Diode characteristic curve

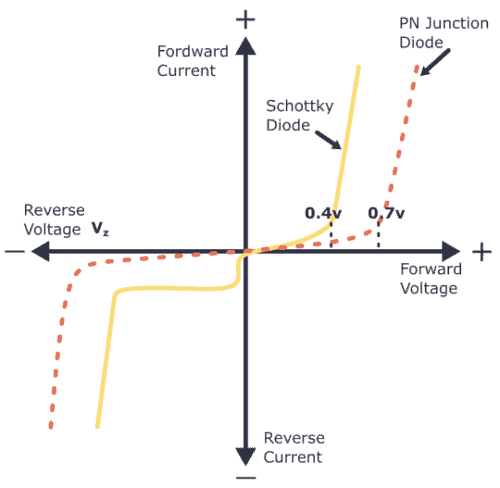
Hence, characteristics of diode can be studied . A negative voltage means the diode is operating with reverse bias.3V, the diode becomes forward-biased. But this plot has an inconsistent current scale, for negative voltages the current may be uA or less, and mA or more for positive voltages. Similar to any other device or electric component, a diode has ratings for maximum voltage and maximum . When the applied voltage to the Schottky diode exceeds 0.Both elements are brittle and have a metallic luster.1: Theory Overview; 3.Diode Characteristic Curve. All diodes should list maximum current, reverse voltage, and power dissipation. However, their I-V characteristics are very different.
Also, the intensity of light emitted by the device varies in proportion with the forward current flowing through it.A typical characteristic curve for a diode is shown in Figure 1.Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\): Characteristic curve of forward-biased silicon PN junction using log scale. It should also be observed that the slope is a function . Basic DC circuit operation will also be examined.The diode equation gives an expression for the current through a diode as a function of voltage.video demonstrates how to draw Current Voltage(IV) characteristics curve of an ordinary diode and a Zener diode in Proteus.Graphing the V-I Curve If you plot the results of the type of measurements shown in Figure on a graph, you get the V-I characteristic curve for a forward-biased .This method is used to approximate the diode characteristic curve as a series of linear segments. For negative voltages (reverse-bias) the Shockley equation predicts negligible diode current. For example, we can imagine a .3: Schematics; 3.The linear model of the diode approximates the exponential I - V characteristics by a straight line that is tangent to the actual curve at the DC bias point. Electronic Devices MID Term Handnote. With a diode, I and V have an exponential relationship. import numpy as np import matplotlib. An equation that models the I-V characteristic of a non-ideal diode is shown below. diode-characteristic-curve. Rectifier diode. In general, a particular diode might have a combination of these two effects going on, and so people often use a more general form for the diode equation: I = IsateqVa nkT I = I sat e q V a n k T.
Transistor Characteristic Curves
Non-Ideal Diode I-V Curve and an approximation to the non-ideal diode Figure 3. When it is forward biased (the higher potential is connected to the p-type lead), it will pass current.The objective of this exercise is to examine the operation of the basic switching diode and to plot its characteristic curve. Some specialized diodes have a breakdown voltage that is only 5 V.Three important characteristics of a diode are, first of all, the forward voltage drop.Diode Attributes.
Diode Characteristics
This example shows the I/V curve of a diode. This characteristic is useful in building electronic logarithmic converters.4: Procedure; 3.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 min
Diode Characteristic Curve
ExampleTools import find_libraries from .setup_logging() from PySpice. Electronic Devices 100% (2) 7. where n n is called the ideality factor and is . Before two explains the purpose of the silicon doping.

Resistors, for example, .
Device exp 4 lab report Study of Zener Diode.The characteristic curves of a transistor provide the relationship between collector-emitter voltage and collector current for different values of the base current.
Manquant :
This curve shows the variation of the diode current versus the voltage across the diode.The Shockley diode equation, or the diode law, named after transistor co-inventor William Shockley of Bell Labs, models the exponential current–voltage (I–V) relationship of .A semiconductor diode's current–voltage characteristic can be tailored by selecting the semiconductor materials and the doping impurities introduced into the materials during manufacture. It has low forward voltage loss that's why its characteristic curve is close to current axes as compared to normal diodes.The breakdown voltage for a diode depends on the doping level, which the manufacturer sets, depending on the type of diode. Diodes are often used as rectifiers in power supply circuits to convert an AC voltage to a voltage containing an AC and a DC component.6: Questions; This page titled 3: Diode Curves is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4. Electronic Devices 100% (2) 13. A typical curve is shown in Figure 2a, and a set of . Device Lab Report-1 - extra. A diode is a semiconductor device made of a PN junction which is a sandwich of two doped silicon layers.Non-Linear CharacteristicsI-V Characteristic Curves or Current-Voltage Curves
The most important diode characteristic is its current-voltage (i-v) relationship. That chart points out another important diode characteristic -- the maximum forward current.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 minThe diode law for silicon - current changes with voltage and temperature. The Ideal Diode Law, expressed as: I = I 0 ( e q V k T − 1) where: I = the net .
3: Diode Curves
Critiques : 81
PN Junction Diode
These techniques are used to . The curve intersects the horizontal axis at the voltage V D0.Determination of Characteristic Curve of a Diode.A plot of \(I\) as a function of voltage or an I-V characteristic curve might look something like Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\).The Zener diode receives forward voltage, which is positive voltage across its anode and cathode terminals, on the right half of the characteristics curve. Consider the following circuit with AC input voltage .
Vin Vo Vg slope=1 Figure 15. the diode From figure 3, we see that both diodes and resistors are two .

Shockley diode equation
For a given current, the curve shifts by approximately 2 mV/°C.Critiques : 34
PN Junction Diode and its Forward bias & Reverse bias characteristics
Hint : The characteristics curve of a diode is sufficient for us to infer that a diode is not an Ohmic device. A diode in its most basic form is simply made by the . Google Classroom. The real diode is modelled as 3 components in series: an ideal diode, a . A low-pass filter then removes the AC component, resulting in a DC output voltage. The basic difference between a forward bias and reverse bias is in the direction of applying external voltage. If it converts a half-wave of alternating current into direct then this process is called half-wave rectification. The picture below shows the symbol of PN junction . The light blue curve shows the effect on the IV curve if I 0 does not change with temperature. When it is reverse biased (the higher potential is connected to the n-type lead), the current is blocked. the diode From figure 3, we see that both diodes and resistors are two terminal devices.From this characteristic of the ideal diode, we see that it is highly nonlinear. Voltage transfer characteristic of the rectifier circuit.2 volts in magnitude that the reverse current is the value for I S and is independent of reverse voltage –this is why it is referred to as the reverse saturation current. Under a forward bias condition, this should be about .the logarithm of the current through the diode. 6: Recombination dominated diode behavior.The dotted section of the curve indicates the ideal curve, which would result if it were not for avalanche breakdown. The direction of external voltage applied in reverse bias is opposite to that of external voltage applied in forward bias.The i-v curve of a diode, though, is entirely non-linear. In reality, I 0 changes rapidly with temperature resulting in the dark blue curve.

The Complete V-I Characteristic Curve Consequently, we cannot use the superposition technique to solve diode circuits unless we have a priori knowledge about it, that is, whether or not it is forward- or reverse-biased.
Diode Characteristic Curve Explanation
This nonlinear voltage . An Ohmic device is a device which does not obey ohm's law.I = IsateqVa 2kT I = I sat e q V a 2 k T. The current is tiny for .Now, let's discuss the voltage and current characteristics of the Schottky diode. When the reverse voltage is large enough, the diode will start to . Complete step by step answer A diode is generally stated to be a device which allows current to flow in one direction only.
A diode characteristic curve is a plot between
There are two ways in which we can bias a pn junction diode. This is true up to a point.V-I Characteristics curve of Zener Diode. A positive voltage . However, the diode behaves this way because the straight-line segments are at 90° to each other. The resistor vs.The voltage transfer curve for this circuit is shown on Figure 15 and it is derived from the I-V characteristic of the diode model and Kirchhoff’s voltage law.This example shows how to simulate and plot the characteristic curve of a diode.pyplot as plt import PySpice. Theory ¶ A diode is a semiconductor device made of a PN junction which is a sandwich of two doped silicon layers. In this region, the diode is forward biased.8 shows the curve with the tangent line at the point (V D, I D). Just like any component, diodes can only dissipate so much power before they blow.
Diode graphical solution (video)
The following figure shows the static characteristic of a . We will give a quick and simplified look on the atomic world.Read in details:https://www. Note that once the reverse voltage exceeds about -0. One way to cause a metalloid to conduct electric current freely is to heat it up.Diode Characteristics 5 Near Zero Bias A theoretical plot of the diode current for the near zero bias condition is shown in Figure 4. It looks something like this: . When the diode is forward biased, anode positive with respect to the cathode, a forward or positive current passes . This defines what the current running through a component is, given what voltage is measured across it. A positive voltage means the diode is forward biased. Because there are two parameters that affect IC, a set of individual curves shown together denote various operating conditions. Explore the effects of bias voltage, diffusion, depletion layer and rectification on the diode's current .Diode i -v curve of a silicon diode. The equation does not model the effects of breakdown. From the voltage transfer curve we observe the following: • Vo = Vin-Vg for Vin ≥ Vg,5: Data Tables; 3.
The diode characteristic curve is a plot between,
2: Equipment; 3. On the right-hand side of the vertical axis (the current axis), a diode is forward biased because the voltage applied across it is positive. The Zener diode goes through several different stages or zones, which are described here. Each of these elements has an outer electron shell that contains four electrons; this property of silicon and germanium makes it difficult for either element in its purest form to be a good electrical conductor. Then there is the reverse voltage . Electronic Devices 100% (2) 60.Diode graphical solution (video) | Diode | Khan Academy.In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Voltage Current Characteristics of Diode.














