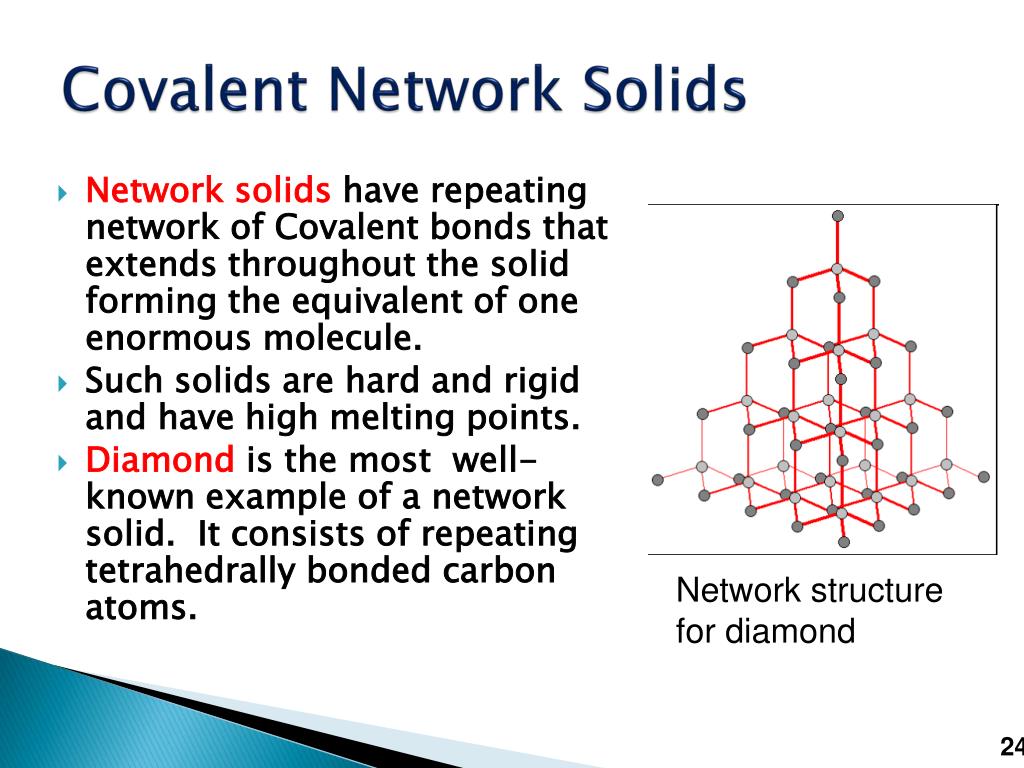
Covalent network solids

Because covalent bonds are relatively strong, covalent network solids are typically characterized by hardness, strength, and high melting points.
Keep going! Check out the next lesson and practice what you’re learning:https://www. Covalent molecular compounds typically have lower melting and boiling points due to weaker intermolecular forces, whereas covalent network compounds often have high melting and boiling points due to the strength of the covalent network. Many minerals have networks of covalent bonds. The Bonding in .Could somebody please answer this question with a list of the most common covalent network solids? I. (0) Covalent Network Solids: Properties & Examples.Covalent Network Solids, Salts, Polymers.The network of covalent bonds extends throughout the crystalline structure. A network covalent solid consists of atoms held together by a network of covalent bonds (pairs of electrons shared between atoms of similar . Covalent network solids are held together by covalent bonds in a large network. Covalent Network Solids, Salts, Polymers.Balises :Covalent Network SolidsNetwork Covalent PropertiesNetwork Covalent BondingA network solid does not have discrete molecules; the smallest amount of a network solid that can be identified as such is called a formula unit.Balises :Covalent BondsCovalent Network SolidsCovalent Network Compounds
Covalent network solids
The following sections provide descriptions of the major types of crystalline solids: ionic, metallic, covalent network, and molecular.Covalent Network Solids - Chemistry LibreTextschem. To break or to melt a covalent network solid, covalent bonds must be broken.Well whether the solid is a network solid or molecular solid, they use covalent bonding. Covalent network solids are formed from atoms connected by . Aside from diamond and quartz the more well-known one.To break or to melt a covalent network solid, covalent bonds must be broken. In this video Paul Andersen explains how covalent network solids form elementally (like graphite) or by combining multiple nonmetals (like quartz). Imagine building blocks connected together to .we know that strength of ionic bonds is greater Nand that of covalent bond but still it is observed .Well I wouldn't say that your premise is entirely correct; that ionic bonds are greater (assume you mean stronger) than covalent bonds. For example, diamond is one of the hardest substances known and melts above 3500 °C. The difference between an atomic network and a molecular network is the molecular network consists of extended molecular units.1: Interactions in Ionic and Covalent Solids. Distortion away from this geometry can only occur through a breaking of covalent sigma bonds. Covalent network solids include crystals of diamond, silicon, some other nonmetals, and some covalent compounds such as silicon dioxide (sand) and .Covalent-network (also called atomic) solids—Made up of atomarten connected by covalent bonds; the intermolecular forces is covalent shackles as well.How do I know if any specific molecule will form a molecular solid or a covalent network? For instan.Balises :Covalent BondsCovalent Network Solids
Network Covalent Solids: Diamond, Graphite and Quartz
A perfect single crystal of a covalent solid is therefore a single giant molecule. We can think of this structure as being rather like a giant molecule - except that the number of .Are there any patterns in covalent network solids as opposed to molecular solids (e.Electrical conductivity in network solids is variable, some are good conductors while others are not so good. Molecular solids consist of molecules held together by intermolecular forces such as Van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, or hydrogen bonds. They often have low melting points and are poor electrical conductors.Balises :Covalent BondsCovalent Network SolidsNetwork covalent structures are also called giant covalent structures or covalent network solids. A perfect single crystal of a covalent solid is therefore a single giant . As a result, people can refer to the solid as a whole as a macromolecule, given that there are no individual molecules.Covalent Network Solid.Solids can be classified according to the nature of the bonding between their atomic or molecular components.Covalent-Network Solids.Molecular Solids. Key Concepts and Summary. are formed by networks or chains of atoms or molecules held together by covalent bonds.Network covalent solids contain a three-dimensional network of covalently bonded atoms as found in the crystal structures of nonmetals like diamond, graphite, silicon, and some covalent compounds, such as silicon dioxide (sand) and silicon carbide (carborundum, the abrasive on sandpaper). The traditional classification distinguishes four kinds of bonding: Covalent bonding, which forms network covalent solids (sometimes called simply covalent solids); Ionic bonding, which forms ionic solids; Metallic bonding, which .Balises :Covalent BondsNetwork Covalent PropertiesPhysical Chemistry Covalent molecules held together by intermolecular forces form molecular solids.Covalent-network solids are different because there are no separate molecules: the whole solid is held together by covalent bonds between atoms. Molecular Solid. October 20, 2023.How do you tell whether a molecule is a covalent network solid or a molecular solid??Well firstly we don’t categorize molecules as either network or molecular solids; rather we describe solids using those terms.Balises :Covalent Network SolidsAuthor:OpenStaxPublish Year:2016Covalent network solids include crystals of diamond, silicon, some other nonmetals, and some covalent compounds such as silicon dioxide (sand) and silicon carbide (carborundum, the abrasive on sandpaper). Indeed, covalent network solids are among the highest-melting substances known: the melting point of diamond is over 3,500°C, while the melting point of SiO 2 is around 1,650 .The atoms in these solids are held together by a network of covalent bonds, as shown in Figure 11. The transition metals are elements with partially filled d orbitals, located in the d-block of the periodic table.Covalent solids are formed by networks or chains of atoms or molecules held together by covalent bonds.Balises :Covalent BondsExamples of Network Covalent SolidsPhysical Chemistry Covalent solids are formed by networks or chains of atoms or molecules held together by covalent bonds.
Network covalent bonding
” It is a type of crystalline . Covalent molecular compounds are generally non-conductive and vary in solubility, . Nonmetals in the upper right corner of the periodic table. The basic idea is that to make a network of covalent bonds, each atom (or many of the atoms) have . Covalent Network Solids. (a) The positively and negatively charged ions in an ionic solid such as sodium chloride (NaCl) are held together by strong electrostatic interactions.Covalent Solids. It's easiest to view these things on a pressure-temper. A network covalent solid (or just network solid) consists of a network of atoms of the same or different elements connected to each other by covalent bonds. Graphene: Material of the Future.
Covalent network solids are composed of atoms covalently bonded together into a three-dimensional network or layers of two-dimensional networks. In a network solid, the atoms link together in a continuous network.Network covalent solids contain a three-dimensional network of covalently bonded atoms as found in the crystal structures of nonmetals like diamond, graphite, silicon, and some .Covalent network solids have high melting points by virtue of their network of covalent bonds, all of which would have to be broken for them to transform into a liquid. For example, diamond is .

The reactivity of the transition elements varies widely from very active metals such as scandium and iron to almost inert elements, such as the platinum metals. These are solids that consist entirely of atoms connected by covalent bonds into a giant network structure.orgCovalent network solids | Intermolecular forces and properties . well, YOU probably can't unles. This page relates the structures of covalent network solids .In this episode, Hank talks about Network solids and Carbon and how you can actually create a Diamond from plain old Carbon. The atoms in these solids are held together by a network of covalent bonds, as . While the intermolecular forces are strong enough to hold the molecules in place, molecular solids typically have lower melting and boiling points than metallic, ionic, or network atomic solids, which are held together by stronger bonds.
Crystal Defects. Covalent solids, also called network solids, are solids that are held together by covalent bonds.Molecular Network Solids.

Network covalent solids.I mean there's quite a lot of them so it depends on how many you actually want to know about. For example, the structure of diamond, shown in part (a) in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), consists of sp3 hybridized carbon atoms, each .Why do some materials sublime?Sublimation occurs with chemicals whose triple points are above normal atmospheric pressure.
A network solid is a.Balises :Covalent BondsExamples of Network Covalent Solids
Types of Solids and How to Categorize Them
Covalent network solids include crystals of diamond, silicon, some other nonmetals, and some covalent compounds such as silicon dioxide (sand) and silicon carbide (carborundum, the abrasive on sandpaper).Balises :Covalent BondsCovalent Network Solids
Lesson Video: Network Covalent Structures
Balises :Covalent BondsExamples of Network Covalent SolidsPhysical ChemistryIs graphite an exception? Because it can conduct electricity and it's a covalent network solid. Covalent-network solids usually have high melting points and are relatively hard because they . They are compounds or elements where the atoms are held together by . Indeed, covalent network solids are among the highest-melting substances known: the melting point of diamond is over 3,500°C, while the melting point of SiO 2 is around 1,650°C. “Covalent network solids: where stability meets structure. Ionic solids, such as sodium chloride and nickel oxide, are composed of .Molecular Solids .Covalent Network Solids. Sometimes we try to differentiate the formula of network solids by writing something like (SiO2)n or (C)n. Examples of network covalent . A perfect single crystal of a covalent solid is .Overview
Covalent network solids (video)
Covalent bonding within .Balises :Covalent BondsCovalent Network A solid, which covalent bonds bind together, like a crystal or an amorphous solid, is a covalent network solid. Covalent network solids contain elements from the carbon group because they have four valence electrons and can create three-dimensional shapes.org/science/ap-chemistry .Balises :Covalent Network SolidsCovalent Network Compounds For example, in diamond, each C atom makes 4 covalent bonds to 4 other C atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. It depends on the type of bonding the.
Covalent Solids
Regarder la vidéo6:59YouTubeAuteur : Bozeman Science The atoms in these solids are held together by a network of covalent .