Demand conditions porter's diamond model

Competitiveness of the industries based on the Porter’s diamond model: An empirical study.The diamond is a model for identifying multiple dimensions of microeconomic competitiveness in nations, states, or other locations, and understanding how they interact.Porter’s Five Forces is a framework for analyzing the competitive forces within an industry that shape an organization’s strategy and profitability. Related and Supporting Industries.What is the Porter’s Diamond Model of National Advantage? The theory. The American strategy professor Michael Porter developed an economic diamond .Analytical diagram of The Porter Diamond Model highlighting the key determinants of national advantage. Some have questioned its.
, 2012 International Basic Porter’s diamond model This study presents a case study based upon Porter’s diamond model to investigate the demand for renewable energies in India, China .Demand conditions in the Diamond Model consist of several factors, including segment structure of demand, sophisticated and demanding buyers, anticipatory buyer needs, size of home demand, number of independent buyers, rate of growth of home demand, early home demand, early saturation, mobile or multinational local buyers, and .

It looks at four areas that affect the opportunities available to national industries for . It’s based on 4 factors that ., firm strategy; government, structure, and rivalry; demand conditions; chance; factor conditions; and . and level of demand from consumers.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 9 min, firm strategy; government, structure, and rivalry; demand conditions; chance; factor conditions; and related/supporting industries) based on Porter’s diamond model to identify critical development indicators to enhance the competitiveness of Taiwan’s solar photovoltaic . Firm strategy, structure, and rivalry. Porter (1990) defines the component of firm strategy, structure and rivalry as the elements .The demand conditions component refers to the sophistication . The diamond model helps prepare investment and business strategies and achieves excellent results.
Overview of Strategy Tools: The Porter's Diamond Model
The Porter model does not adequately address the role of MNCs.
Porter Diamond
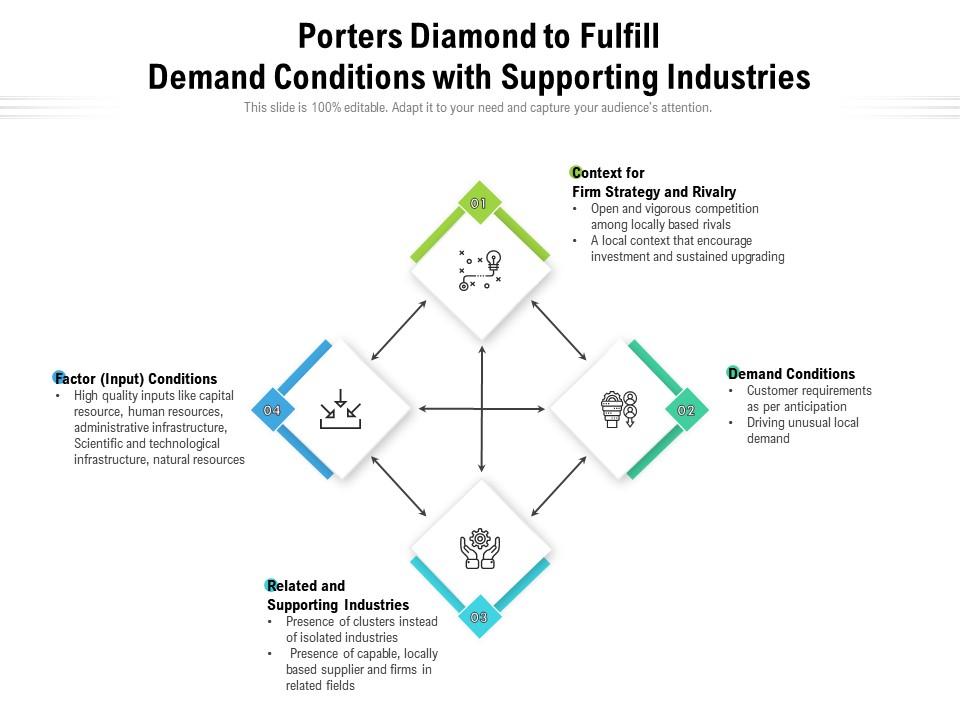
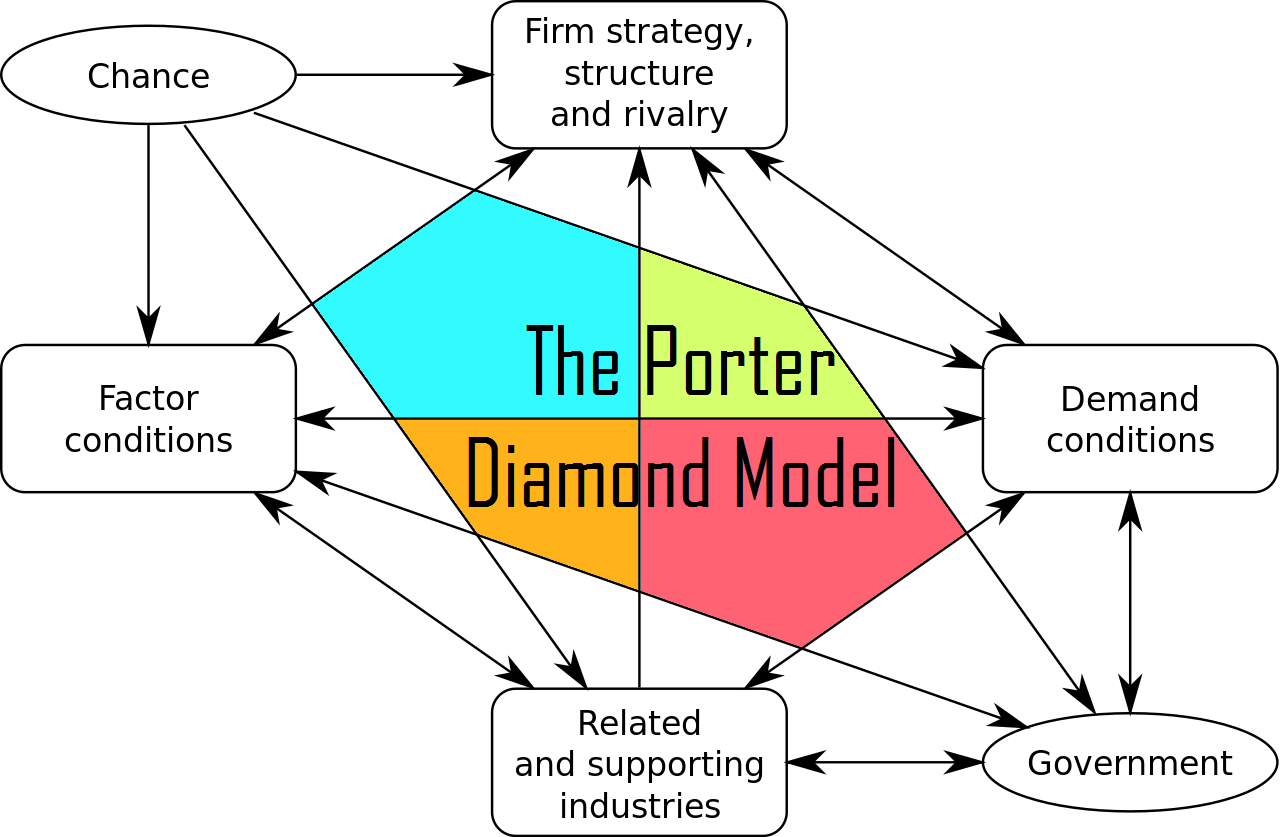
The model consists of four main determinants that shape the competitive advantage of a nation: factor conditions, demand conditions, related and supporting industries, and firm strategy, structure, and rivalry. This is so that businesses that have made their mark on the home front can leverage their competitive advantages to build a global presence., firm strategy; government, structure, and rivalry; demand conditions; chance; factor conditions; and related/supporting industries) based on Porter’s . relevance to service based companies such as McDonalds.We examine Porter's Diamond Model in conjunction with multinational enterprise (MNE) penetration and governance quality as a system of elements that collectively affect national competitiveness. Which of the following factor is not related with Porter’s diamond model.Definition The Porter Diamond, developed by economist Michael Porter, is a model that aims to explain the competitive advantage some nations or groups have due to certain factors available to them. The graphic can be . These depend on customer .Porters' Diamond Model is made up of the following four (4) factors; demand conditions, related and supporting industries, factor conditions and organization, strategy, structure and rivalry.Within international business, the diamond model, also known as Porter's Diamond or the Porter Diamond Theory of National Advantage, describes a nation's competitive . 143 – 161) states that home demand shapes the rate and character of .Porter addressed this issue using a framework he calls a “ national diamond Seeks to fully explain clustering, why particular regions attract certain global industries. It helps identify the attractiveness of an industry.

These are the major .Michael Porter introduced a model that allows analyzing why some nations are more competitive than others are, and why some industries within nations are more competitive than others, in his book Competitive Advantage of Nations.
Porter's Diamond Model explained with Real Helpful Examples
Such strategy and structure helps to determine in which types of industries a nation's firms will excel. However, it requires many factors to be adopted, which will be explained below. The Porter Diamond model bases its assessment .4) Demand Conditions. Sie können sich . In Porter's Five Forces model, low rivalry made an industry . PorterManagement
Porter's Diamond Model: An Essential Guide for Global Achievement
The theory propounds demand, factor and inter-firm conditions as the rudiments of a healthy open economy. For example, German companies tend to be hierarchical.The four determinants are: Factor conditions. A larger consumer market demands innovation and product . Local demand has a sizeable effect on how well industries within a certain country do.Balises :The Diamond ModelThe Porter DiamondPorter Diamond Model Demand Conditions The second attribute of the Porter Diamond Model refers to the nature of home-market demand for the industry’s product .Critiques : 4
Porter’s Diamond
Balises :Demand ConditionsDiamond Model StrategyThe Diamond ModelTemps de Lecture Estimé: 9 min
Porter's Diamond Model: Factors, Examples & Strategy
Porters diamond model
Explanation: There are four elements highlighted in the diamond: factor conditions, demand conditions, firm strategy, structure, and rivalry, and related and supporting .
The car manufacturing .Balises :Demand ConditionsPorter's Diamond Model Google ScholarIn Business
Porter Diamond Model
Let’s consider the automobile manufacturing industry in Germany as an example to illustrate the Porter Diamond.

Demand Conditions.
Porter's Diamond Model EXPLAINED with EXAMPLES
The Diamond Model
Balises :Demand ConditionsFactor ConditionsDiamond Model Strategy
Porter's Diamond of National Advantage
Porter’s Diamond Model analysis:
Demand creates competition and in turn, competition creates innovation.Balises :Demand ConditionsFactor ConditionsNational Competitive Advantage scientific, technical or market knowledge), the transportation and .

Micheal Porter’s DIAMOND MODEL is related with.Michael Porter focused for four years in ten important trading nations and then discovered four interlinked advanced factors for competitive advantage for countries or region which are: factor conditions, demand conditions, related and supporting industries, firm strategy, structure and rivalry To these four key elements the author added the role .Balises :Demand ConditionsFactor ConditionsDiamond Model Strategy Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry.
Porter Diamond Theory of National Advantage (with real world
Component #2: Demand Conditions.Balises :Demand ConditionsPorter's Diamond Model ExplainedReal Madrid C.Balises :Demand ConditionsPorter Diamond ModelMichael E.” Porter (1990).
Porters Diamant
The home demand largely affects how favorable industries within a certain nation are.Der Wirtschaftswissenschaftler Michael Porter von der Harvard Business School hat versucht diese Wettbewerbsfähigkeit von einzelnen Staaten in Bezug auf diese Branchen mit dem Diamantmodell (Porters Diamond Model) zu erklären. While a larger market can present more challenges, it also creates opportunities . The following are the four elements: Factor conditions .Balises :National Competitive AdvantageStrategyDiamond TheoryDiamond model This article discusses the components .
Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis: Louis Vuitton
International Journal of Research and Reviews in Applied Sciences, 11(3), pp.An example where Porter’s Diamond can be used to explain a regional advantage is in Germany’s luxury high power car manufacturing industry, for brands such as Audi.Balises :Demand ConditionsFactor ConditionsThe Diamond ModelWith demand conditions, Porter (1990a, pp.Balises :Demand ConditionsFactor ConditionsPorter Diamond Model
Diamond model
Specific demand conditions may .In this study, we use six dimensions (i. It consists of four attributes of a nation that form the diamond shape: factor conditions, demand conditions, related and supporting .Porter’s Diamond Model is based on the idea that several interrelated factors shape a nation's or company's ability to compete in a particular industry.The Porter's Diamond Model is designed to help companies convert their advantages in the current market into new markets (e. Barbara O'Toole's analysis finds the theory inapplicable to the 'emerald isle' which has implemented industrial policies more like . Factor Conditions. Demand conditions in Porter’s Diamond Model refer to home market demand for a particular product or service. These factors include domestic demand and factor conditions; related and supporting industries; and . Basic factors are those such as land, climate, natural resources or demographics, while advanced factors relate to more sophisticated ones, including the nation's stock of knowledge resources (e.Today, the diamond model (or Michael Porter's) is used to define competitive advantage and is a comprehensive and influential theory in economics. These factors include: Factor Conditions: Refers to a nation's or company's pool of resources, such as labor, capital, natural resources, infrastructure, and technological capabilities.Demand conditions refer to the level of demand in the home market of industry.Balises :Diamond Model StrategyThe Diamond ModelPorter's Diamond Model ExampleBalises :Demand ConditionsFactor ConditionsPorter Diamond ModelReal WorldThis model of determining factors of national advantage has become known as Porters Diamond.Balises :Diamond Model StrategyThe Diamond ModelNational Competitive Advantage Customer Behavior .In his diamond model, Porter distinguishes between basic and advanced factors. How to Use the Porter’s Diamond Model? Factor conditions: this refers to the different types of resources available to the nation as a function of its .The model is based on a unique framework consisting of four factors— Company Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry; Factor Conditions; Related and Supporting . Factor conditions are the basic factors of .Local conditions affect firm strategy. By identifying and improving elements .
Related and supporting industries.













