result of various processes that controlled the rock’s genesis and, along with mineralogy and chemical composition, provides information that we may use to interpret the rock’s origin and history Table 3. Result of this formed, glass occupies more than 80 % and that have seeming conchoidal fracture and vitreous luster. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. These rocks, with large crystals (known as phenocrysts) suspended in a matrix of fine crystals (known as groundmass), often have a cooling history similar to the following description: The parent magma of the rock .1: Classification of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks are classified based on texture and composition.A type of igneous rock that forms inside the Earth. Composition Changes: As a magma cools and minerals .
FELDSPARS AND THE THERMAL HISTORY OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
Each igneous rock has a name that distinguishes it from other igneous rocks.Igneous rock formed by rapid cooling of lava, such that crystal lattices are unable to form; rock with the structure of a supercooled liquid.
8: Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the Earth or while the melted rock is still inside the . Identify, when possible, the minerals present in an igneous rock. Silica (SiO2) content also controls the minerals that crystallise and is used to further classify igneous rocks as follows: Acid: rocks with above 63% silica (mostly feldspar minerals and quartz), e. This is easily seen in igneous rock, which may cool at variable rates.

Once you know the texture of an igneous rock, you .netA Test of the Feldspar Method for the Determination of the . The three types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks: Igneous Rocks. They can also look different based on their cooling conditions.org(PDF) Igneous Rocks and Processes - Academia. Magmas that cool slowly form large crystals, and those that cool quickly form small crystals. It usually colours dark, black, grey-black to grey.Therefore, igneous rocks are defined as those rock types that form by the cooling of magma or lava. This classification is based on the origin of each of the rock types. It is a dynamic system that recycles Earth’s materials in different forms, from molten magma deep below . mafic A type of igneous rock composition that is made mostly of dense, dark minerals like olivine and pyroxene.The references to mineral color are necessary, as the color of any mineral is primarily due to the chemical elements that are in the minerals, and therefore the color of igneous rocks will be dependent on the mineral content (or chemical composition) of the rock. For the rock to be called . Publication date: 05/04/1989.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/about-igneous-rocks-1438950_final_CORRECTED2FINAL-f8d738e151b9437caa256d21155d091f.png)
The mineral composition is a central concept in Bowen’s Reaction Series, as it helps us understand how and why different minerals form in igneous rocks as they cool from molten magma. The Role of Mineral Composition.

Igneous rocks comprise . Molten rock material is known as magma until it is erupted onto the surface when it then is termed lava.Igneous rocks form through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.Combined with the thermal history modelling results, these AFT ages and the elevations of samples revealed two rapid cooling episodes at ~10 Ma and ~4 Ma, . This means that something which cools very quickly will have smaller crystal formations, and something which cools slowly will have larger crystal formations.
Chapter 3: Igneous Textures
5: Igneous Processes and Volcanoes
The team returned to MIT with whole rock samples of banded iron formations — a rock type that appears as stripes of iron-rich and silica-rich .
Igneous Rock Textures
× Close definition The sizes, shapes, and .comLecture Notes - Feldspars - Clark Science Centerscience. Intrusive igneous rock samples: granite, rhyolite, gabbro, basalt Igneous rocks form below Earth’s surface where pockets of magma get trapped.
Obsidian Rock : Properties, Formation, Occurrene and Uses Area
Glasses are sometimes referred as supercooled liquids.Igneous rocks are classified based on texture and composition. We have an expert-written solution to this problem! List the two criteria by which . Aphanitic = Small crystals = fast cooling. They fall into two main categories: Intrusive rocks are those which are caused by .What does a porphyritic texture indicate about the cooling history of an igneous rock? the magma sat and cooled a bit below the Earth's surface, thus giving time for the large crystals to grow, before erupting onto the surface and cooling very quickly. This explains why a cooling magma can have some crystals within it and yet remain .All rocks found on the Earth are classified into one of three groups: igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. Vesicular = holes = gases escaped when magma solidified.Igneous rocks can have many different compositions, depending on the magma they cool from.Feldspars: Life-Sustaining Minerals on the Earth - .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
4 Igneous Processes and Volcanoes
Erin Johnson (Atlas Obscura User) This seven-story giant boulder has attracted UFO conferences, Hopi spiritualists, and the . Each igneous rock has a name that distinguishes it from other igneous rocks; so, these igneous rocks .The cooling history at depth of magmatic systems lead to processes governing the rheological changes of igneous rocks that are actively debated in modern geology. Igneous rocks form from the cooling and .Some igneous rocks have a complex cooling history that results in them containing grains of distinctly different crystal sizes. The material of the rock had no time to differentiate into individual grains or crystals.
Origins of Igneous Rocks — Harvard University Press
For example, two rocks from identical magma can become either rhyolite or granite, depending on whether they cool quickly or slowly. The two main categories of igneous rocks are .Andesite is the name of a family of fine-grained, extrusive igneous rocks that are usually light to dark gray in color.eduRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • AvisStudy with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is the difference between extrusive igneous rocks and intrusive igneous rocks?, What does a porphyritic texture indicate about the cooling history of an igneous rock?, What is Bowen's reaction series? and more. Igneous rocks are formed .Felsic: igneous rocks rich in light-colored minerals such as orthoclase and quartz. Each kind of texture has a variety of different characteristics that make them unique.Igneous rocks that are noncrystalline can also be glassy.An igneous rock with large crystals embedded in a matrix of much finer crystals is indicative of a two-stage cooling process, and the texture is porphyritic (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)).
Geology Chapter 4 Flashcards
Therefore, igneous rocks are defined as those rock types that form by the cooling of magma or lava. What does the porphyritic texture tell you about the cooling history of the magma? Silica content.Igneous rock (igneous from Latin igneus 'fiery'), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Andesite is a rock typically found in volcanoes above convergent plate boundaries between continental and oceanic plates.2: Igneous Rock Origin is shared under a CC BY-SA license and . This relates to the cooling .Igneous rocks are rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten rock.