Copper chloride wikipedia

En synthèse organique.Tin(II) chloride should not be confused with the . On standing [clarification needed], vinyl chloride can form peroxides, which may then explode. Anhydrous magnesium chloride is the . Copper (I) chloride, also called cuprous chloride, is an inorganic chemical compound, with the chemical formula CuCl. Its chemical formula is CuCl 2.
It is a white, almost insoluble salt which is slowly oxidized by air to Cu (II).Alexey Ekimov or Aleksey Yekimov [1] ( Russian: Алексей Екимов; born 1945) is a Russian [2] solid state physicist and a pioneer in nanomaterials research.

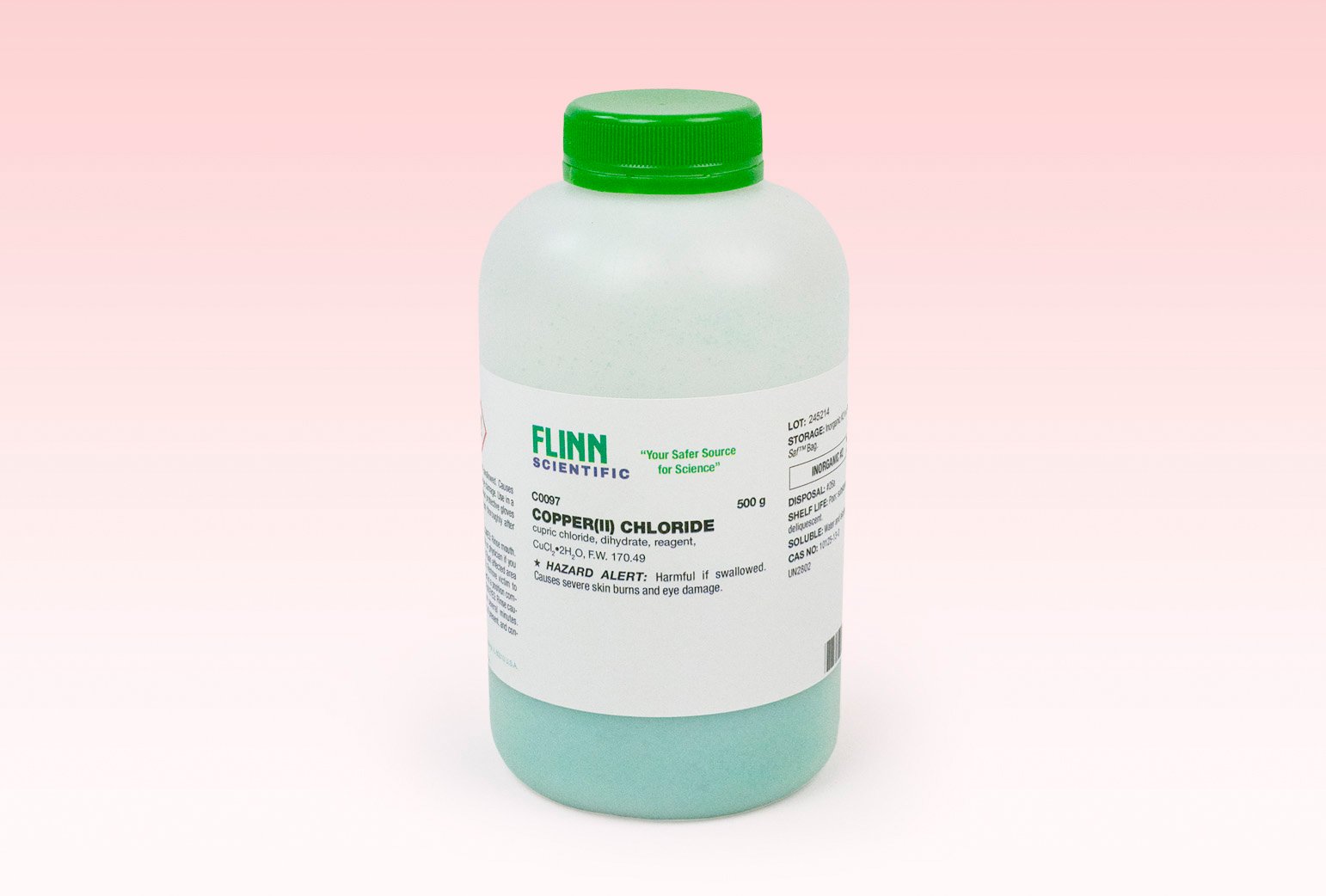
Copper–chlorine cycle.Copper (II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuCl 2. Cupric chloride.JPG 1,536 × 2,048; 1. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and . HgCl 2 + 2 Cu → 2 CuCl + Hg.
Category:Copper(I) chloride
Vinyl chloride
Copper (I) chloride.Copper (II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu Cl 2. Binary compounds. This spectral perspective was first noted in . It has two forms, the monohydrate (AuCl 3 ·H 2 O) and the anhydrous form, which are both hygroscopic and . It reacts with sodium hydroxide to make copper(II) hydroxide .Aluminium chloride is manufactured on a large scale by the exothermic reaction of aluminium metal with chlorine or hydrogen chloride at temperatures between 650 and 750 °C (1,202 and 1,382 °F). The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt-like taste. 97,898 g / mol. As with other elements, the simplest compounds of copper are binary compounds, i.Gold(III) chloride, traditionally called auric chloride, is an inorganic compound of gold and chlorine with the molecular formula Au 2 Cl 6. The substances are listed in alphabetical order. He discovered the semiconductor nanocrystals known as quantum dots in 1981, while working at the Vavilov State Optical Institute.Copper(II) chloride: Wikipedia CUL: PDBeChem DB09131: DrugBank View more database links: Registry Numbers Types Sources 7447-39-4: CAS Registry Number NIST Chemistry WebBook 7447-39-4: CAS Registry Number ChemIDplus 8128168 . Copper (II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu Cl 2.0042: Copper(I) sulfide: Cu 2 . The Cu–Cl cycle is a hybrid process that employs both thermochemical and electrolysis steps. It contains copper in its +2 oxidation state.Tin(II) chloride, also known as stannous chloride, is a white crystalline solid with the formula Sn Cl 2.They are available both in anhydrous and in hydrated forms which are both hygroscopic.It is a white crystalline solid and a molecular compound that is very toxic to humans.Copper Chloride. The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly . Đồng (I) chloride là hợp chất chloride của đồng hóa trị một, công thức hóa học là CuCl.Iron(III) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula Fe Cl 3 (H 2 O) x. Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). It has a maximum temperature requirement of about 530 degrees Celsius. It also contains two chloride ions. [9] Aluminium chloride may be formed via a single displacement reaction between copper (II) chloride and aluminium.Similarly copper(I) chloride can be produced as a white precipitate (reaction described below).Đồng (II) chloride là một hợp chất vô cơ với công thức hóa học CuCl2. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very .In the interest of protecting public health, especially in healthcare environments with their susceptible patient populations, an abundance of peer-reviewed antimicrobial efficacy studies have been conducted in the past ten years regarding .
Copper(I) chloride
Its melting point is 498 °C.
Cloruro de cobre(I)
It forms a stable dihydrate, but aqueous solutions tend to undergo hydrolysis, particularly if hot.Copper (I) chloride is a chloride of copper that occurs naturally as the rare mineral nantokite. Hợp chất này tồn tại dưới dạng một chất rắn màu trắng rất ít tan trong nước, nhưng tan nhiều trong dung dịch acid .602×10 −9: Copper(I) hydroxide: CuOH: 8.It releases chlorine and turns into copper(I) chloride when heated very hot.
Đồng(I) chloride
Phổ IR của đồng (I) chloride.

Sodium chloride / ˌ s oʊ d i ə m ˈ k l ɔːr aɪ d /, commonly known as edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chlorine ions. Provided this is separated from the solution and dried as quickly as possible, it .The color of chemicals is a physical property of chemicals that in most cases comes from the excitation of electrons due to an absorption of energy performed by the chemical.It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The copper – chlorine cycle (Cu–Cl cycle) is a four-step thermochemical cycle for the production of hydrogen.Magnesium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Mg Cl 2.Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major .
Copper compounds
As a gas mixed with air, vinyl chloride is a fire and explosion hazard.
Tin(II) chloride
those containing only two elements, the principal examples being oxides, sulfides, and halides. Copper (I) chloride. Copper(I) chloride was first prepared by Robert Boyle in the mid-seventeenth century from mercury(II) chloride (Venetian sublimate) and copper metal: [7]. Units of solubility are given in grams per 100 millilitres of water (g/100 mL), unless shown otherwise. Copper (II) chloride. Copper(I) Chloride Precipitate. Copper (I) chloride is a chloride of copper that occurs naturally as the rare mineral nantokite.Le chlorure de cuivre (I), communément appelé chlorure cuivreux est le plus bas chlorure du cuivre avec la formule CuCl. These salts are colorless or white solids that are highly soluble in water. These compounds and their solutions, both of which occur in nature, have a variety of practical uses.png 754 × 546; 100 KB. The table below provides information on the variation of solubility of different substances (mostly inorganic compounds) in water with temperature, at one atmosphere pressure.SnCl 2 is widely used as a reducing agent (in acid solution), and in electrolytic baths for tin-plating. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and food preservative.Copper(I) chloride: CuCl: 0.jpg 1,146 × 1,065; 182 KB.

Chlorure de cuivre (I) Pour les articles homonymes, voir Chlorure de cuivre . This colorless, sharp-smelling liquid, the diacyl chloride of oxalic acid, is a useful reagent in organic synthesis. Name Chemical Formula Anion Image .
Antimicrobial properties of copper
The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green dihydrate CuCl2·2H2O, with two water molecules of hydration. The color changes to the more familiar orange when it reacts with air. strong oxidisers and metals such as copper and aluminium, with fire or explosion hazard.Media in category Copper(I) chloride The following 20 files are in this category, out of 20 total.Mercury(II) chloride (or mercury bichloride [citation needed], mercury dichloride), historically also known as sulema or corrosive sublimate, is the inorganic chemical compound of mercury and chlorine with the formula HgCl 2, used as a laboratory reagent.Structure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for: Copper (II) chloride, 7447-39-4. copper chloride biocrystallization) ist ein anthroposophisches Verfahren zur Beurteilung und Qualitätsbegutachtung zu analysierender Substanzen, vor allem von Lebensmitteln. Copper(II) chloride reacts with .Appearance : yellow-brown solid (anhydrous), blue-green solid (dihydrate)
Copper(II) chloride
Name Chemical Formula Anion Image copper(I,II) sulfite dihydrate (Chevreul's salt) Cu 3 (SO 3) 2 ·2H 2 O Sulfite (Sulfurous acid) Copper(III) salts.Oxalyl chloride is an organic chemical compound with the formula Cl−C(=O)−C(=O)−Cl.
Lewis acid catalysis
Đồng (II) chloride là một trong những hợp chất đồng (II) phổ biến nhất, chỉ sau hợp chất . En chimie des polymères.The first Lewis acid-catalyzed Diels–Alder reaction.Die Kupferchloridkristallisation oder Biokristallisation, (engl.They feature iron in its +3 oxidation state. Copper(I) chloride'.The III in the name indicates that the gold has an oxidation state of +3, typical for many gold compounds. [3] [4] [5] In 2023, he was awarded the Nobel . In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. It is also used in organic and polymer chemistry. It forms hydrates MgCl 2 ·nH 2 O, where n can range from 1 to 12.Copper (I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl.055×10 −7: Copper(I) iodide: CuI: 0.Copper (I) chloride, also called cuprous chloride, is an inorganic chemical compound, with the chemical formula CuCl.Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine.copper ( II) chloride ( CHEBI:49553 ) has role EC 5.Copper (II) chloride is a brown powder that turns red when molten.
Color of chemicals
Potassium chloride can be obtained from ancient dried lake deposits.
Copper
[ editar datos en Wikidata] El cloruro de cobre (I) o cloruro cuproso es una combinación química de cobre +1 y cloro -1 de fórmula empírica CuCl. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical .Infobox references. He prepared CuCl by heating CuCl 2 at red heat in the absence of air, causing it to lose . It is also used in organic .
Oxalyl chloride
Recently processed copper is a pink color.Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin cuprum) and atomic number 29. What is seen by the eye is not the color absorbed, but the complementary color from the removal of the absorbed wavelengths. Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29.Copper alloy surfaces have intrinsic properties to destroy a wide range of microorganisms.
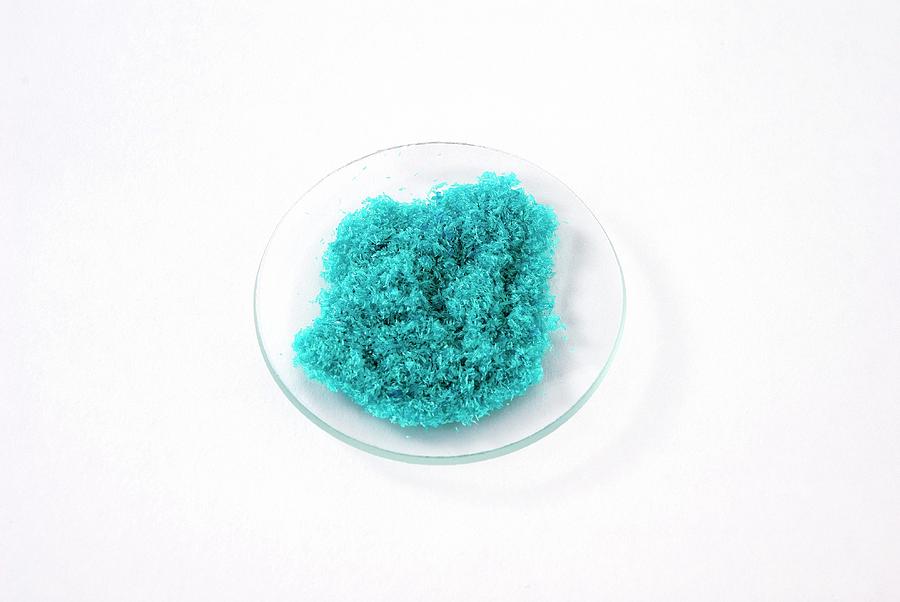

Tribasic copper chloride and certain organic forms of copper appear to be more bioavailable than copper sulfate when dietary molybdenum and sulfur are high.
Copper(II) chloride
5 (cholestenol Δ-isomerase) inhibitor ( CHEBI:86385 ) copper ( II) chloride ( CHEBI:49553 ) is a copper molecular .
Copper(II) chloride
Hydroxide and chloride: Copper(II) naproxen: C 28 H 26 CuO 6: naproxen: Copper(II) ibuprofenate: C 52 H 68 Cu 2 O 8: Ibuprofenate Copper(I, II) salts.