Criteria for depressive disorder
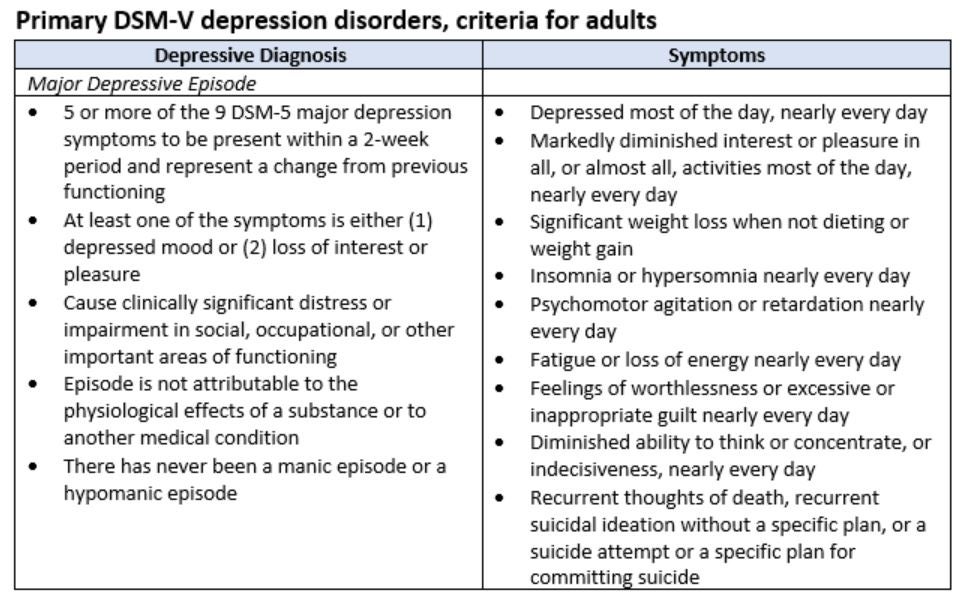
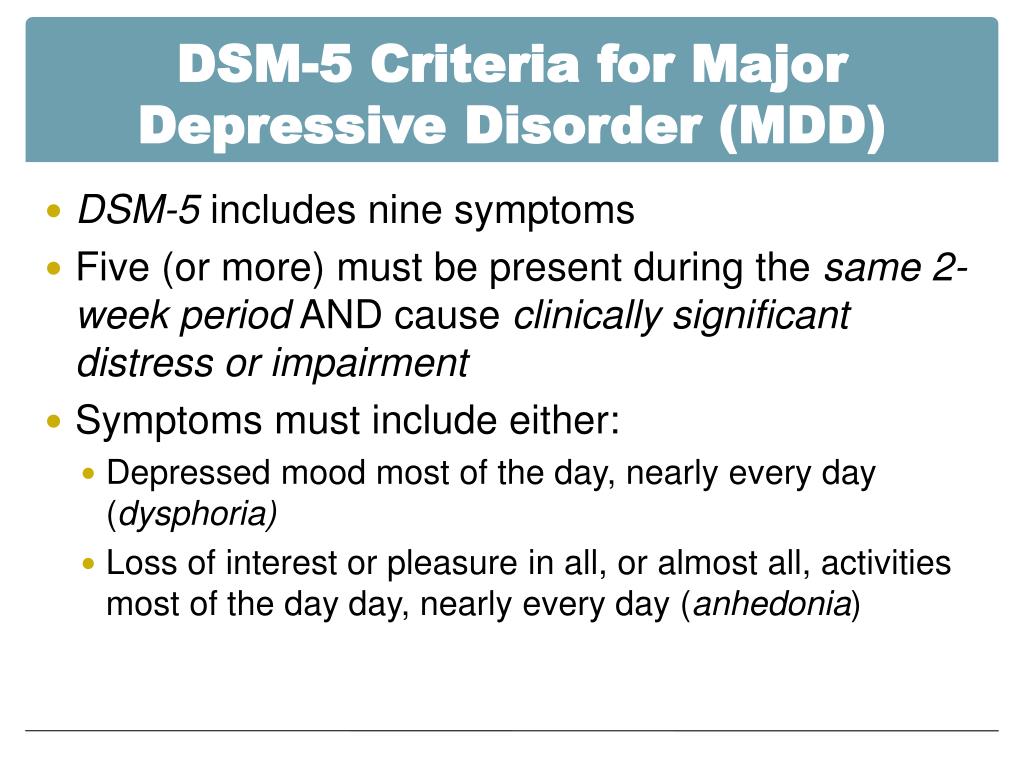
When the diagnosis of major depressive disorder with mixed features (MDD-MX) was .DSM-5 Criteria: Major Depressive Disorder Major Depressive Episode: F Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and .
Major depressive disorder (MDD), or clinical depression, is a common mood disorder that can affect anyone.Criteria have never been met for major depressive disorder, dysthymic disorder, panic disorder, or GAD Criteria are not currently met for any other anxiety or mood disorder (including an anxiety or mood disorder in partial remission) The symptoms are not better accounted for by any other mental disorder: Open in a separate window. Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is a mental disorder characterized by persistent, often daily, low mood and/or decreased interest (anhedonia). Schizophrenia Spectrum and . Reprinted with permission from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, (Copyright .How severely the symptoms of MDD affect a veteran’s life and ability to function will influence this rating. VA disability ratings range from 0% to 100%. The manic episode may have been preceded by and may be followed by hypomanic or major depressive episodes.
What’s Remission in Depression?
Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Symptoms and DSM-5 Criteria
It causes severe symptoms that affect how a person feels, thinks, and handles daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, or working. A January 2014 German metastudy has provided a useful overview of the efficacies of PDD treatments. The impact of depressive symptoms on .Major depressive episodes are characterized by the triad of low mood, self-attitude, and vital sense. By contrast, in a major depressive episode, there is a more generalized depressed mood that is not specifically related to the loss.In order to be diagnosed with psychotic depression, officially known as major depressive disorder with psychotic features, a person must first meet the criteria set forth in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5-TR) for major depressive disorder. To diagnose depression (major depressive disorder), the following DSM-5 criteria need to be met: The patient must have had five or more of the symptoms . MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER, CRITERION A. Manic Episode: F A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or .
Treating Major Depressive Disorder
Your mental health professional may use the criteria for depression listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), published by the .

Conditions for Further Study.Depression (also known as major depression, major depressive disorder, or clinical depression) is a common but serious mood disorder. Tolentino, Sergio L. Older adults with depressive symptoms, ranging from mild to more severe, are at increased risk of being overlooked and undertreated across care settings, and especially in the context of cancer and other medical comorbidities.
DSM-5 Changes: Depression and Depressive Disorders
The two main diagnostic criteria for depression (depressed mood and loss of interest or pleasure) differ regarding their discrimination ability when the level of . Here's a digestible overview of the diagnostic criteria for MDD or major depressive disorder in . Its most prevalent symptom includes persistent sadness and losing the ability to .To be diagnosed with major depression, a person's symptoms must fit the criteria outlined in the DSM-5.Background Suicide stands as both a primary symptom and the direst outcome of major depressive disorder (MDD).from the significant interpersonal loss. In addition, when other There are also associated neurovegetative symptoms, such as a change in sleep, appetite, cognition, and energy levels. classifies the depressive disorders into: Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder. Tactful enquiry using an open-ended .Treating Major Depressive Disorder 9 • Integrate treatment with psychiatric management and any other treatments provided for other co-occurring psychiatric disorders and .Depression is a mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest.According to the DSM-5, you must meet the following criteria to establish a diagnosis of depression., bereavement, financial ruin, losses from a natural disaster, a serious medical illness or disability) may include the feelings of intense sadness, rumination about .Major Depressive Disorder and the Bereavement Exclusion; Mild Neurocognitive Disorder; Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders; Paraphilic Disorders; Personality Disorder ; Posttraumatic Stress Disorder; Schizophrenia; Sleep-Wake Disorders; Specific Learning Disorder; Social Communication Disorder; Somatic Symptom Disorder; . The symptoms last most of the day, on most days, over a long period of time.Per the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5), an individual must have five of the above . What is clinical depression (major depressive disorder)? People who have a history of sleep disturbances, medical illness, chronic pain, anxiety and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are .The DSM-5 criteria helps diagnose major depressive disorder based on an array of depressive symptoms (9 out of which at least 5 must be met) and four additional required criteria.Clinical depression, formerly known as major depressive disorder in the DSM, is commonly diagnosed.
Changes to its diagnostic criteria were limited. DSM-5 symptom criteria for Major Depressive Disorder include: A depressed mood all the time. Globally, an estimated 5% of adults suffer from depression.
Psychotic Depression: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Recurrent depressive disorder, currently in full remission is diagnosed when the definitional requirements for recurrent depressive disorder have been met but currently there are no significant mood symptoms. The depression symptoms focus on the following: Depressed mood; Loss of interest/pleasure; Weight loss or gain; Insomnia or hypersomnia;
DSM-5 Changes: Depression and Depressive Disorders
Auteur : Julio C.
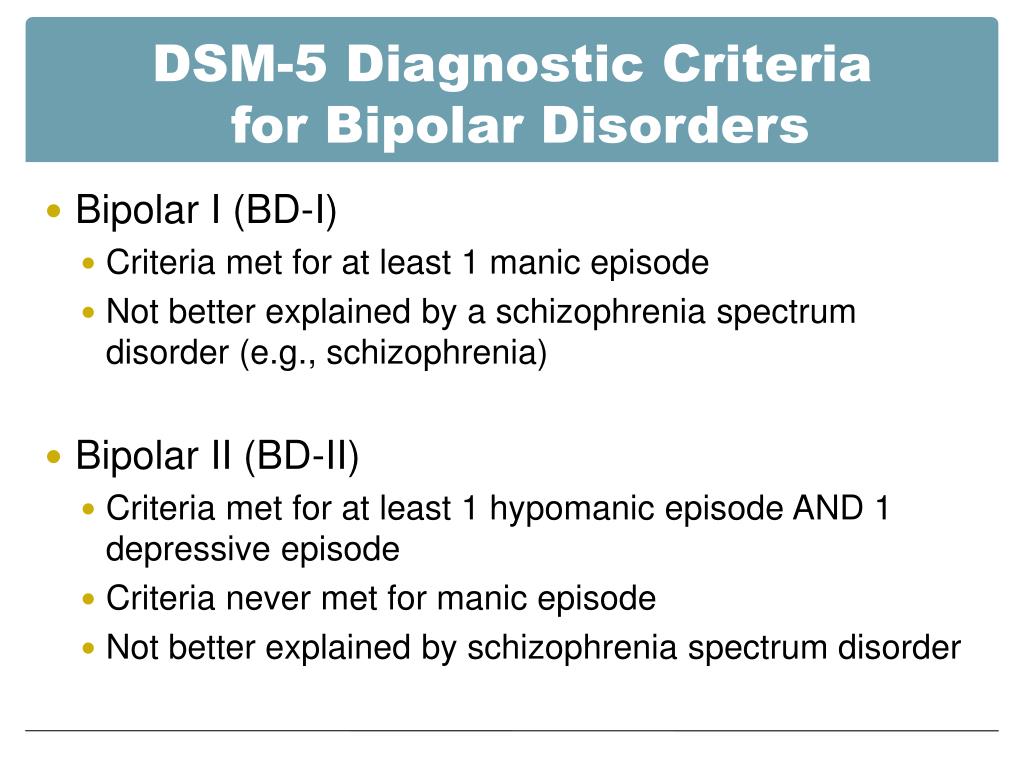
DSM-5 Criteria: Bipolar Disorders
The panel recognizes this as an important sub Not - set of depression.9 (CRITERIA UPDATE) MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER (TEXT .
Low self-attitude may manifest as self-blame, self-deprecation, guilt, lack of self-confidence about the future, or hopelessness.psychotic disorders from the exclusion criterion (i.treatments for depression, costs of treatment, long-term benefits of treatment, mechanisms of change, bipolar disorder, or efficacy of treatments for disorders other than depression. Depressive Episodes With Short-Duration Hypomania: Proposed Criterion A [August 2015] Text Updates . [2] Low mood may manifest as persistent sadness, anxiety, apathy, irritability, or emotional numbness. Depression is a common mental disorder.
Depression Definition and DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria
History of the ICD-10 Criteria for Depression.
Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia)
When assessing for GAD, clinical professionals are looking for the following: The presence of excessive anxiety and worry about a variety of topics, events, or activities.Other Specified Depressive Disorder 311 (F32. The symptom must either be new or must have clearly worsened compared with the person’s pre-episode status and must persist most of the day, daily, for at least 2 weeks . A 100% rating means the veteran cannot function in everyday life. The individual must be experiencing five or more symptoms during the same 2-week period and at least one of the symptoms should be either (1) depressed mood . Healthcare professionals rely on the DSM-5 to determine mental health diagnoses. NOTE: Do not include symptoms that are clearly . This study found that interpersonal psychology with medication is more efficacious than . In addition, the person must exhibit signs of psychosis, such .
DSM-5 Criteria: Major Depressive Disorder
DSM-5 Criteria: Bipolar Disorders biPolar i disorder: For a diagnosis of bipolar I disorder, it is necessary to meet the following criteria for a manic episode.
Major Depressive Disorder
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.Depressive disorder with mixed features (also referred to as mixed-episode, mixed state, or agitated depression ) is a mood disorder in which a person has symptoms of both depression and mania or hypomania at the same time.
Decoding the DSM-5 Depression Criteria
Criteria for Diagnosing GAD.The diagnostic criteria for each depressive disorder differ.

Depressive disorders are characterized by sadness severe enough or persistent enough to interfere with function and often by decreased interest or .DEPRESSIVE DISORDERS.
Depressive disorder (depression)
Depression (major depressive disorder)
Children and adolescents diagnosed with cancer often experience psychological distress, encompassing anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress . The scarcity of effective treatment . A 0% rating means a veteran may have MDD symptoms, but their ability to function normally is not impaired.The severity of major depression, according to the DSM-5, increases with the number of criterion symptoms present and degree of functional disability.Auteur : Navneet Bains, Sara Abdijadid
Depressive Disorders
To be diagnosed with depression, the symptoms must be present for at least 2 .DSM-IV, updates in DSM-5-TR included changing the respective exclusion criteria to clarify that the mood disorder can be diagnosed if the basic episode requirements for that disorder have been met (i. A person with PDD has a sad, dark, or low mood and two or more other symptoms of depression. Healthcare providers used to call the condition dysthymia or dysthymic disorder.DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for depression.Persistent depressive disorder (PDD) is mild or moderate depression that doesn’t go away.Major depression is a risk factor for and is often associated with substance abuse, including that of alcohol, which may be under-recognised in elderly patients. 1e that psychotic depression is not covered by this guideline. The manual has updated its classifications of depressive disorders .The ICD-10 criteria for depression are a set of symptoms and signs that indicate the presence of the disorder.