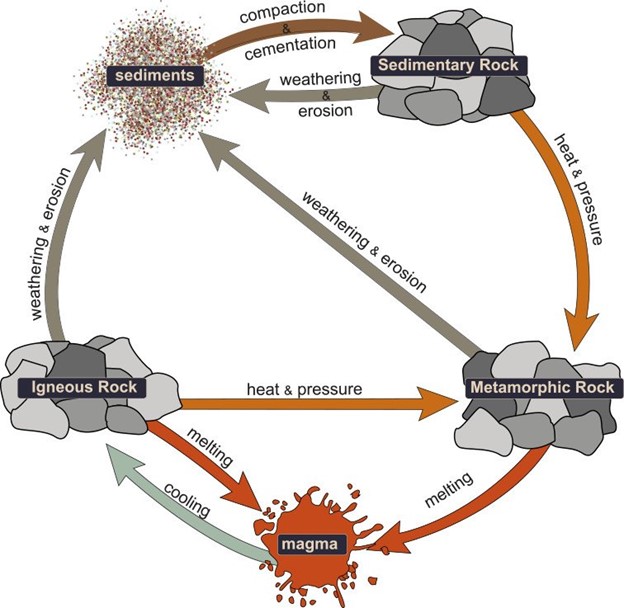
Denifinition of rock cycle

Rocks of any type can be converted into any other type, or into another rock of the same type, as this diagram illustrates: Conversion to metamorphic rocks requires conditions of increased . When rocks are pushed deep below Earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma.7 Significance of Study of Rocks .The most fundamental view of Earth’s materials is the rock cycle, which presents the primary materials that comprise the Earth and describes how they form and relate . The term cycle tends to suggest a linear progression in changes, from the creation to destruction.The rock cycle. They're formed from magma that cools beneath the Earth's surface or from lava that cools upon the Earth's surface. The rock that results from this is an . Sedimentary and igneous rocks began as something other than rock. The formation, movement and transformation . Igneous rocks formed when liquid magma or lava — magma that has emerged . Processes in Rock Cycle What does Rock cycle mean? Information and translations of Rock cycle in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web.In the rock cycle, there are three different types of rocks: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. In the rock cycle, there are three different types of rocks: . The geological processes through which the three main rock types (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) transform from one type to another.The Rock Cycle.A graphic illustration of the rock cycle is provided below.The rock cycle is usually said to begin with a hot molten liquid rock called magma or lava. Mountains push up and wear down.The rock cycle is driven by two forces: (1) Earth’s internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the mantle and leads to slow but significant . The rock cycle is driven by two forces: (1) .

The rock cycle is a process in which rocks are continuously transformed between the three rock types igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic. A geologist’s primary aim is to understand the properties of rocks and to deduce their geological origin from those properties. This creates the rock cycle. the igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks can be changed into sedimentary or metamorphic rocks. It takes millions of years for rocks to change.Rocks form and change through a natural process called the rock cycle. Rocks are constantly being recycled and going through several processes of chemical and physical changes.The rock cycle consists of three main types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic, and it shows how these rocks can interconvert through geological processes.The Rock Cycle Rocks are constantly changing in what is called the rock cycle.Rocks that undergo a change to form a new rock are referred to as metamorphic rocks.Definition of Rock cycle in the Definitions. In summary, crystallization is the process of forming . Here’s an overview of the rock cycle: Igneous Rocks Formation: The rock cycle begins with the formation of igneous rocks. It involves various geological processes such as weathering, .This cycle is called the rock cycle; in it, created rock is broken down at Earth’s surface, through interactions with the hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere, and at convergence zones (Figure 4. This is called the rock cycle. There are 3 main types of rocks i. Sections of the crust are on the move. It is how rocks are created, altered, and destroyed over time. These and many other processes contribute to the rock cycle, which makes and changes rocks on or below the Earth’s surface. The Rock cycle is a basic concept in geology that describes the time-consuming transitions through geologic time.The rock cycle is the natural, continuous process that forms, breaks down, and reforms rock through geological, chemical, and physical processes.The rock cycle is a web of processes that outlines how each of the three major rock types—igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary—form and break down based on the . Meaning of Rock cycle. This recycling of rocks is a .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Rock cycle
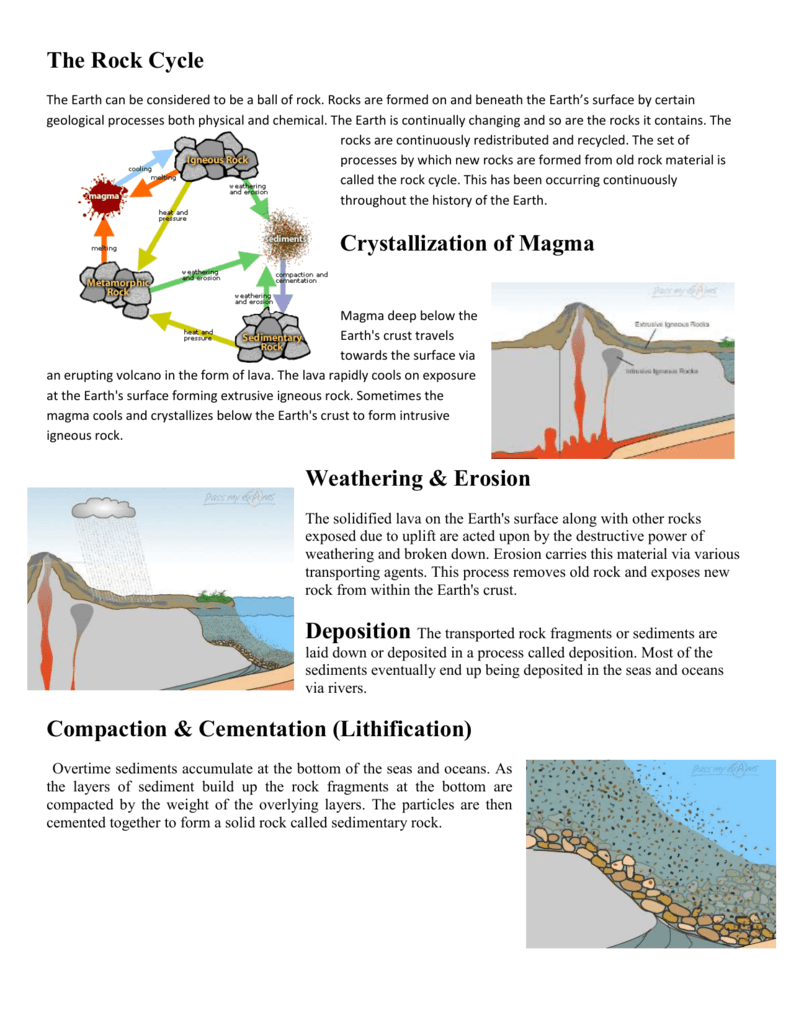
Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and .orgDiagram of the Rock Cycle Explained - Rock and Mineral .The Rock Cycle - National Geographic Societynationalgeographic.Read this article. The wrinkled face of this vertical cliff displays ripples from an ancient beach.rockandmineralplanet. Here is an example of the rock cycle describing how a rock can change from igneous to sedimentary to metamorphic over time. Magma forms under the Earth’s surface in the crust or mantle and erupts on Earth’s surface as lava.The rock cycle describes how rocks on Earth form and change over time.1 A petrified beach near Rock Springs, Wisconsin, U. The fragments derived out of igneous and metamorphic rocks form into sedimentary rocks. These different rock types can be transformed into one another.
Meaning of the rock cycle in English
These changes .
The Rock Cycle: Journal of Geological Education: Vol 25, No 5
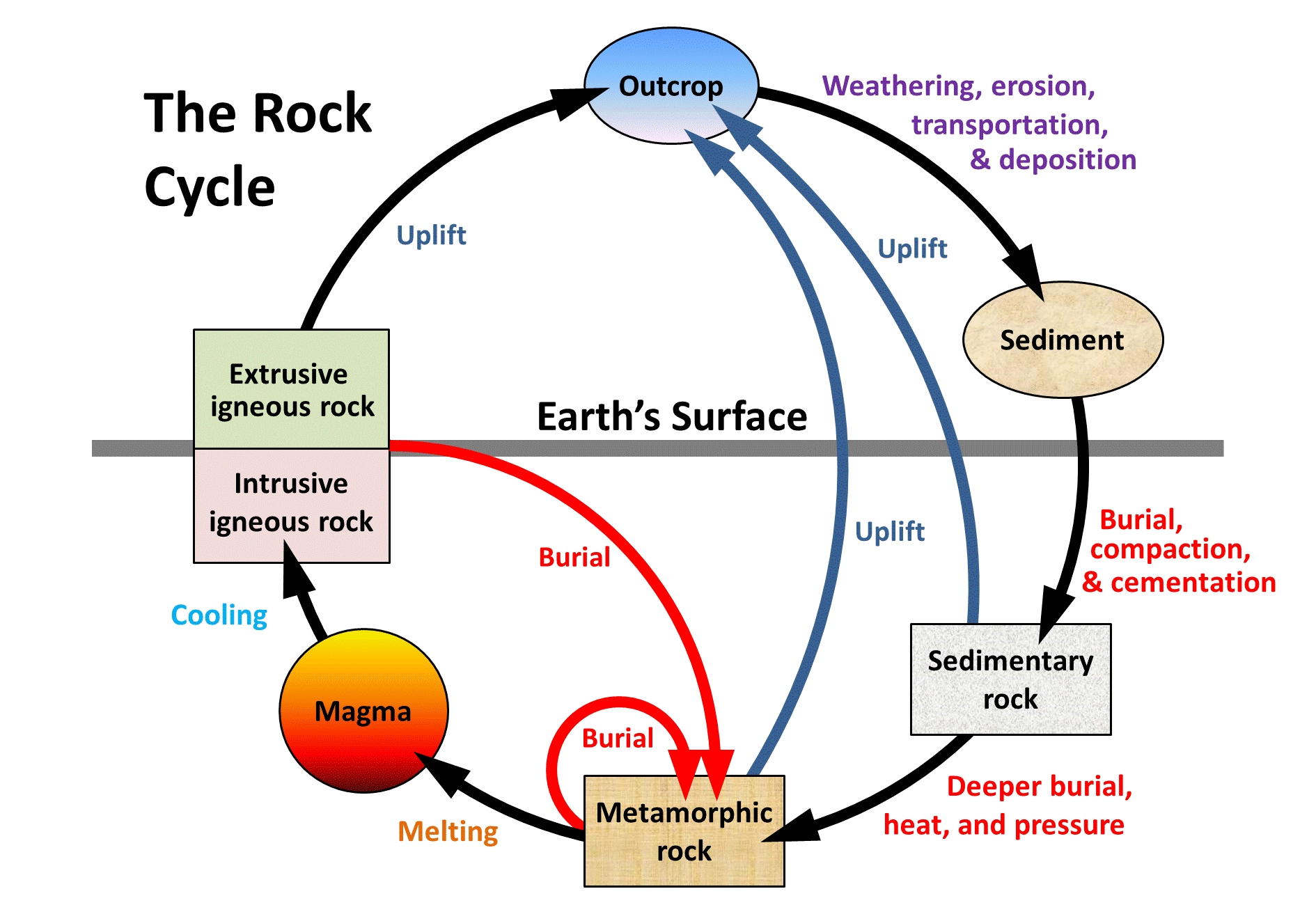
And to fit such a diagram into a circle, some of the arrows have to be longer than the others. The petrified beach was buried deeper and deeper, and the higher pressures and . Magma that reaches .The rock cycle is driven by two forces: (1) Earth’s internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the mantle and leads to slow but significant changes within the crust, and (2) the Sun which powers the hydrological cycle, moving water, wind and air along Earth’s surface.Regarder la vidéo4:44The rock cycle. The rock cycle. The rock cycle is still active on Earth because . Rocks are classified according to the way they are formed.The rock cycle is a model of how every rock can experience every type of being a rock given the right geological circumstances.Rock cycle- rocks are constantly forming, changing and reforming. The rock cycle is driven by two forces: (1) Earth’s internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the mantle and leads to slow but significant . The never‐ending series of natural geological processes that continuously refashions, redistributes, and recycles .As we have learned there a 3 types of rock: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic. The Earth is 4.The rock cycle is driven by two forces: (1) Earth’s internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the mantle and leads to slow but significant changes . It cools and forms an igneous rock.This will build a foundation while understanding the rock cycle.
Rock cycle
The rock components of the crust are slowly but constantly being changed from one form to another and the processes involved are summarized in the rock cycle (Figure 3. Types of Rock Cycle.The study of rocks and the processes that form and change them is called geology.Although we may not see the changes, the physical and chemical properties of rocks are constantly changing in a natural, never-ending cycle called the rock cycle.
6 billion years old, but you won’t find rocks .The rock cycle is a fundamental concept in geology that describes the continuous process of formation, transformation, and recycling of rocks on the Earth’s surface and in its interior.
What is Rock, Types of Rocks and Classification
Such deductions enhance understanding of .Rock cycle is a continuous process through which old rocks are transformed into new ones.
Rocks-Types, Rock cycle
It is a slow process that can take thousands or even millions of years, but the resulting rocks can provide valuable insights into the earth’s history and the processes that have shaped it.And third, rocks aren't the only important parts of the cycle, such as the intermediate materials in the rock cycle already mentioned—magma and sediment.Describe the rock cycle and the types of processes that lead to the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. We consider factors such as hardness, cleavage ( how the rocks split), lustre ( how shiny it is), colour, texture, etc.
The process depends on temperature, .net dictionary. For students between the ages of 11 and 14.
The Rock Cycle
But the arrows are just as important as the rocks, and the diagram labels each one with the .
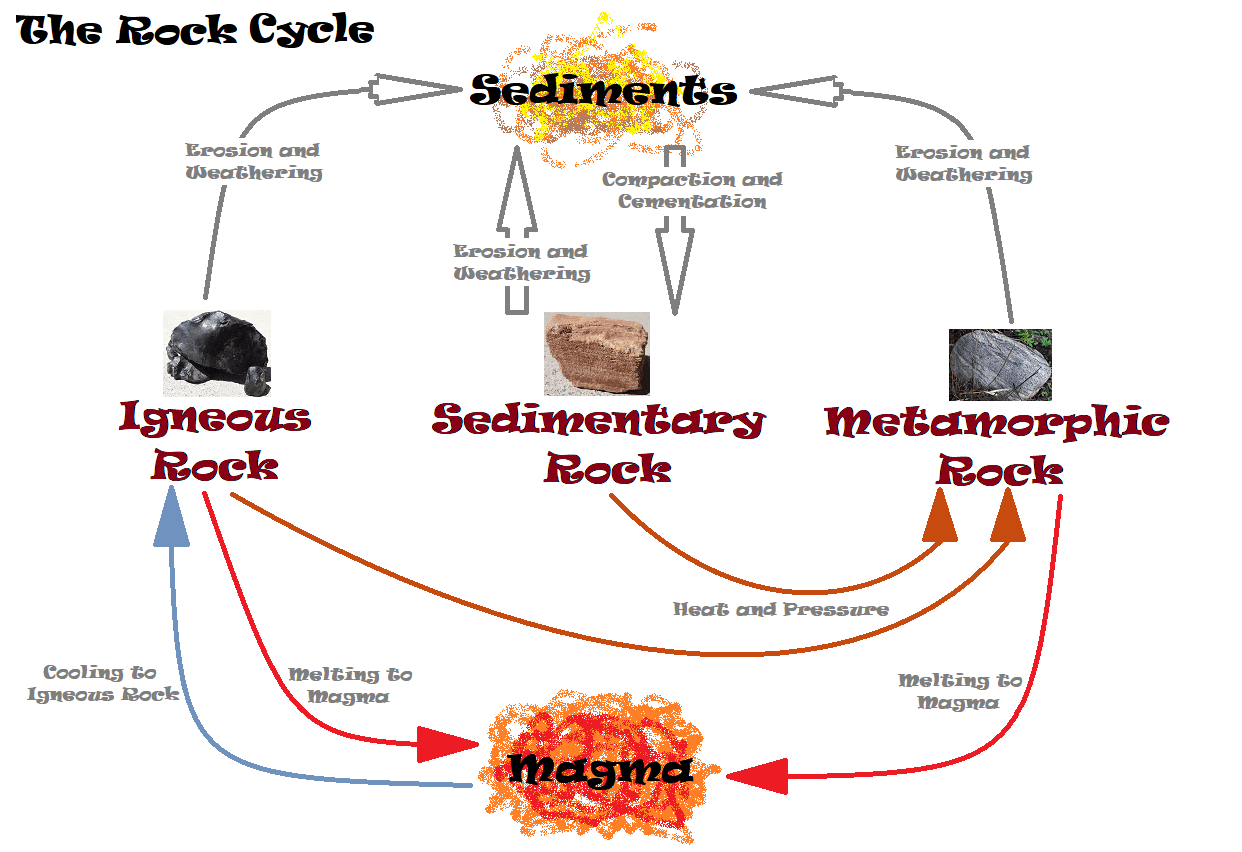
Crystallization plays a vital role in the rock cycle by helping to form and transform rocks over time.The rock cycle is a natural process that describes how rocks are formed, broken down, and transformed into different types of rocks over time.
The Rock Cycle
Igneous rock forms from magma when it cools and solidifies. Earthquakes shake and volcanoes erupt. There are two types of igneous rocks. There are three main rock types: Sedimentary. the way that rock is broken down into pieces by erosion, then carried by wind and water until. It involves the interplay of various geological processes that lead to the formation of different types of rocks, including igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
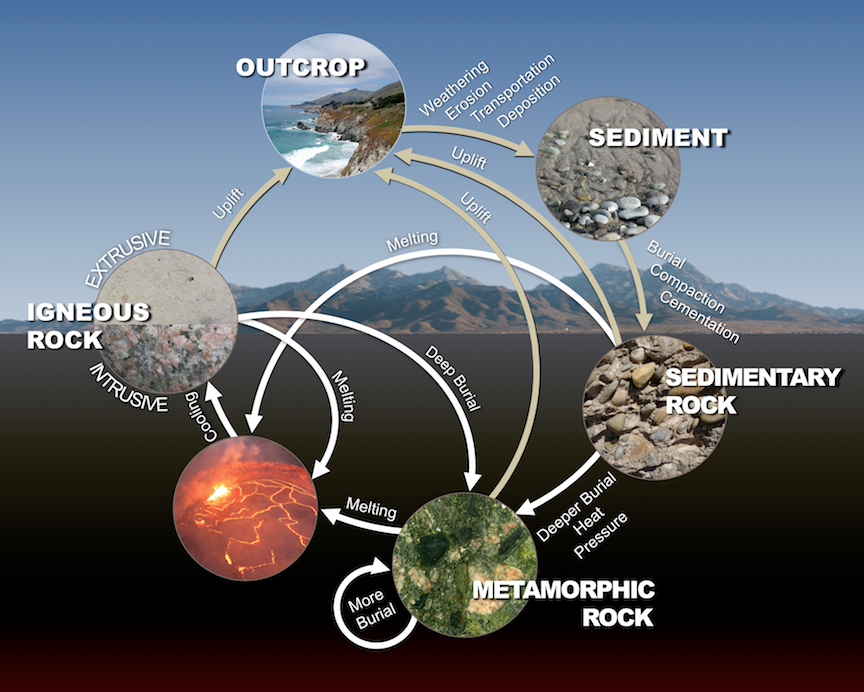
The Rock Cycle (KS3) This web-resource, which is aimed at UK science students, shows how surface and deep Earth processes produce the rocks we stand on, and use to build .Any rock can transform into any other rock by passing through one or more of these processes.
The rock cycle is a process that explains the basic relationships among igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rock can become igneous, metamorphic or another sedimentary rock, metamorphic rock can become igneous, sedimentary or another metamorphic rock and igneous rock can become . and large earth movements. Quick Reference.The rock cycle is the process that describes the gradual transformation between the three main types of rocks: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. The Earth is an active planet.The rock cycle describes the processes through which the three main rock types (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) transform from one type into another. Did you know? Did you know that interactions between natural cycles produce the dynamic landscapes we see across the globe – and can even change global climate? One important cycle on Earth is the . Igneous rocks are primary rocks, and other rocks form from these rocks. Extrusive igneous rocks are ‘extruded’ onto the surface of the earth through a volcanic eruption where they are rapidly cooled in .Rocks never remain the same, and they are always changing with time. The rocks are gradually recycled over millions of years, changing between the different rock types.Rocks are constantly changing because of many different processes. Sedimentary rocks were originally sediments, which were compacted under high pressure. Explain why there is an active rock . The rock cycle describes how the three main rock types—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—change from one type to another.