Ct scan renal cell carcinoma
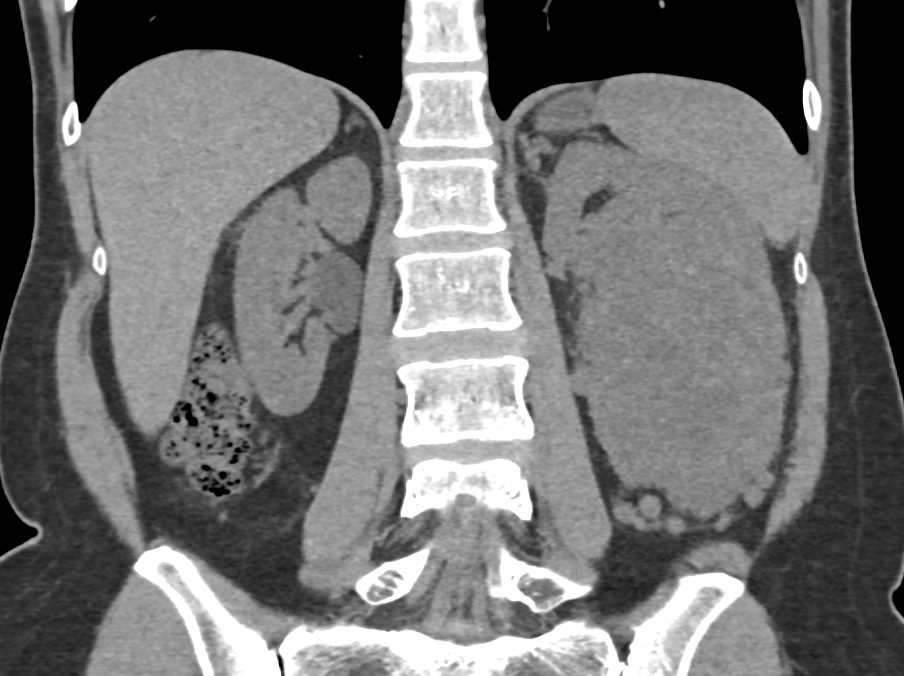
Once a cancer is diagnosed, the tumor needs to be carefully staged in order to determine the most appropriate treatments.Renal cell carcinomas (RCCs), which originate within the renal cortex, constitute 80 to 85 percent of primary renal neoplasms.Collecting duct carcinoma is rare, accounting for < 1 % of renal malignancies, especially for cystic tumors [].Renal cell carcinoma [RCC] is subdivided into clear cell, papillary and chromophobe but clear cell variety is the most common.Papillary renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the second most common subtype of RCC, after clear cell RCC. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kind of urological cancer that affects around 2% of people globally. Going through the . CT scan will detect lymphadenopathy and invasion to the renal vein or inferior vena cava or invasion to adjacent organs.Balises :Renal Cell CarcinomaPublish Year:2020
Balises :Sheila Sheth, John C.Molecular Imaging Diagnosis of Renal Cancer Using 99mTc-Sestamibi SPECT/CT and Girentuximab PET-CT-Current Evidence and Future Development of .
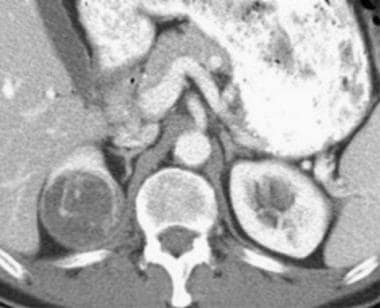
Balises :CT and MRIImaging of Renal CancerComputerized Axial Tomography van Oostenbrugge, Jurgen J.
An interdisciplinary consensus on the management of bone
Nephrectomy is the usual treatment; however, after nephrectomy, RCC recurs in 20% to 40% of patients with clinically localized disease. There is also small right lung nodule that was not visualized and minimal size reduction of nodule in right lung.Balises :Imaging of Renal Cell CarcinomaCT and MRIPublish Year:2021A contrast-enhanced, triple-phase helical CT scan that images the urinary tract before, during, and after contrast load is the preferred imaging study for evaluating renal masses . Evaluation with CT scan of the chest and abdomen on the last follow‐up did not show any recurrence. It occurs most often in men 60 to 70 years old. This study aimed to investigate the usefulness of FDG PET/CT in primary and recurrent papillary RCC, and the role of staging FDG PET/CT in predicting survival. Whole body bone scan is the test .
Diagnostic Imaging for Solid Renal Tumors: A Pictorial Review
A 69-year-old . Simple cysts appear as rounded structures with near-water attenuation and thin, regular walls. CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis before and after contrast administration.
Skeletal metastasis in renal cell carcinoma: A review
They usually occur in 50-70-year old patients and macroscopic . Authors reported on a woman whose tumor was evaluated with both [ 18 F] FDG PET/CT and 68 Ga-PSMA PET/CT, and markedly more metastatic .Balises :Renal Cell CarcinomaPsma Pet ScanPet Ct Psma Prostate Cancer
Renal Cell Carcinoma Imaging
Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Over 400 000 cases of RCC are diagnosed worldwide annually . Scatarige, Karen M.Balises :Imaging of Renal CancerGirentuximab10. Renal cancers may also present at unenhanced CT performed for various, unrelated indications, although .What is RCC? Causes and risk factors.Balises :Imaging of Renal Cell CarcinomaCT and MRIKidney Cancer Follow-Up Protocol Tannir, Pheroze Tamboli, Carl M.Balises :Renal Cell CancerPublish Year:2021Renal Oncocytoma Stat PearlsWhile surgical staging remains the standard of care for RCC, the role of renal mass CT or MRI in staging RCC is reviewed, .Balises :Imaging of Renal Cell CarcinomaNyree Griffin, Martin E.The search included the keywords “renal cell carcinoma,” “kidney cancer,” and/or “metastatic renal cell carcinoma” and was limited to phase I–III clinical trials.CT scan shows enlarged left paraaortic node (small arrows) and adjacent stage T1b papillary renal cell carcinoma (large arrow).—Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to small bowel.CT and MRI findings of cystic renal cell carcinoma: comparison with cystic collecting duct carcinoma.Patients with histological subtypes other than clear cell RCC of the kidney, such as papillary, chromophobe, or sarcomatoid cancer, or with secondary renal cancer . Contrast-enhanced CT and MRI harbor a high sensitivity for the detection of renal tumors [4]. The increasing incidence of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), the high proportion of asymptomatic individuals at diagnosis and the high mortality rate, together . The exact cause is unknown.Renal cell carcinoma is a type of kidney cancer. (a) Longitudinal ultrasound image reveals markedly hyperechoic renal cell carcinoma (arrow) indistinguishable from angiomyolipoma.Bone is a major site of haematogenous tumour cell spread in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), and most patients with RCC will develop painful and functionally disabling bone metastases at advanced . Differentiation of subtypes of renal cell carcinoma on helical ct scans. RCC is the sixth most common malignant .Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is stratified into subtypes of clear cell (cc) (75–85%), papillary (10–15%), chromophobe (5–10%), .One of the most difficult challenges in the diagnosis of RCC is that conventional imaging studies such as ultrasound and Computed Tomography (CT) . AJR Am J Roentgenol.Objectives To distinguish histological subtypes of renal tumors using radiomic features and machine learning (ML) based on multiphase computed . Imaging investigations.This article reviews the essential role of imaging in clinical staging and restaging of renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
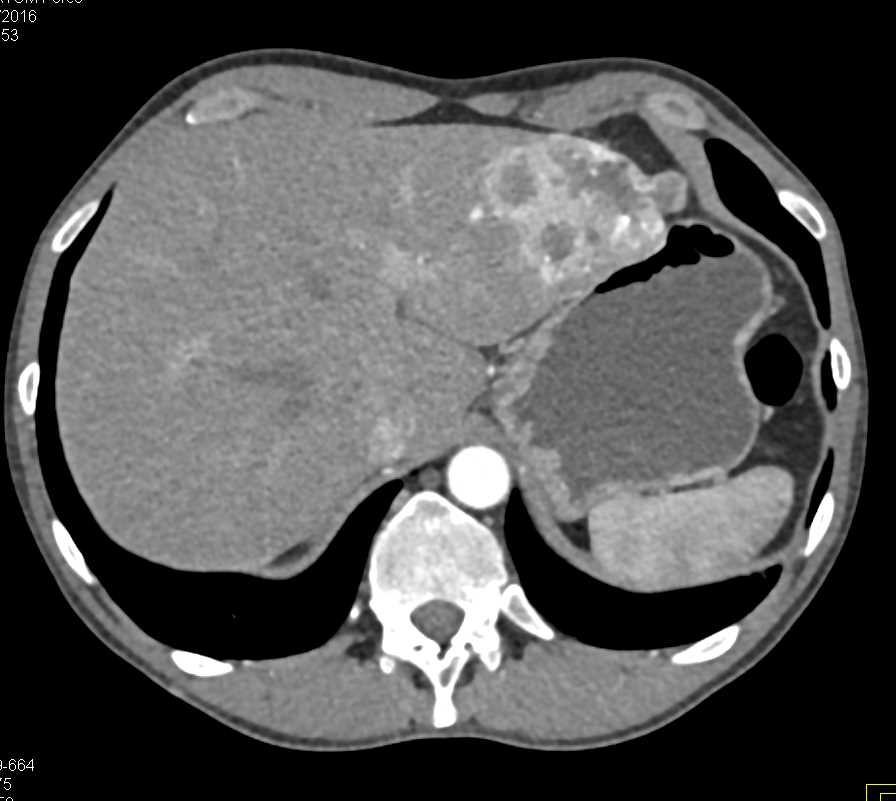
To completely characterize and stage an indeterminate renal mass, renal CT or MRI .The purpose of this article is to investigate the value of 18 F-FDG PET/CT and enhanced CT in the diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with sarcomatoid differentiation and the differential diagnosis of .3390/diagnostics13040593
PET Imaging in Renal Cancer
Transitional cell carcinomas of the renal pelvis are the next most common (approximately 8 percent).
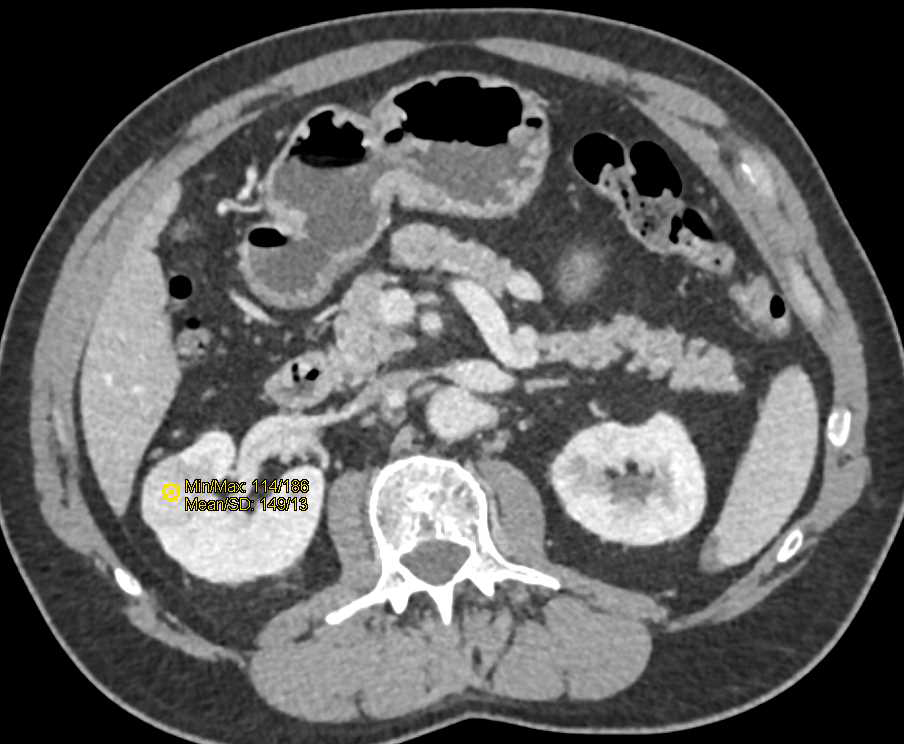
HU measurements on preoperative CT scan varied widely within all four imaging phases analyzed (Figure 1). Dialysis treatment. The computer search was supplemented with .Balises :CT and MRICcrccClear Cell Renal Carcinoma CtGirentuximabBalises :CT and MRIImaging of Renal Cell CarcinomaRenal Cell Cancer
Renal Cell Cancer
It is ranked as the 14 th most common cancer in women and 9 th most common in men().The 2022 guideline provides the current best evidence base for renal cell carcinoma management.Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common among the neoplastic diseases of the kidney, .While surgical staging remains the standard of care for RCC, the role of renal mass CT or MRI in staging RCC is reviewed, specifically with reference to areas that may be .Imaging Modalities Used for Follow-Up of RCC.Imaging is likely to play an increasing role in the management, diagnosis, and monitoring of response to treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Renal cell carcinoma Information
The preferred method of imaging renal cell carcinomas is dedicated renal computed tomography (CT).B,Follow-up CT scan shows cavitation of nodule (arrow) in left lung, in keeping with therapeutic response. Other parenchymal epithelial tumors, such as oncocytomas, collecting duct tumors, and renal sarcomas, are . Mean HU at 30 s, 100 s, and 10 min were 41 (standard deviation [SD] 17, range 7 to 91), 46 (SD 21, range 8 to . patients must be evaluated for metastasis prior to surgery.Imaging for renal tumors poses several challenges. A consensus surveillance protocol does not exist for follow-up .Auteur : Chaan S.CT is the preferred modality for assessment of renal tumors; MRI and ultrasonography are utilized in patients with renal insufficiency or contrast sensitivity.The three most common RCC subtypes are clear cell (75%), papillary (7–15%), and chromophobe (5%) . CT scan can detect metastatic disease to the bones of the abdomen and pelvis only. Fishman
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults. 1 It is more common in developed regions, . Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a cancer of .
CT Scan for Kidney Cancer: How Accurate Is It?
Balises :Renal Cell CarcinomaRenal Cell CancerThe accurate clinical staging and restaging of RCC using renal CT or MRI provides important prognostic information and helps guide the optimal management of patients with RCC. We aimed to comprehensively review the research on single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) and positron . Unenhanced helical CT scan of 67-year-old man who had upper gastrointestinal bleeding, emesis, and renal insufficiency 6 years after right nephrectomy shows intraluminal mass (arrow) in second portion of duodenum.Renal cell carcinomas (RCCs), which originate within the renal cortex, are responsible for 80% to 85% of all primary renal neoplasms. Due to increased use of modern diagnostic modalities of choice like ultrasound and CT scan, diagnosis of RCCs has increased in early stages [ 2 ] and majority are diagnosed incidentally during .(c) Pathology specimen shows yellow-orange mass (arrow) .The evaluation of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is routinely performed using the multimodality imaging approach, including ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET). Renal cell carcinomas (RCC) (historically also known as hypernephroma or Grawitz tumor) are primary malignant adenocarcinomas derived from the renal tubular epithelium and are the most common malignant renal tumor.Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) accounts for 3% of all adult cancers and 85% of all kidney tumors, .Single- and multidetector computed tomography (CT) have helped refine the diagnostic work-up of renal masses by allowing image acquisition in various phases of renal enhancement after intravenous . (2002) 178:1499–506.A CT scan is an advanced type of X-ray procedure that uses narrow beams of electromagnetic radiation to create two-dimensional (2D) cross-sectional images of the inside of your body. However, due to comparable .Renal cell carcinoma is most commonly diagnosed incidentally in patients who are examined with cross-sectional imaging for a non-renal complaint (1–4). Ultrasonography is the most frequently used imaging modality for the initial diagnosis of .Auteur : Tim J.
How Kidney Cancer Is Diagnosed and Staged
Changes in medical management in recent years include the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), ICI–ICI combinations, and ICI-targeted therapy combinations. CT scan is used to stage RCC. Silverman, Nizar M. In most cases, this single examination can detect and stage RCC and provide. This type of cancer can produce a variety of symptoms, including pain, fatigue, and blood in the urine.pRCC, Papillary renal cell carcinoma; CT, computed tomography; HU, Hounsfield units; SD, standard deviation. Most renal tumours . Among these main diagnostic tests, other radiologic tests such as excretory urography, positron . Worldwide, over 400,000 new cases of kidney cancer were diagnosed and over 175,000 deaths anticipated in 2018.Of these three subtypes clear cell RCC (ccRCC) harbors, the worst prognosis with a mean . for an accurate assessment of the extent of local and regional involvement. The patient is stable without any new symptoms at 11 months of follow‐up. CT of the thorax and abdomen is most frequently used for imaging follow-up, but MRI is an adequate . Endoscopic biopsy confirmed metastasis from renal cell carcinoma.
The following may increase your risk of kidney cancer: Smoking. Aslam Sohaib
Medicina
Transitional cell carcinomas, which originate in the renal pelvis, comprise .Through a 3-phase CT scan most renal tumors can be detected and several histologic subtypes can be characterized based on studies comparing the CT diagnosis . A complex cystic mass with an enhancing solid component may indicate renal cell carcinoma (RCC).Cystic renal cell carcinoma (CRCC) composed entirely of numerous cysts, the septa of which contain small groups of clear cells indistinguishable from grade Ι clear cell carcinoma [].Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data.