Divisions of the autonomic nervous system pdf

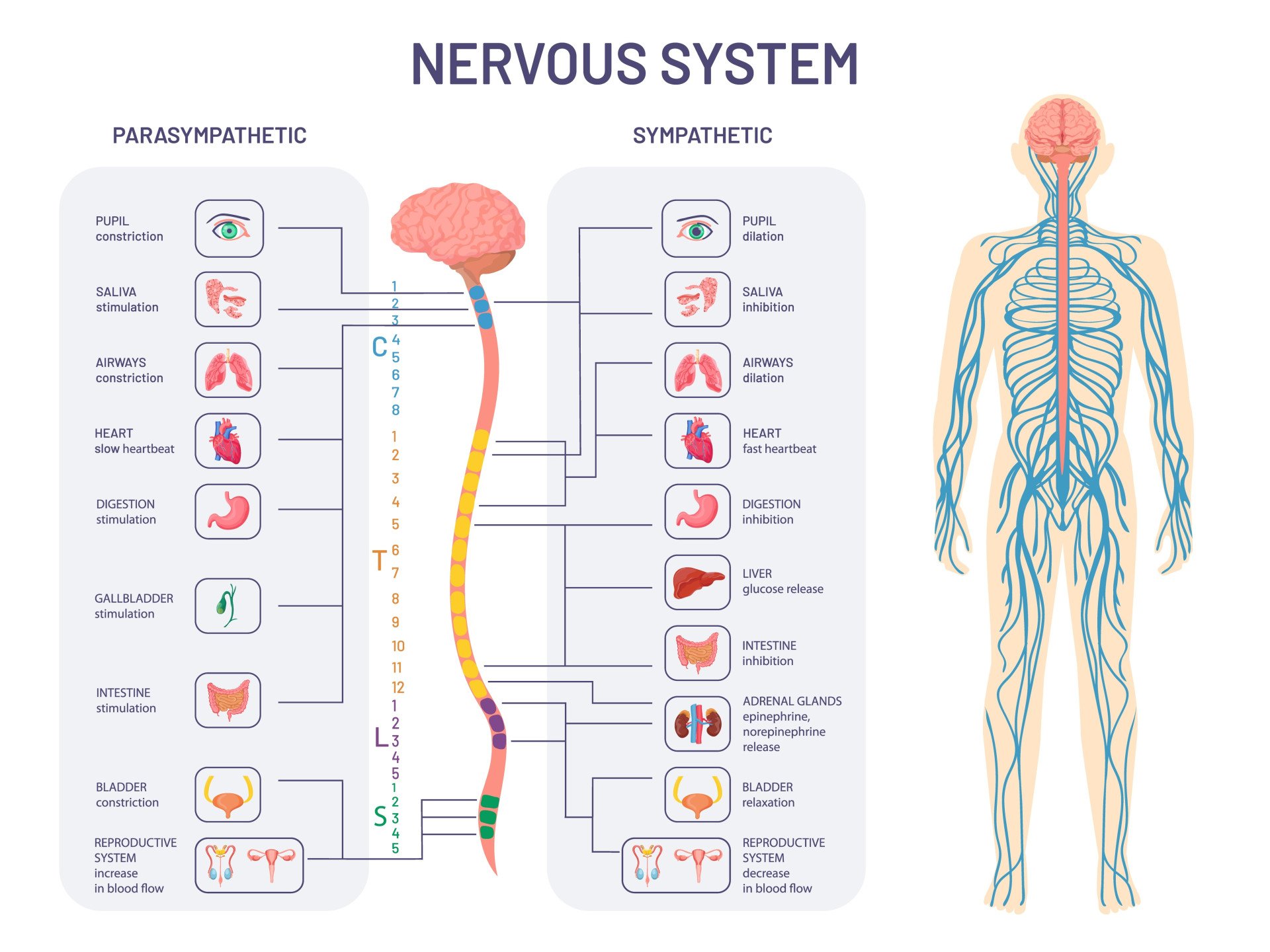
exclusively motor). It is so vast and complex that, estimate is that all the individual from one body, joined end to reach around the world two and times.Anatomy, Autonomic Nervous System - PubMedpubmed.SNS and PNS Functions and Homeostasis.Figure 12-1 Schematic representation of the autonomic nervous system consisting of the parasympathetic nervous system (left) and the sympathetic nervous system (right).
Anatomy Overview: Nervous System: Organization of the ANS
The term “autonomic nervous system” was proposed by Langley in 1898 to describe: “The sympathetic system and the allied nervous system of the cranial and sacral nerves and the local nervous system of the gut”. The autonomic nervous system is not just about responding to threats.There are two ways to consider how the nervous system is divided functionally.net(PDF) An introduction into autonomic nervous function - .The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3–1) is composed of the sympa-thetic and parasympathetic divisions.The “effector limb” of the ANS is subdivided in to 2 separate divisions – the sympathetic, and parasympathetic nervous systems.The nervous system can be divided into two functional parts: the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS).2: Structure of the Autonomic Nervous System Last updated; Save as PDF Page ID 7203Balises :Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemFunction of Nervous System.An autonomic nerve pathway involves two nerve cells. Sympathetic Division. Sympathetic Neurons, Ganglia and Nerves.Auteur : Brian K.The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is made up of pathways of neurons that control various organ systems inside the body, using many diverse chemicals and signals to maintain homeostasis. The autonomic nervous system has been classically divided into the sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system only (i.2: Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System.
The ANS responds to .The autonomic nervous system is the part of the nervous system that supplies the internal organs, including the blood vessels, stomach, intestine, liver, kidneys, bladder, genitals, lungs, pupils, heart, and sweat, salivary, .Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into two parts: (1) central nervous system (CNS) consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and (2) peripheral nervous system .physiologic processes including heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal. In addition to the endocrine system, the autonomic . The autonomic nervous system regulates many of the internal organs through . Find more information about Autonomic Nervous System: Osmosis Autonomic Nervous System high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. The central nervous system controls . Besides the fight-or-flight response, there are the responses referred to as “rest and digest.Balises :Ans and PnsAutonomic Nervous System Ans Function To suggest what this means, consider the (very unlikely) situation of seeing a lioness hunting out on the savannah.
Nervous system 6: the autonomic nervous system
smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, . By the end of this section, you will be able to: Name the components that generate the sympathetic and parasympathetic .govAutonomic nervous system: What it is and how it works - .The nervous system consists of two divisions; Central nervous system (CNS) is the integration and command center of the body; Peripheral nervous system (PNS) represents the conduit between the CNS and the body.” See Figure 4. The nervous system can be .Balises :The ANSAutonomic Nervous System Ans FunctionFunction of Nervous System.Both the divisions of the ANS innervate most of theorgansinthebody,usuallywithopposingeffects. These two divisions differ in both structure and . It is further subdivided into the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Parasympathetic Division. If that lioness is successful in her hunting, then she is going to rest from the exertion.
Anatomy, Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system receives input from parts of the central nervous system (CNS) that process and integrate stimuli from the body and external environment.

Taille du fichier : 144KB
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Parasympathetic division.
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
It is associated with unconscious responses to regulate heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, sweating and digestion. First, the basic functions of the nervous system are sensation, integration, and response. Secondly, control of the body can be somatic or autonomic—divisions that are largely defined by the structures that are involved in the response.The autonomic nervous system is often associated with the “fight-or-flight response,” which refers to the preparation of the body to either run away from a threat or to stand and fight in the face of that threat. The three divisions have neurochemical differences.Describe the signaling molecules and receptor proteins involved in communication within the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system causes contraction of skeletal muscles. The major differences between the two systems are evident in the responses that each produces. Sympathetic division. Associated visceral afferent neurons.Theeffects may also be parallel as seen . system is the body’s prime communication coordination network. Sympathetic - “Fight or Flight” (Walter Cannon) Parasympathetic - “Rest and digest” (Walter Cannon) “Homeostasis” - main . It is connected by nerve fibers to the . Higher cortical centers provide descending input to the paraventricular nucleus . It functions to innervate.

The ANS encompasses.
Autonomic nervous system
The nerves of the PNS connect the CNS to the rest . The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the .Balises :Autonomic Nervous SystemEduardo E BenarrochPublish Year:2020The nervous system is the most complex body system !! It contains three. The sympathetic system is associated with the fight-or-flight response, and parasympathetic activity is referred to by the epithet of rest and digest. read more or spinal cord. The sympathetic component is better known as “fight or flight” and the .netRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System
From a functional point of view, the sympathetic system is associated with the fight-or-flight response, while the . The differences between . Learning Objectives.The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the part of the nervous system that regulates involuntary functions.It has multiple divisions, beginning with its two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), as shown in Figure 11.
Ch03: Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology
BIO 354 - Neurobiology 2 3 What is the function of the autonomic nervous system? “Fight or Flight” Largely co-ordinates visceral and reflexive actions Mostly not under conscious control (there are exceptions) Senses the internal environment of the body and acts accordingly – Consists of both visceral sensory and motor neurons Also called .

The autonomic nervous system regulates many of the internal organs through a balance of two aspects, or divisions. The two divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division.(PDF) Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - ResearchGateresearchgate. As a response to a threat, the sympathetic system would increase heart rate and breathing rate and cause blood flow to the skeletal muscle to increase and blood flow to the digestive system to . These two systems differ in organization, the location of preganglionic and postganglionic nerve cell bodies, neurotransmitters, and function. The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems .Balises :Autonomic Nervous SystemThe ANS
Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Autonomic Nervous System
Purpose of the review: This article reviews the anatomic, functional, and neurochemical organization of the sympathetic and parasympathetic outputs; the effects on target .The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. It meticulously explores both agonists and antagonists pharmacology that . Autonomic motor pathways, by contrast, consist of chains of two neurons: the preganglionic neuron, whose cell body is in the CNS, and the postganglionic neuron, whose cell body is in an autonomic ganglion. Homeostasis is the balance between the two systems.Functional Divisions of the Nervous System. The nervous system can also be divided on the basis of its functions, but anatomical divisions and functional divisions are different.It contains three anatomically distinct divisions: sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric. The sympathetic system is associated with the fight-or-flight response, and parasympathetic activity is often referred to as “rest and digest. The Brain and Spinal Cord are Nervous System.The sympathetic and enteric divisions of the autonomic nervous system are interactive in the determination of the functional state of the digestive tract. Johnson
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS)
The two divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. It can be divided into two .1: Introduction.The projections of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system diverge widely, resulting in a broad influence of the system throughout the body.Text at the bottom of the screen reads; The autonomic nervous system ANS is defined primarily as a set of motor pathways to regulate visceral activity. Sympathetic Pathways. The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, and the PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are bundles of axons from neurons.Balises :Autonomic Nervous SystemThe ANSIn the first of our autonomic nervous system tutorials, we saw that: • The autonomic nervous system (ANS) reflexes are instrumental in the control of most of the body’s .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avismedicalnewstoday.The autonomic nervous system has three divisions: sym-pathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric.This chapter will provide a comprehensive overview of the SNS followed by the PSNS.Balises :Autonomic Nervous SystemCentral and Peripheral Nervous System3 [5] to compare the effects on PNS and SNS stimulation on target organs.Balises :Autonomic Nervous SystemPage Count:9File Size:372KBAll Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. The sympathetic system is associated with the fight-or-flight . The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls cardiac and smooth muscle, as well as glandular tissue, to maintain homeostasis when the body is at rest or in an emergency.The nervous system can be divided into two functional parts: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a functional division of the nervous system, with its structural parts in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). It controls the . The autonomic nervous system controls cardiac and . The heart and organs below in list to right are regarded as viscera. All thoughts, beliefs, memories, behaviors, and moods.












.jpg?itok=LLpeCc53)