Critical information infrastructure protection

RAND addresses homeland security and critical infrastructure needs through objective research that assists national, state, and local . Discover what sectors are covered by CIP .5 Supply Chain Management 21Infrastructure Protection.Critical Information Infrastructure Protection — ENISA.REPORT on critical information infrastructure protection – achievements and next steps: towards global cyber-security. Critical Infrastructure Protection Download book PDF.The International Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIIP) Handbook is the product of a joint effort within the CRN partner network.European Programme for Critical Infrastructure Protection (EPCIP)7. Critical Infrastructure are those assets, systems, and networks that provide functions necessary for our way of life. CIP is a national program to ensure the security of vulnerable and interconnected infrastructures of the United States. Download book PDF.Subcommittee on Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Protection . Critical Infrastructures (CI) are defined as: “Those infrastructures which are .The present volume aims to provide an overview of the current understanding of the so-called Critical Infrastructure (CI), and particularly the Critical Information .
Critical Information Infrastructure Protection — ENISA
Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIP) This course examines the security of information in computer and communications networks within infrastructure sectors critical to national security.The National Infrastructure Protection Plan (NIPP)—NIPP 2013: Partnering for Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience —outlines how government and .Best Practices for Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIIP .
Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIIP) Full guide
What is Critical Infrastructure and How Should We Protect It?
1 National Level Governance 17 2.5 Exception Approval 15 2.1 Governance for CIIP Program 2.Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIIP) is a complex but important topic for nations. Committee on Homeland Security .The UAE Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIIP) Policy described herein supports the implementation of the NCSS. Resilience and Protection. Council Directive 2008/114/EC, adopted on 8 December 2008, is an integral part of the European programme for critical infrastructure protection, which emerged in the aftermath of the devastating terrorist attacks that shook the US and Europe in the early 2000s.Critical infrastructure, or critical national infrastructure ( CNI) in the UK, describes infrastructure considered essential by governments for the functioning of a society . National Cyber Security Strategies - Interactive Map.The resolution on “Creation of a global culture of cybersecurity and the protection of critical information infrastructures” (58/199), prepared under the United States’ leadership and co-sponsored by a total of 69 countries including China, but not Russia, was adopted in 2005. In May 1998, President Bill Clinton .CIIP refers to a collection of rules, regulations, and practises designed to ensure the resilience and preservation of a nation's sensitive framework details, including . IP acts on behalf of the Secretary of Homeland Security, implementing the national critical infrastructure . It is mandated to guard CIIs from unauthorized access, modification, use, disclosure, disruption, incapacitation or distraction. Thorough investigation of various elements of critical information infrastructures .The term is also used for the totality of interconnected computers and networks and their critical information flows”.Critical Infrastructure Protection is also defined as: “All activities aimed at ensuring the functionality, continuity and integrity of CI in order to deter, mitigate and neutralise a threat, risk or vulnerability. Transportation, commerce, clean water, and electricity all rely on these vital systems. The Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology . Online, Instructor-Led.“In the event of any threat to critical information infrastructure the National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre may call for information and give directions to the critical sectors or persons serving or having a critical impact on Critical Information Infrastructure,” the NCIIPC website adds.
Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience
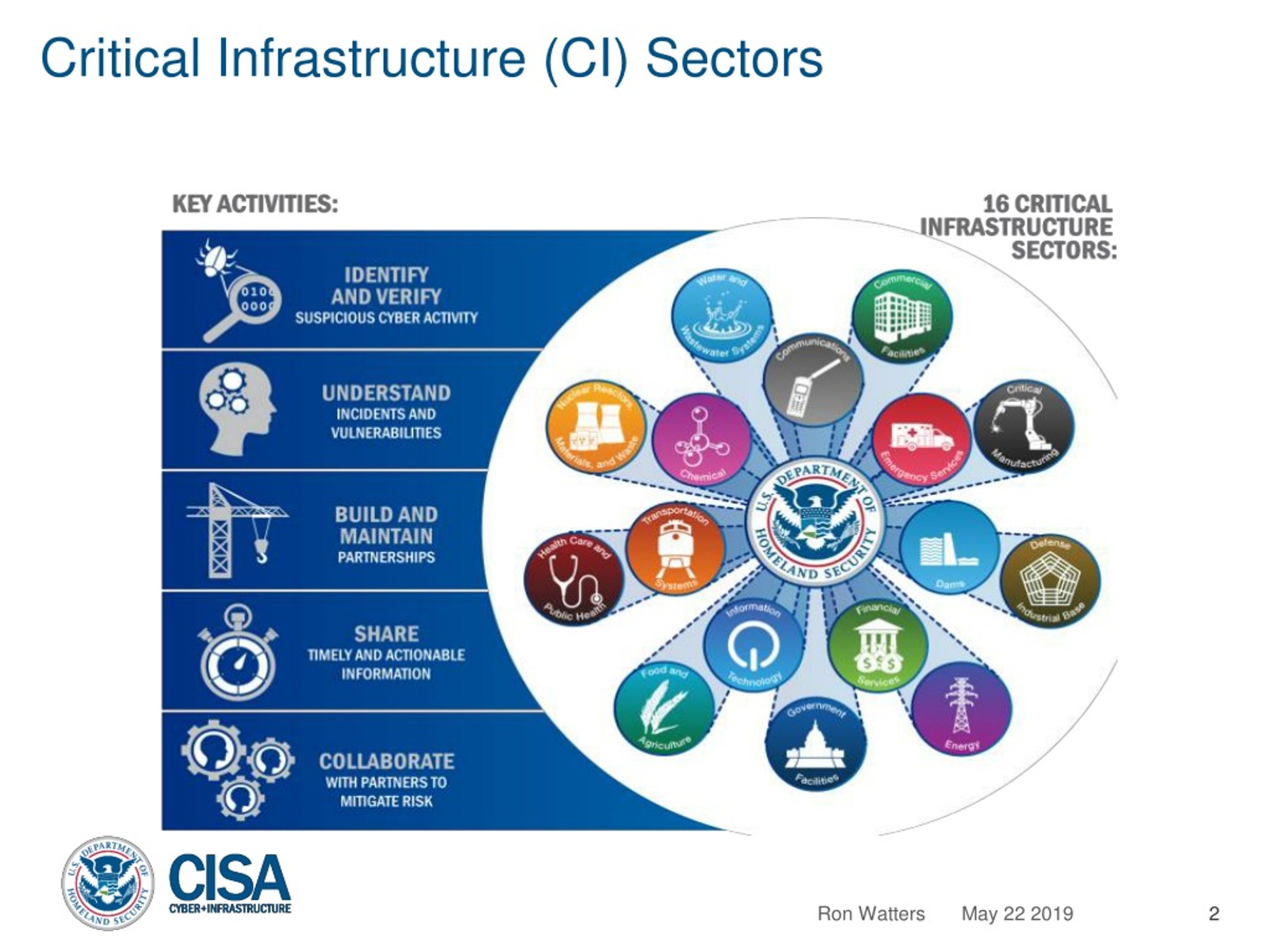
The nation’s 16 critical infrastructure sectors provide essential services— such as electricity distribution, transportation, and hospital care—that underpin American society and are vital to the nation’s safety and .
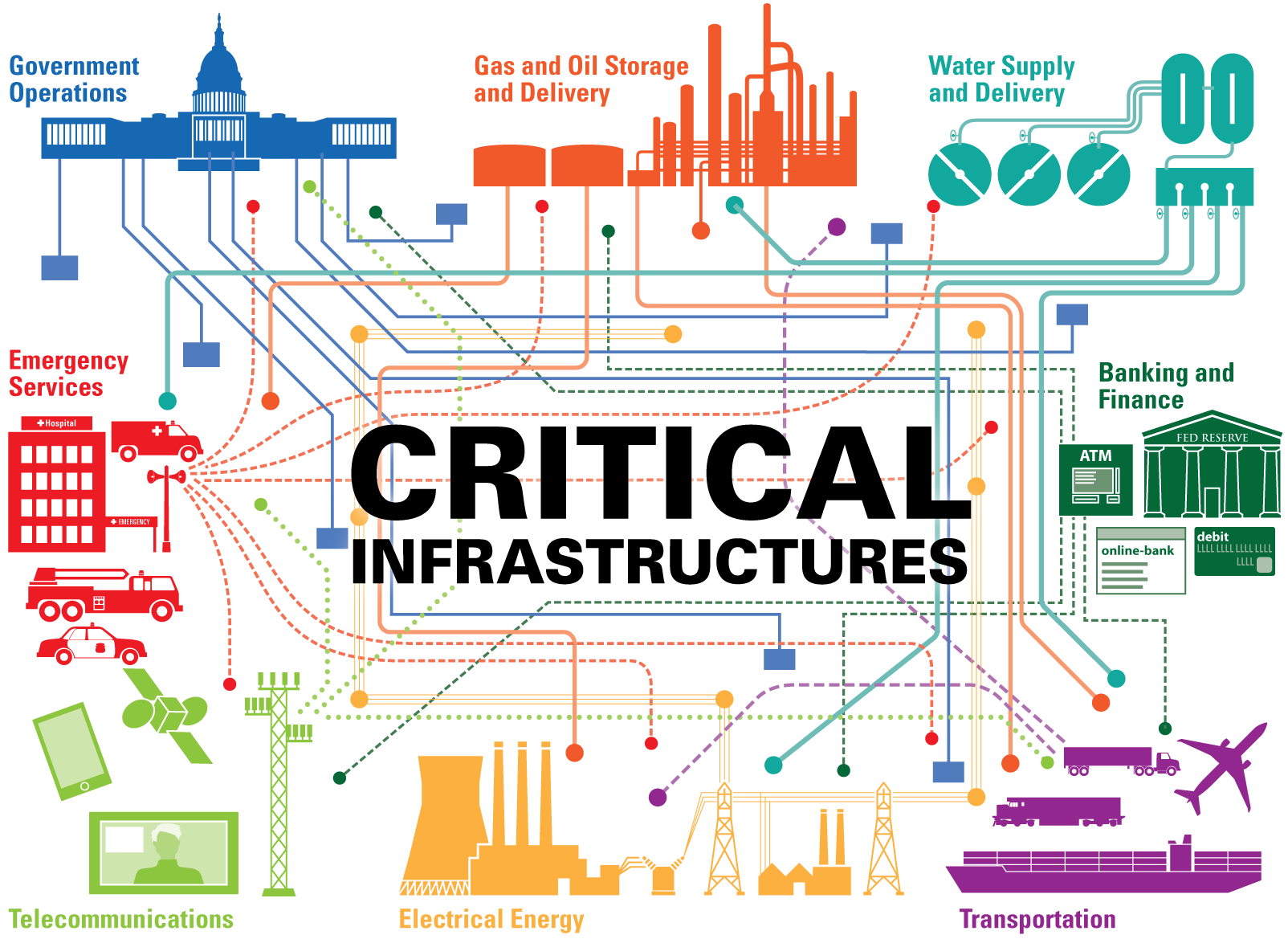
Safety components of critical infrastructure, including critical digital infrastructure, are systems used to directly protect the physical integrity of critical .Many of the critical infrastructure protection examples discussed above use the following enterprise technologies: Deep CDR: Content disarm and reconstruction (CDR) disassembles a file into its constituent parts and eliminates any potential threats.There is no designated European Critical Infrastructure Element in Hungary yet.Critical Infrastructure Protection is also defined as: “All activities aimed at ensuring the functionality, continuity and integrity of CI in order to deter, mitigate and neutralise a . We acknowledge that Ghana’s digital ecosystem cannot be fully insulated from cyber-attacks but these strides undoubtedly position our country with respect to our readiness to mitigate potential cyber-attacks.” [EC2008] It involves: Understanding meaning, intent and rationale of CI and CII classification and the need for CIIP.eu’, – having regard to its resolution of 15 June 2010 entitled ‘Internet governance: the next . National Cybersecurity Strategies (NCSSs) Map. Nations at large critically depend on Critical Infrastructure (CI) services such as energy supply, telecommunications, financial systems, drinking water, and governmental services.De très nombreux exemples de phrases traduites contenant critical information infrastructure protection – Dictionnaire français-anglais et moteur de recherche de traductions françaises. Authors: Maitland Hyslop.
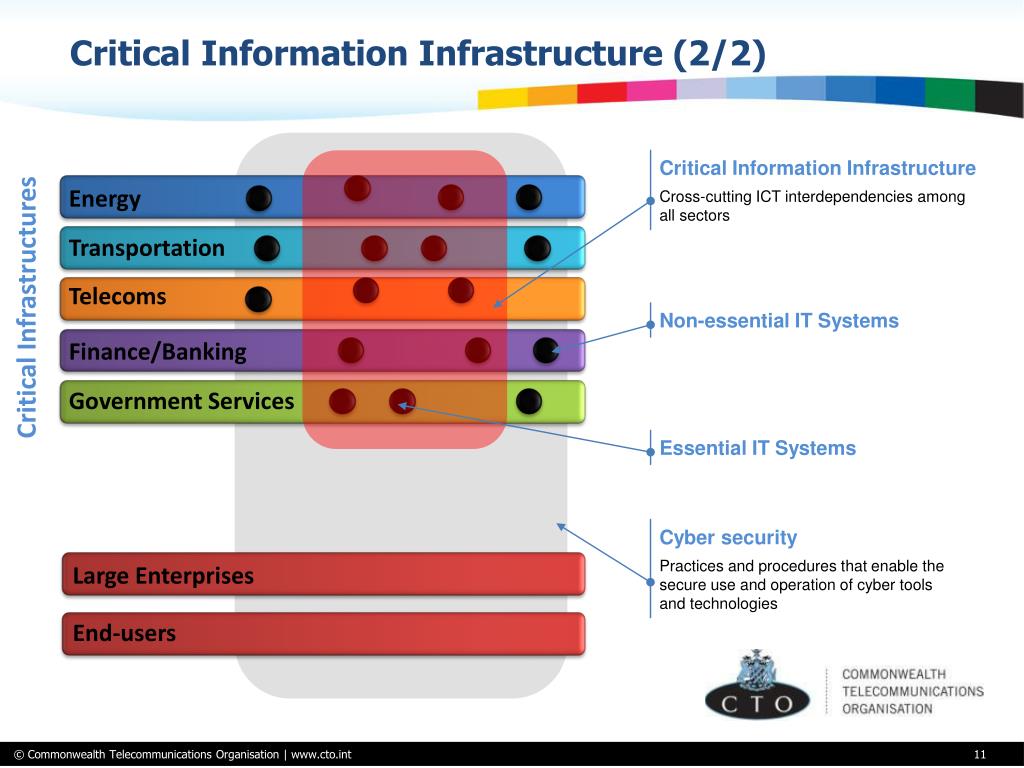
Despite its terrorism-related roots, the EPCIP takes a broad approach .Created in January 2014, the National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) is the nodal agency for taking all measures to protect the nation’s critical information infrastructure. National Cybersecurity Strategies.
Protected Critical Infrastructure Information (PCII) Program
Department of Computer Science, University of .
This is a package of measures aimed at improving the protection of critical infrastructure in Europe, across all EU States and in all relevant sectors of economic activity.Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIP) Classroom.
Critical Information Infrastructures Protection approaches in EU
2012 - (2011/2284 (INI)) Committee .2 Emirate Level Governance 18 2. A key element of EPCIP is the Directive8 on the identification and designation of European Critical . This document outlines the activities the CIIP program will use to accomplish three key objectives: • Identify critical sectors and national services • Identify the information infrastructures supporting critical .
Critical Information Infrastructure Protection and CIRT
Critical Infrastructure Protection Advances in Critical Infrastructure Protection: Information Infrastructure Models, Analysis, and Defense.Critical Information Infrastructures.
National Infrastructure Protection Plan and Resources
This course examines the security of information in computer and communications .
Texts adopted
on critical information infrastructure protection – achievements and next steps: towards global cyber-security (2011/2284(INI))The European Parliament, – having regard to its resolution of 5 May 2010 entitled ‘A new Digital Agenda for Europe: 2015.Overview
REPORT on critical information infrastructure protection
These include the sectors of banking, securities and commodities markets, industrial supply chain, electrical/smart grid, energy production .4 Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIIP) Principles 14 1. The present volume aims to provide an overview of the current understanding of the so-called Critical Infrastructure (CI), and particularly the Critical Information Infrastructure (CII), which not only forms one of the constituent sectors of the overall CI, but also is unique in providing an element of interconnection between sectors . Editors: Javier Lopez 0, Roberto Setola 1, Stephen D. There are 16 critical infrastructure sectors whose assets, systems, and networks, whether physical or virtual, are considered so vital to the United States that their incapacitation or destruction would have a debilitating effect on security, national economic security, national public health or safety, or any . 15 Dunn, refers to CI and CII as follows: “That the two concepts are closely interrelated is apparent from the current debate in protection necessities: the debate jumps from a discussion of protecting critical physical . Wolthusen 2; Javier Lopez. Critical infrastructure includes the country’s vast network of highways, connecting bridges and tunnels, railways, utilities, and buildings necessary in daily life.Critical Infrastructure Sectors.There are 16 critical infrastructure sectors that are part of a complex, interconnected ecosystem and any threat to these sectors could have potentially debilitating national security, economic, and public health .To reduce the vulnerabilities of critical infrastructures, the European Commission has launched the European Programme for Critical Infrastructure Protection (EPCIP). The first edition of the CIIP .

Building on previous attempts, it proposes two models of CIIP: the national security model and the business continuity model.National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) is an organisation of the Government of India created under Sec 70A of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (amended 2008), through a gazette notification on 16th Jan 2014 Based in New Delhi, India, it is designated as the National Nodal Agency in respect of .Information Technology Sector functions are operated by a combination of entities—often owners and operators and their respective associations—that maintain and reconstitute the network, including the Internet.
the protection of critical information infrastructures and this has been done to safeguard our investments in our digitalisation programmes.
Critical Information Infrastructure Protection — ENISA
This paper advocates the need to conceptualize or model critical information infrastructure protection (CIIP) in order to explain regulatory choices made by governments regarding CIIP.













