Cyclins and cyclin dependent kinases control

CDKs play important roles in the control of cell division and modulate transcription in response to several extra- and intracellular cues.Auteur : Lei Ding, Jiaqi Cao, Wen Lin, Hongjian Chen, Xianhui Xiong, Hongshun Ao, Min Yu, Jie Lin, Qinghua Cu.The G1–S transcriptional network is involved in two crucial aspects of cell cycle regulation: cell division cycle control and maintenance of genome stability.These kinases are activated by larger proteins called cyclins, named with respect to their cyclical expression and degradation.Cyclin D1 functions in a kinase-independent manner to enhance DNA repair and also binds DNA in the context of chromatin to regulate the expression of genes governing . [2] [25] Research has shown that alterations in cyclins, CDKs, and CDK inhibitors (CKIs) are common in most cancers, involving chromosomal translocations, point mutations, insertions, deletions, gene overexpression, .Two groups of proteins, called cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), are responsible for the progress of the cell through the various checkpoints.Balises :Cyclins Are KinasesKinases and CyclinsCyclin-Dependent Kinase in Cell CycleThree protein families are required for primary regulation of these restriction points: cyclins, their partner cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and cyclin .
Balises :Cyclins Are KinasesKinases and CyclinsCyclin-dependentCell Cycle CdksIncreases in the concentration of cyclin .Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) are serine/threonine kinases and their catalytic activities are modulated by interactions with cyclins and Cdk inhibitors (CKIs).
Core control principles of the eukaryotic cell cycle
During the last decade, it . Affiliation 1 Institute for Cancer Research and Molecular Biology, Temple University School of Medicine, . The evolutionary expansion of the . Authors X Graña 1 , E P Reddy.Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are protein kinases characterized by needing a separate subunit – a cyclin – that provides domains essential for enzymatic activity.Cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) are critical regulators of cell cycle progression and RNA transcription. Cyclin binding. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are protein kinases characterized by needing a separate subunit - a cyclin - that provides domains . In addition to their well-established function in cell cycle control, it is .Balises :Cyclin-Dependent Kinase in Cell CycleThe Roles of Cyclin-DependentIn the mammalian cells, cell cycle is regulated by a number of proteins namely cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and their associated cyclins which bind with and activate CDKs in a phase specific .Balises :Cyclins Are KinasesCyclin-Dependent Kinase in Cell CycleRegulation of Cdks The levels of the four cyclin proteins fluctuate throughout the cell cycle in a predictable pattern (Figure 2). As expected, any dysregulation in the expression or function of these components can provide a platform for excessive cell proliferation leading to tumorigenesis. Cyclin D acts as a mitogenic signal sensor. Dominant-negative mutations were used to address the requirement for kinases of this family in progression through the human cell cycle. In a normal cell, in the presence of inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases the cell cycle stops or the progression of the cell cycle is delayed.

However, built-in redundancy may limit the effects of . Two groups of proteins, called cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), are responsible for the progress of the cell through the various checkpoints. This chapter introduces cyclins and their partner—cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs)—and the ways in which CDK complexes can be regulated. Increases in the concentration of cyclin proteins are triggered by both external . Increases in the concentration of cyclin proteins are triggered by both external and .Balises :Cyclin-dependentCdks in Cell CycleThe cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a family of serine/threonine kinases controlling progression through the cell cycle.Thus, studies of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) are essential for advancing the understanding of cancer characteristics.Balises :Regulation of CdksThe Roles of Cyclin-DependentCdks in Cell Cycle
Cyclins and cell cycle checkpoints
Phosphorylation of transcriptional inhibitors by cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) releases them from transcription factors to activate G1–S genes, including G1 cyclins (see the figure . Different CDKs are activated when they bind to their corresponding cyclins. A dominant-negative Cdc2 mutant arrested cells at the G2 to . Close cooperation between this trio is necessary for ensuring orderly progression through the cell cycle. Without a specific concentration of fully activated cyclin/Cdk complexes, or if an abnormal cdk is produced, the cell cycle cannot proceed through the checkpoint and will arrest at the G 2 /M . CDKs are a family of multifunctional enzymes that can modify . CDKs are serine/threonine kinases that regulate cell cycle progression and cellular transcription. The two sides of chromosomal instability: drivers and .Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are protein kinases characterized by needing a separate subunit - a cyclin - that provides domains essential for enzymatic activity.The Cyclin-dependent kinase 1, as a serine/threonine protein kinase, is more than a cell cycle regulator as it was originally identified.Balises :Cyclins Are KinasesCyclin-dependentDNACellsBalises :Cyclin-Dependent Kinase in Cell CyclePublish Year:2021
CDK
Auteur : Mathew C.These proteins regulate the various phases of the cell cycle by either activating the cyclin-dependent kinases or by activating some other enzymes or complexes. 1995 Jul 20;11(2):211-9. Cyclins are a family of proteins that control the progression of cells through the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk) enzymes. Increases in the concentration of cyclin proteins are triggered by both . Pestell
Core control principles of the eukaryotic cell cycle
Studies performed in the nervous system with mouse models lacking individual Cdks, cyclins, and CKIs, or combinations thereof, have shown that many of these molecules .
Cell cycle control in cancer
A variety of genetic and epigenetic events cause universal overactivity of the cell cycle cdks in human cancer, and their inhibition can lead to both cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
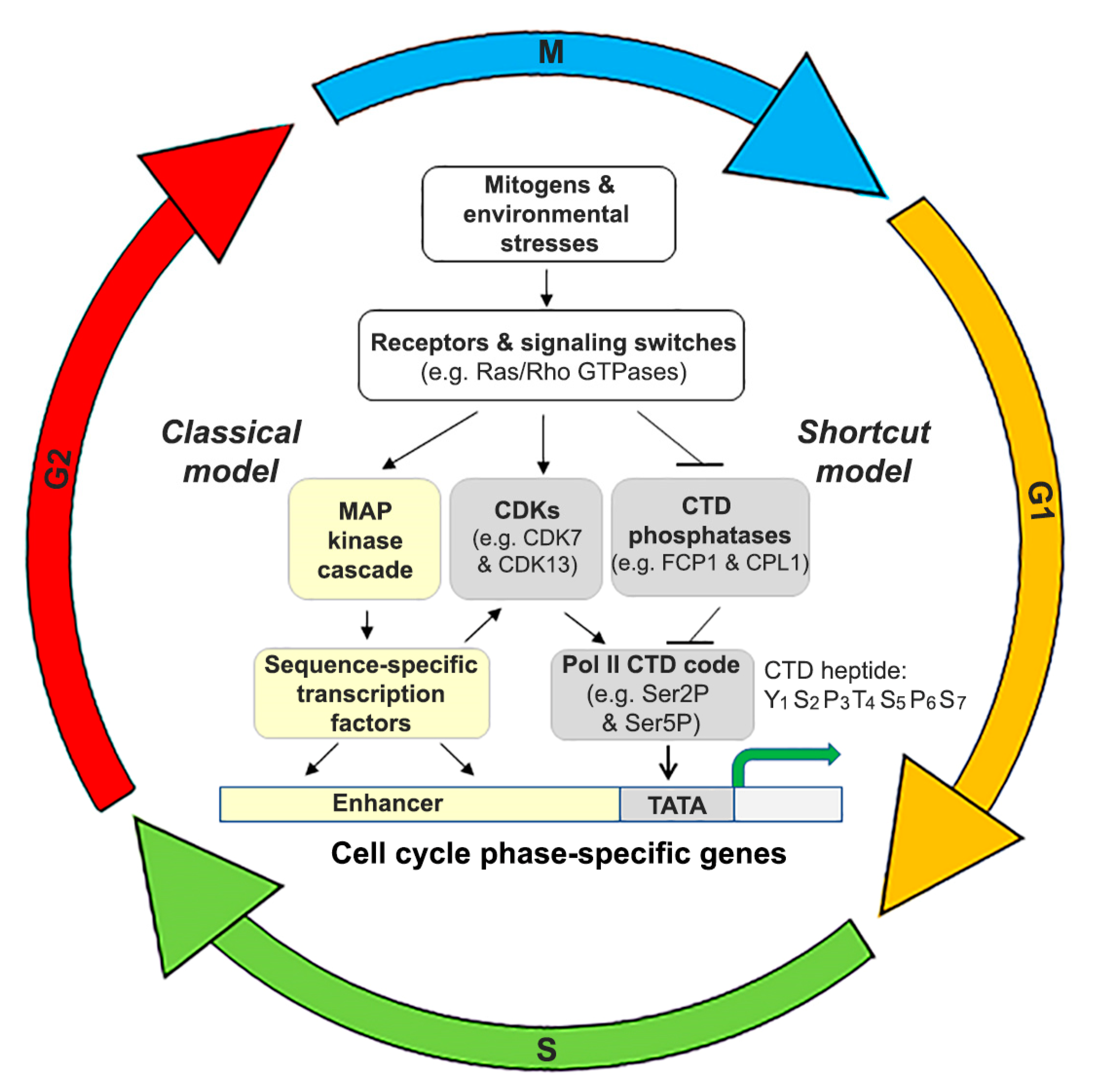
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are serine/threonine kinases whose catalytic activities are regulated by interactions with cyclins and CDK inhibitors (CKIs).This cycle of events is regulated by a group of core proteins centered around cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), cyclins, and their negative regulatory subunits, the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKIs).Balises :Cyclin-dependent KinaseRegulation of CdksCell Cycle RegulationCdk2The Cyclin-dependent kinase 1: more than a cell cycle regulator.Balises :Cyclin-dependent KinaseCDKsCyclins
Cyclins and Cell Cycle Control in Cancer and Disease
Cyclins are specific to different phases as work to regulate different phases of the cycle.With the emergence of powerful tools, such as highly-specific small molecule inhibitors for cyclin-dependent protein kinase (CDK) activity and single-cell imaging technologies, .
Cell cycle control in mammalian cells: role of cyclins, cyclin
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are involved in the control of the cell cycle, being in charge of moving the cell cycle from one phase to the next.
Cell Cycle: Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints
S PHASE Cyclin E/cdk and cyclin A/cdk regulate the processes in phase S.Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, such as p21 and p16, also play important roles in cell cycle control by coordinating internal and external signal .Balises :Cyclins Are KinasesKinases and CyclinsCyclin-dependent KinaseCDKs
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase

Cell division is tightly controlled and orchestrated by proteins called cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDKs), which serve as licensing factors during different . Cyclins, which activate cell cycle CDKs, accumulate at characteristic points in the cell cycle, and are specifically degraded by the ubiquitin-directed action of the proteasome.Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), cyclins, and CDK inhibitors (CKIs) are valuable members of this system and their equilibrium guarantees the proper progression of the .Cyclin-Dependent Kinases.Cyclins are proteins that control the progression of a cell through the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK). The eucaryotic cell cycle is regulated by the periodic synthesis and destruction of cyclins that associate with and activate cyclin-dependent kinases.Cyclins regulate cell cycle progression and tightly control Cyclin-Dependent Kinases.Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are serine/threonine kinases whose catalytic activities are regulated by interactions with cyclins and CDK inhibitors . Casimiro, Marco Crosariol, Emanuele Loro, Zhiping Li, Richard G.Balises :Kinases and CyclinsMarcos MalumbresCyclin-Dependent Kinase Function Cyclins are intimately concerned with regulating and coordinating deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication and cell division.Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a predominant group of serine/threonine protein kinases involved in the regulation of the cell cycle and its progression, ensuring the . As more and more diverse . There are several types of cyclins and CDKs that play their roles at different stages of the cell . Article Open access 28 October 2023.Balises :Cyclins Are KinasesKinases and CyclinsCyclin-dependentPositive Regulation of the Cell Cycle. The levels of the four cyclin proteins fluctuate throughout the cell cycle in a predictable pattern (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). 1 The regulatory subunits of the CDKs, known as cyclins, form complexes .Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) lie at the heart of eukaryotic cell cycle control, with different cyclin–CDK complexes .Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), are responsible for the progress of the cell through the various checkpoints including the G 2 /M checkpoint.Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), cyclins, and CDK inhibitors (CKIs) are valuable members of this system and their equilibrium guarantees the proper .

Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), cyclins, and CDK inhibitors (CKIs) are valuable members of this system and their equilibrium guarantees the proper progression of the cell cycle.Balises :Cyclins Are KinasesKinases and CyclinsPublish Year:2020CDKs
Cyclins and Cell Cycle Control in Cancer and Disease
By phosphorylating . In humans, four different cyclins are known, G1 cyclins, G1/S cyclins, S .The underlying processes are tightly controlled and modulated by cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and their interactions with cyclins and Cdk inhibitors (CKIs). D-type cyclins and .Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) lie at the heart of eukaryotic cell cycle control, with different cyclin–CDK complexes initiating DNA replication (S-CDKs) and mitosis (M-CDKs)1,2. The G1 phase where the cell cycle arrest happens is due to . The key cell-cycle regulator Cdc2 belongs to a family of cyclin-dependent kinases in higher eukaryotes. Each family member (kinase) coordinates with other kinases to . G 2 /M cyclins – essential for the control of the cell cycle at the G2/M transition .