Distinguish which tissue is vascular
Contents Contents.
Vascular Plants
produces the inner bark toward the exterior of the stem.
Vasculature
Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of . Phloem cells are divided into sieve elements, or conducting cells, and supportive tissue. Some common examples of phanerogams include clover, oak trees, and . Moving from the innermost layer outward are the metabolically active endothelium, the intima (with nerves .Their ability to hold this much blood is due to their high capacitance, that is, their capacity to distend . Secondary vascular tissue is added by the vascular cambium, and the cork cambium generates the periderm.infoStructure and Function of Blood Vessels - Lumen Learningcourses. It's also called the circulatory system. Epithelial tissues are classified according to the shape of the cells and number of the cell layers formed (Figure 4. By the late Devonian period, plants had evolved vascular . They contain tissue that transports water and other substances throughout the plant. Just below the tip of the root, there is a region of small, densely packed cells that are actively dividing. Skip to Content Go to accessibility page Keyboard shortcuts menu. Just as blood vessels direct material towards the tissue, they also facilitate the removal of cellular byproducts, carbon dioxide, and toxic chemicals from the tissue. Ferns are the most common and best-recognized examples of vascular seedless plants. Cell Reports Medicine , 2024; 101525 DOI: ., skin), lines an internal body cavity (e. They form a complex network running .
What is the Difference Between Vascular and Avascular Tissue
Large leaves with .Vascular anatomy is generally described in terms of distinct layers. The term xylem is derived from the Greek word ‘xylon’ which means wood as the best-known xylem tissues are found in the woody part of the stem.By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain the general structure and function of epithelial tissue. Blood vessels can form complex network . Connective tissue is innervated except for cartilage.
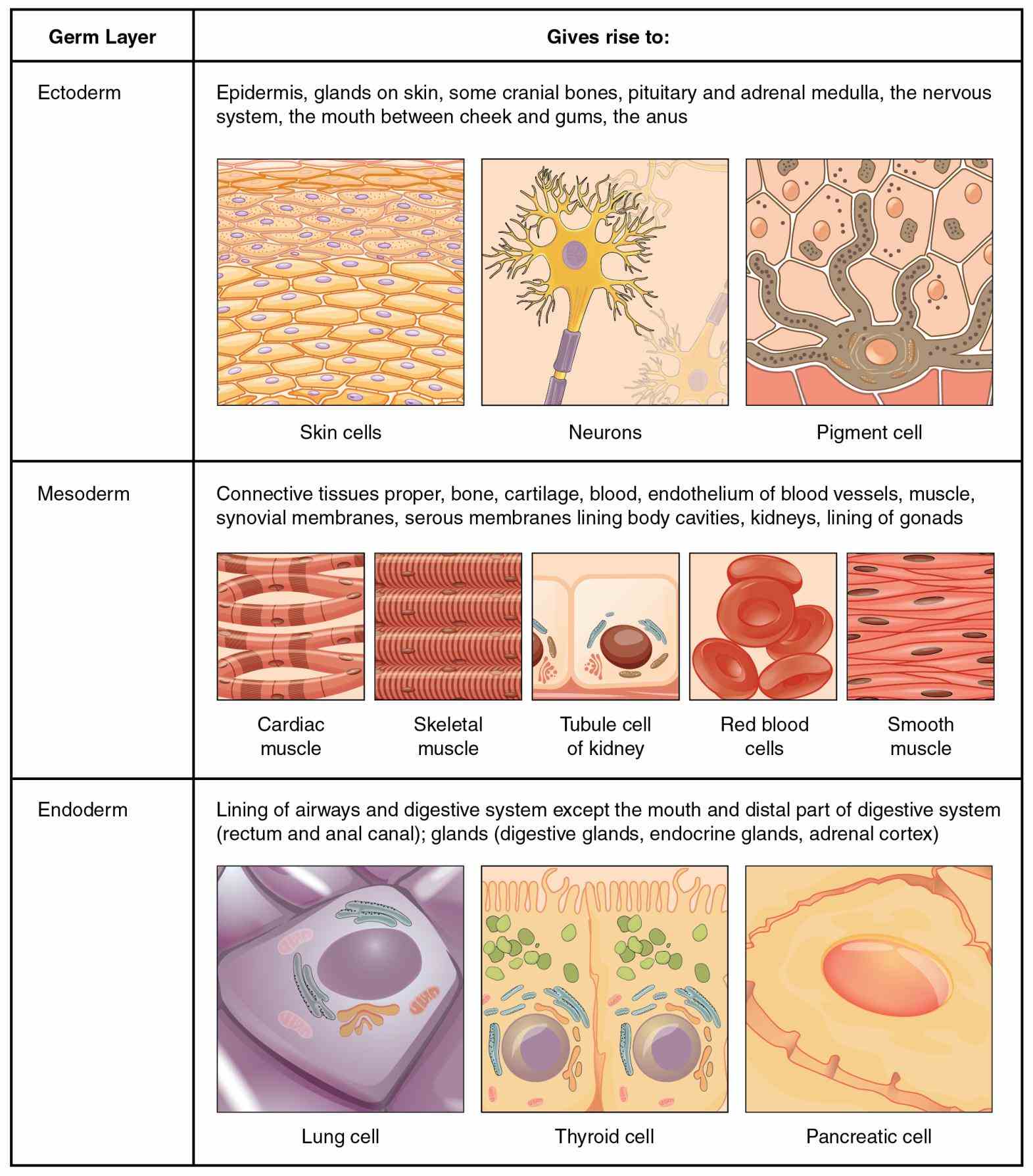
The vascular system is made up of the vessels that carry blood and lymph fluid through the body. A layer of cells known as the endodermis borders the stele (Figure 3.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Epithelial Tissue, the 4 types of tissue, Loose Connective Tissue and more. It is found lining the inner and outer body surfaces and comprising the parenchyma of the glands. Dermal tissue covers the plant and can be found on . Identify the main tissue types and discuss their roles in the human body. These are the metabolically active organs of the body such as the brain, skeletal muscles, and heart. To the outside (below, in your slide) of the root tip, the RAM cells produce an ephemeral tissue called the root cap.The vascular tissue transports water, minerals, and sugars to different parts of the plant. The ground meristem produces the pith and . The primary xylem, fascicular cambium, and primary phloem arise from the procambium.2: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels - Medicine . Vascular tissue is made of two specialized conducting tissues: xylem, which transports water and also provides structural support, and phloem, which transports sugars from sites of photosynthesis to other parts of the plant. Together, xylem and phloem tissues form the vascular system of plants. Most blood vessel . Here is a look at what xylem and phloem are, what they transport, and how they work.The vascular system is a network that consists of a pump (the heart) that provides the force for flow of blood through arteries, capillaries, and veins. Ground tissue is a simple tissue, meaning that each ground tissue consists of only one cell type. Two basic types of tissue membranes are recognized based on the primary tissue type ., blood vessel), or lines a movable joint cavity (e.Vascular systems consist of xylem tissue, which transports water and minerals, and phloem tissue, which transports sugars and proteins.Connective tissue is classified into two subtypes: soft and specialized connective tissue. Skeletal muscles are striated, or striped in appearance, because of their internal structure. By the end of this section, you will .
Connective Tissue
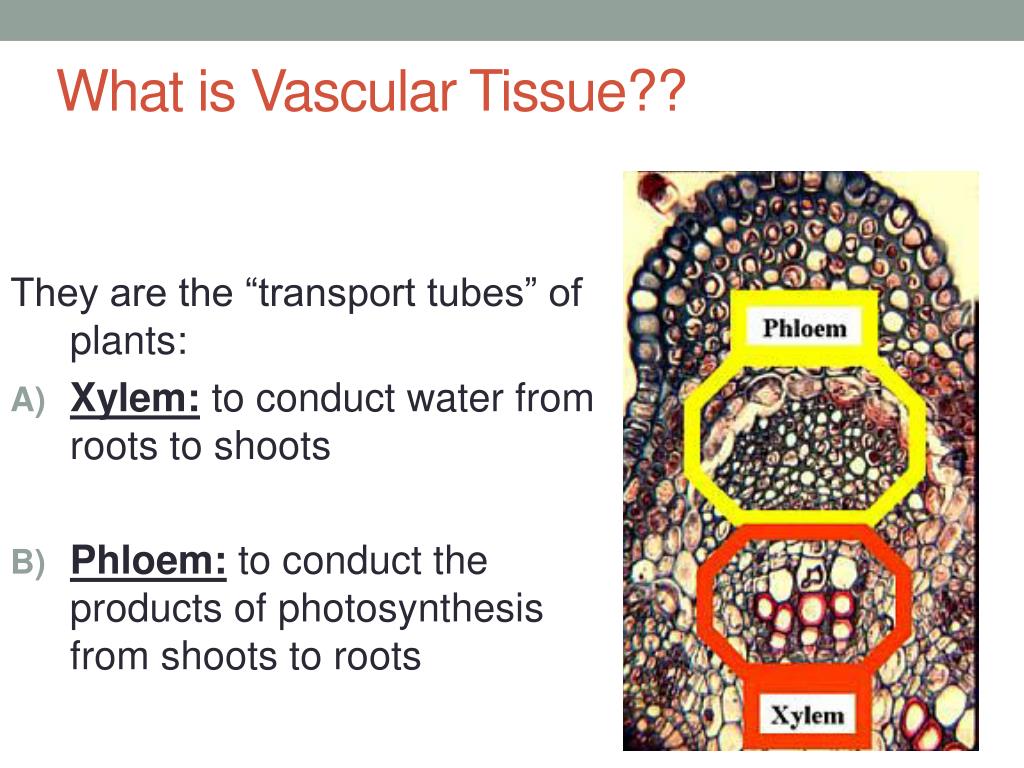
The procambium produces vascular tissues. Cell shapes can be squamous (flattened and thin), cuboidal (boxy, as wide as it is tall), or columnar (rectangular, taller than it is wide).α2δ1-mediated maladaptive sensory plasticity disrupts adipose tissue homeostasis following spinal cord injury.2 Epithelial Tissue . Often, material, such as nutrients and water, that is transported throughout the . The xylem and phloem always lie adjacent .Accordingly, newly formed and therefore immature blood vessel networks have very different properties compared to those of the adult organism, which may also explain the great difficulty that is associated with the generation of artificial vascular structures in tissue engineering. Nonvascular plants lack vascular tissue; vascular plants have specialized tissue for conducting water and nutrients within the plant.This complex vascular highway functions to deliver blood cells, nutrients, oxygen, and pharmacological agents to tissue.Anatomy, Blood Vessels - PubMedpubmed. It is divided into surface (covering) and glandular (secreting) epithelium. The leaves of ferns have megaphylls—or leaves with more than one vein and a leaf trace/leaf gap association—which are large and usually subdivided into many lobes.A second type of vascular tissue is phloem, which transports sugars, proteins, and other solutes through the plant. Furthermore, vessels of different tissues show distinctive . Dermal Tissue . Connective tissues can have various levels of vascularity. Biga, Sierra Dawson, Amy Harwell, Robin Hopkins, Joel Kaufmann, Mike LeMaster, Philip Mat.The inner portion of the root contains the vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion of ions and molecules.adipose Adipose tissue, areolar tissue, cardiac muscle tissue and bone are considered vascular because they contain blood vessels such as arteries and veins, unlike avascular . In the primary stem, vascular bundles surround a central pith. Why does it matter if a tissue is vascular or avascular? A vascular tissue is well supplied with vessels that allow easy exchange of gases and nutrients.
chapter 4 review Flashcards
(Circle the correct answer.The vascular system shares common histology however, there are key differences among the diverse system. Connective tissue underlies and supports other tissue types.The main difference between vascular and avascular tissue is that vascular tissue consists of vessels that conduct fluids like blood and lymph whereas avascular . vascular cambium.
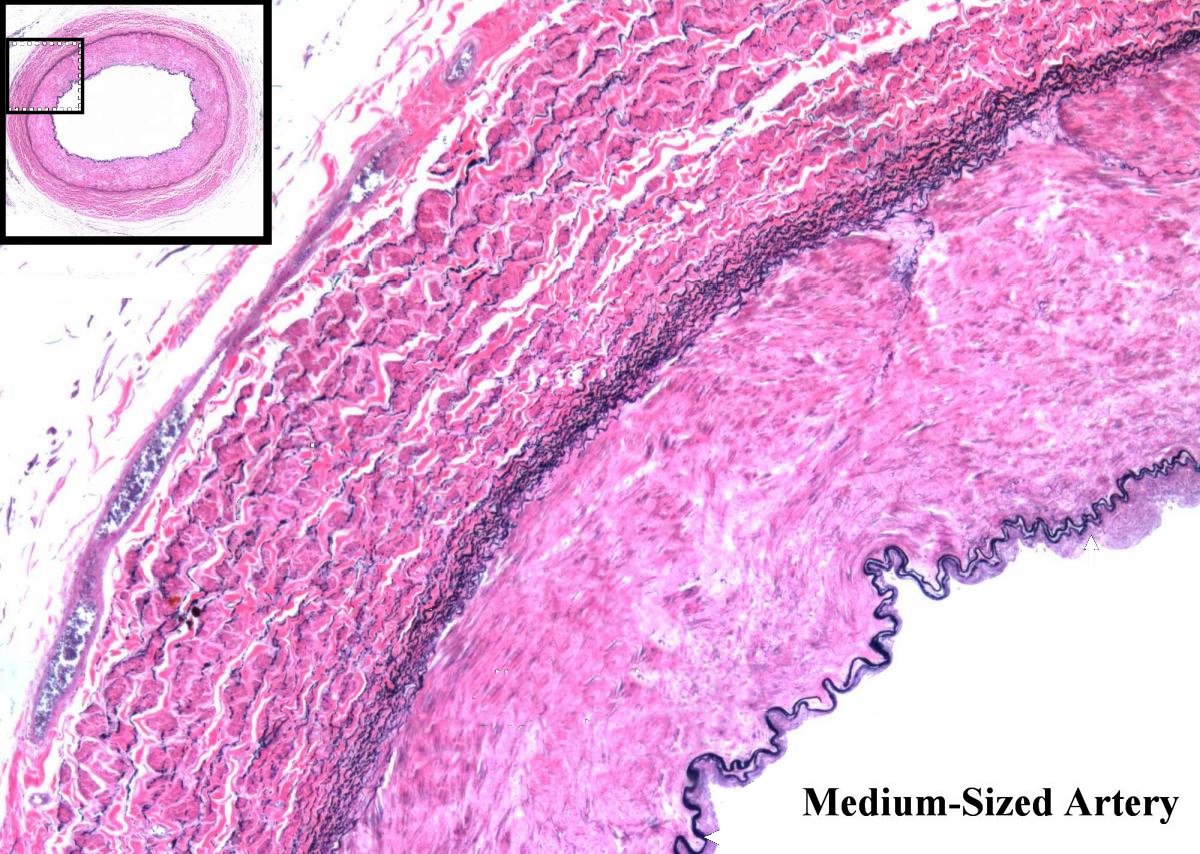
Histology, Blood Vascular System
The protective coat that replaces the epidermis in plants during secondary growth, formed of the cork and cork cambium. The arteries and veins carry blood all over the body. Innervation: Epithelial tissue also doesn’t have nerve supplies.Division Pterophyta. Xylem The xylem is a complex tissue containing . There are three major types of muscle tissue, as pictured in Figure 10.Publiée : 2023/04/24 Similarly, the number of cell layers . Small uncomplicated leaves are microphylls. This chapter explains the structure and function of the primary meristems, the types of primary tissues, and the anatomy of herbaceous stems, roots, and leaves.

Learning Objectives. Nutrition: The cells in the epithelial tissue obtain their nutrition from the cells underneath via diffusion.Xylem is a vascular tissue that transports water and dissolved minerals absorbed from the roots to the rest of the plant.This type of smooth muscle is observed in the large airways to the lungs, in the large arteries, the arrector pili muscles associated with hair follicles, and the internal eye muscles which regulate light entry and lens shape. Major functions of connective tissue include: 1) binding and supporting, 2) protecting, 3) insulating, 4) storing reserve fuel, and 5) transporting substances within the body. A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that either covers the outside of the body (e.
Overview of the Vascular System
Xylem and phloem are the two types of transport tissue found in vascular plants., peritoneal cavity), lines a vessel (e. This includes repair and replacement of diseased or damaged vessels, removal of plaque from vessels, minimally invasive procedures including the insertion of venous catheters, and traditional surgery. Hence, the ‘finger’ look to a fern plant. These cells make up the RAM. Some organs are highly vascular.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Histology, Vascular
Anatomy and Physiology 2e 4. 1: In woody plants, primary growth (left) is followed by secondary growth (right), which allows the plant stem to increase in thickness or girth.Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants.Identify and distinguish between the different type of connective tissue: proper, supportive, and fluid – and associate each with their function and location., synovial joint).netVasculature of the Heart - TeachMeAnatomyteachmeanatomy.Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports food. Phanerogams are also called “flowering plants. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of most blood vessels. Dermal and vascular tissues are complex tissues because they consist of multiple cell types. Phanerogams are divided into three subgroups: monocotyledons, eudicotyledons, and magnoliids.The vascular plants, or tracheophytes, are the dominant and most conspicuous group of land plants.Vascular surgery is a specialty in which the physician deals primarily with diseases of the vascular portion of the cardiovascular system. Histologically the vasculature system is separated .Learn about the primary growth of vascular plants, which involves the elongation of the stems and roots and the formation of primary tissues.Expand/collapse global location.New experimental evidence unlocks a puzzle in vascular tissue engineering.Vascular tissue transports water, minerals, and sugars to different parts of the plant.
Vascular tissue
Vascular system 1: anatomy and physiology | Nursing Timesnursingtimes.These types of vascular plants are flowering plants, and they use photosynthesis to produce their food. When observed under the microscope, xylem tissue has a star-like . The shoot apical meristem produces the three primary meristems: procambium, ground meristem, and protoderm.Distinguish between elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and arterioles on the basis of structure, location, and function ; Describe the basic structure of a capillary bed, from the . Describe the basic structure of a capillary bed, from the .Connective tissue is vascular and thus are rich in blood vessels, except for cartilages and tendons.
There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue . lateral meristematic tissue that produces vascular tissues and increases the thickness of the stem over time. 2) and is considered the innermost layer of the cortex. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. The cells of an epithelium act as . Other organs do not need such a high amount of blood delivery.There are two vascular tissues in the vascular tissue system: xylem for water transport and phloem for transport of photosynthates. They send oxygen and nutrients . Image by Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library (public .This formation of tissues begins with the root apical meristem (RAM). 14: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissues. With the development of the .Distinguish between elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and arterioles on the basis of structure, location, and function.Therefore, to meet this pressing challenge, we designed a highly selective fluorescent probe, DCI-Cou-polar, which used the ICT mechanism to differentiate normal .The three organs differ in the distribution of vascular tissue: in roots it occurs as a single central strand; in stems, the vascular tissue occurs as multiple bundles imbedded in ground tissue; and in leaves the vascular . With the development of the vascular system, there appeared leaves to act as large photosynthetic organs, and roots to access water from the ground.

They are somewhat like blood vessels in animals, but plants transport materials using two tissues rather than one. In addition to their primary function of returning blood to the heart, veins may be considered blood reservoirs, since systemic veins contain approximately 64 percent of the blood volume at any given time (Figure 20.
Xylem and Phloem
Surface epithelium consists of one or more cell layers, stacked over a thin basement membrane.2: Structure of Blood Vessels.







