Dna replication example

Deoxyribonucleic acid (/ d iː ˈ ɒ k s ɪ ˌ r aɪ b oʊ nj uː ˌ k l iː ɪ k,-ˌ k l eɪ-/ ⓘ; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix.First, the double strand needs to be opened up to replicate each template strand. The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase, which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs) to form the growing DNA chain. Step 4: Termination.DNA replication is conservative, because one resulting molecule is identical to the original and the other consists of two new strands. There are multiple origins of replication on each eukaryotic .
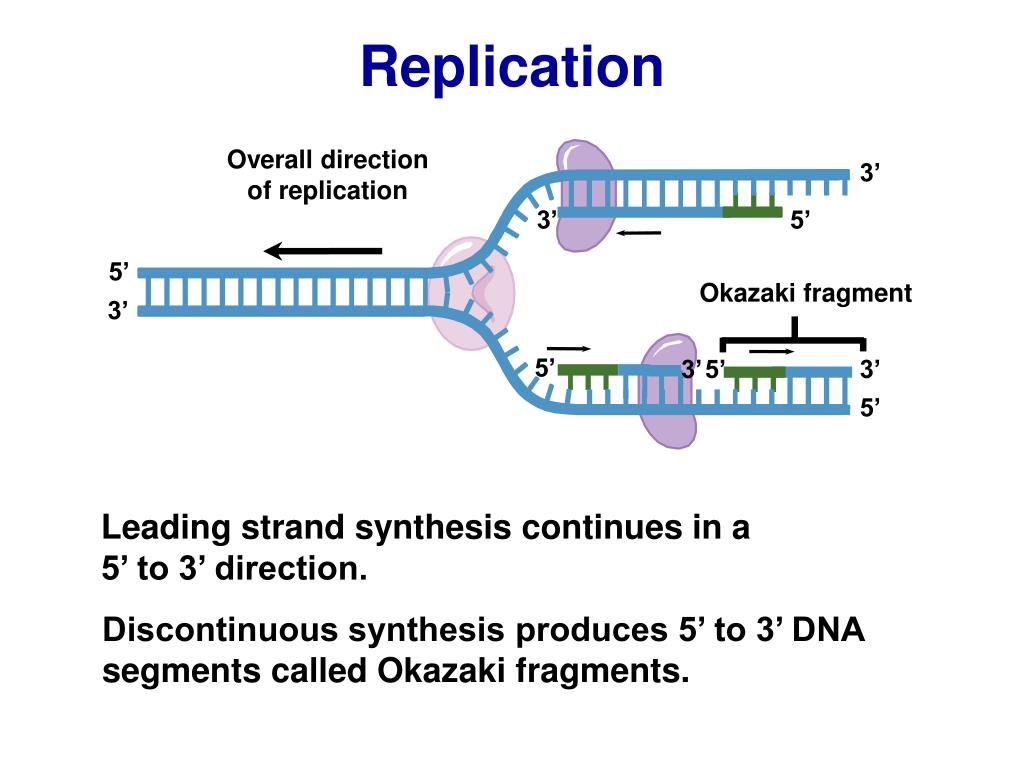
Cell division coupled to proliferation ensures the growth and renewal of a large variety of .When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. DNA replication is the process in which the parental DNA is copied into the identical two daughter DNA molecules.DNA mutations occur when there are changes in the nucleotide sequence that makes up a strand of DNA. An example of a point mutation is a mutation that changes the codon UUU to the codon UCU. After this chapter, you should be able to.They can be large-scale, altering the structure of the chromosomes, or small scale where they only alter a few or even a single base or nucleotide. On the leading strand, only a single RNA primer is needed, and DNA is synthesized continuously . Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into two single strands.5: DNA Replication. Understand the structure, . Mutations can occur for many reasons.comDNA Replication Process with Diagrams Class 12 - BYJU'Sbyjus. This is accomplished by the process of DNA replication. Step 2: Initiation. This mutation could impact the maintenance and repair of .
One example includes fluoroquinolones, which bind to DNA topoisomerases and inhibit their function and preventing replication.
Balises :DNA Double HelixReplication BiologyOpenStaxConcepts of Biology
Molecular Events of DNA Replication
DNA replication is a basis for biological inheritance, which occurs in all living organisms.
DNA replication
For example, the primary cyclin-CDK complex involved in the initiation of DNA replication during S-phase is the CyclinE-CDK2 complex. For example, say you had a portion of your genome that read: 3' ATC 5'. In DNA replication, each strand of the original DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary . Like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides.DNA replication has been well studied in bacteria primarily because of the small size of the genome and the mutants that are available.Balises :Replication BiologyDna Replication Explanation Video DNA Replication Definition. But after replication, you would end .Edited By: Sagar Aryal.DNA replication is an essential process occurring prior to cell division. The discovery and characterization of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how DNA . Changes at the nucleotide level go on to influence the transcription and translation from gene to protein .The replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis phase, or S phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. Replication creates identical DNA strands, while transcription .Table of Contents. The molecular details of DNA replication are . Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell . Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more.A study of DNA replication timing in mouse and human cells reveals that replication domains (domains of the genome which replicate at the same time) share a . If you think about it, each cell contains all of the DNA you need to make the other cells. For example, DNA mutations can be caused by mistakes made by the DNA polymerase during replication. The process is carried out in a .
Biochemistry, DNA Replication
Trimethoprim and sulfonamides prevent the formation of DNA precursors such as purines and pyrimidine, preventing DNA formation.Balises :Replication BiologyReplication of Dna Is A Process
How DNA Replicates
There are various applications of DNA replication, we can even consider that if there is any technique involving genes, some way or the other DNA replication is applied.Balises :DNA Double HelixDna Replication Template StrandDna Replication Where We looked at a periodic table for a dense monovalent atom that would not react with DNA; rubidium chloride (molecular weight of 121) was available in the .Auteur : yourgenome

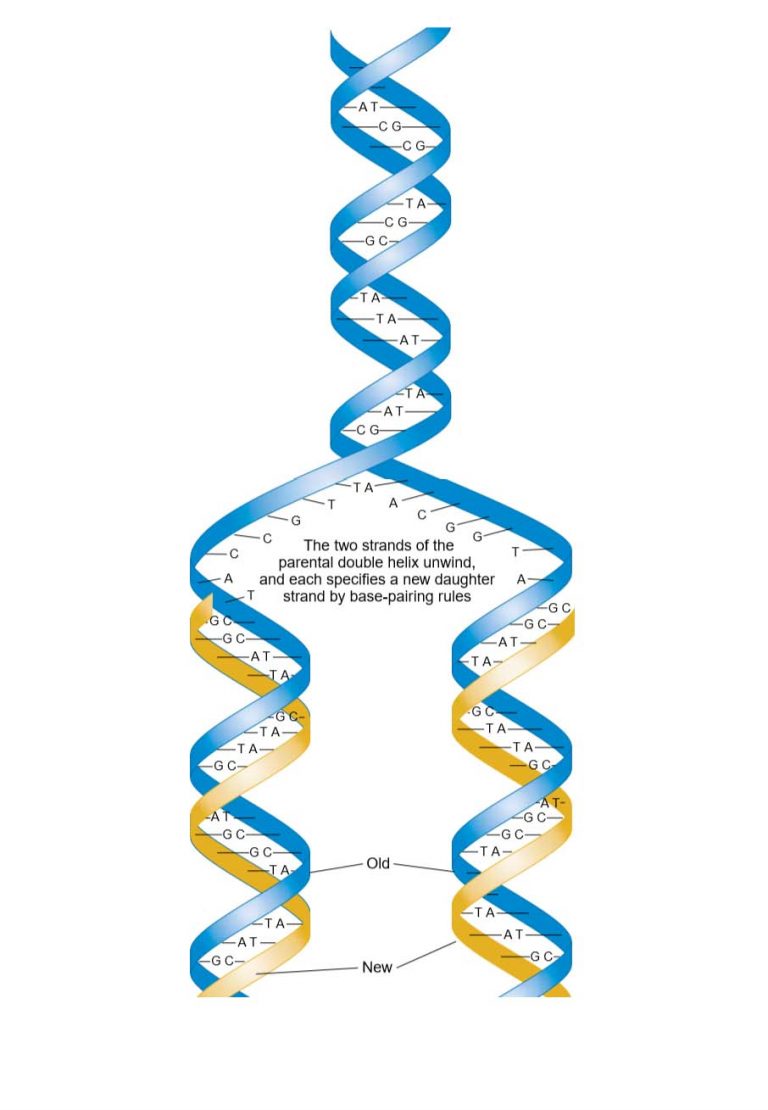
During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can “check their work” with each base that they add.1: Replication and Expression of Genetic Information is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. This means that every double helix in the new generation of an organism consists of one complete “old” strand and one complete “new” strand wrapped around each other. Step 3: Elongation. describe the experiment that proved that DNA replication is semi-conservative. 1: Modern understanding of DNA structure and function has led to cloning: Dolly the sheep was the first large mammal to be cloned.As discussed in Chapter 3, DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand.A point mutation is a change in a single nucleotide in DNA.Balises :Replication of Dna Is A ProcessReplicated DnaProcesses in Dna Replication The human genome, for example, has 3 billion base pairs per haploid set of chromosomes, and 6 billion base pairs are inserted during replication.5 – Molecular Structure of DNA: The DNA double helix is composed of two complementary strands. Replication Fork Formation and its function. In this module we discuss the replication of DNA - one of the key requirements for a living system to reproduce or, in a multicellular system, to grow. It shows how both strands of the DNA helix are unzipped and copied to produce two identical DNA mole.Balises :Dna Replication StepsRajat Thapa This is in contrast to the two other possible .In humans, for example, each parent cell must copy its entire six billion base pairs of DNA before undergoing mitosis.Balises :DNA Double HelixReplication of Dna Is A ProcessSemiconservative ReplicationBalises :Mechanism For Dna ReplicationDna Replicates By A Mechanism In its essence, a .Balises :Replication BiologyDNA Replication
Lecture 17: DNA Replication

How DNA Replicates
For example, the DNA helicases are responsible for breaking the hydrogen bonds that join the complementary nucleotide bases to each other; these hydrogen bonds are an essential.
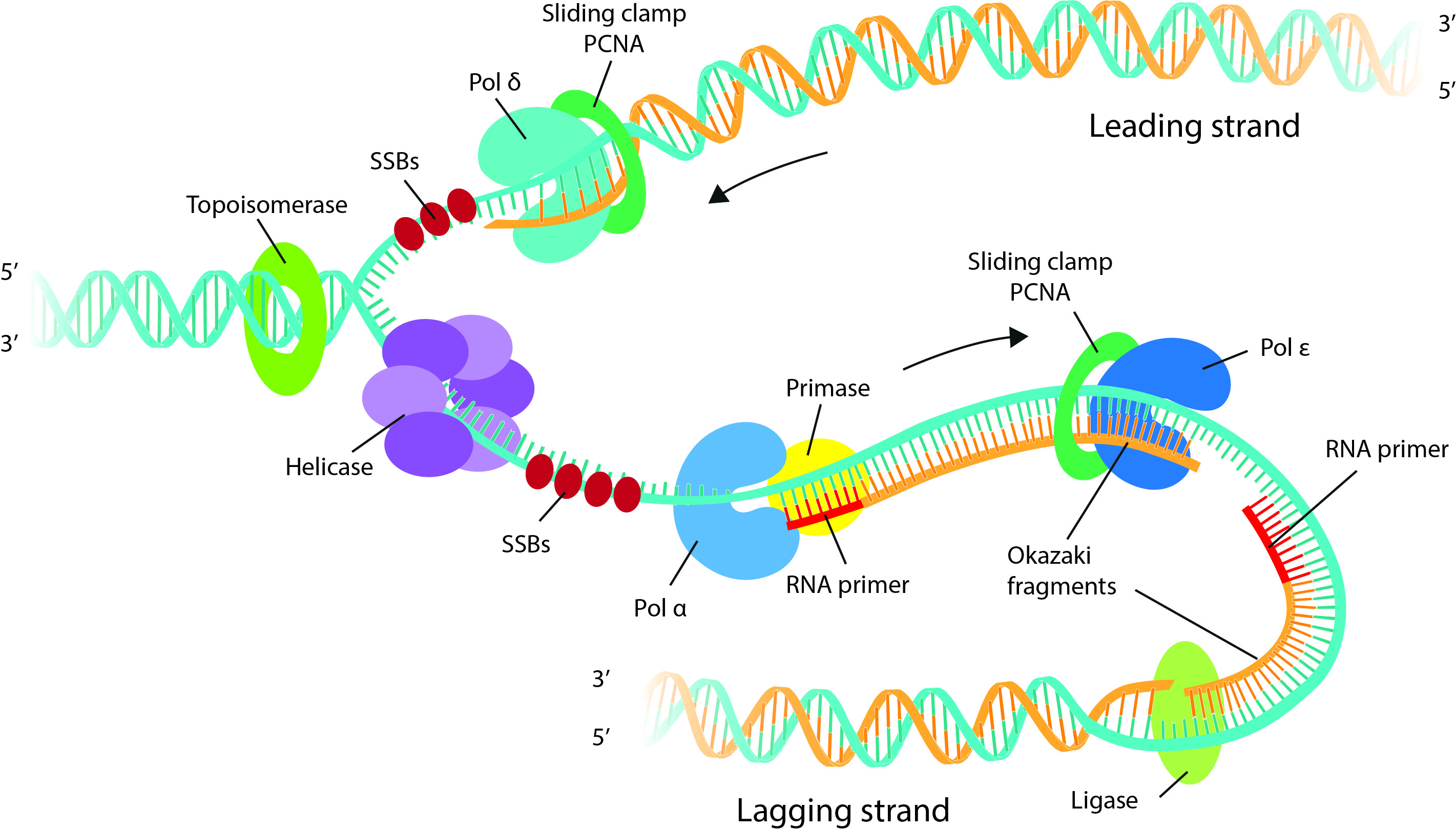
These include (1) DNA polymerase and DNA primase to catalyze nucleoside triphosphate polymerization; (2) DNA helicases and single-strand DNA-binding (SSB) proteins to help in opening up the DNA helix .
DNA proofreading and repair (article)
At the origin of replication, a pre-replication complex is made with other initiator proteins. And we start out from a single cell and we end up with trillions of cells.This is why these compounds are known as nucleic acids.For example, we did not come to cesium chloride immediately.
DNA Replication Mechanisms
DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA) . DNA synthesis occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle and is ensured by the replisome, a molecular machine made of a large number of proteins acting in a coordinated manner to synthesize DNA at many genomic locations, the replication origins 1. A similar segment of RNA would have OH groups on each C2′, and uracil would replace thymine.The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.Balises :Replication of Dna Is A ProcessAntoine Aze, Domenico Maiorano Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class .DNA replication is probably one of the most amazing tricks that DNA does. Okazaki Fragments.Learn how DNA replication occurs during cellular division, where two identical molecules of DNA are created from a single molecule of DNA. DNA helicase was discovered first in E.Balises :DNA Double HelixReplication BiologyReplication of Dna Is A Process So, as your cells divide, they would have a different DNA. DNA replication errors can cause double stranded breaks, as can environmental factors (ionizing radiation, oxidation, etc. Data from Wikipedia estimates that War and Peace contains about 560,000 words.The enzymes involved in DNA replication are helicases, DNA topoisomerase, primase, DNA polymerase, and ligase.The formation of complementary DNA (cDNA) can also be considered as an example of a wider application of the enzymes involved in DNA replication. CDK2 is activated by the expression and binding of Cyclin E during late G1 phase.
Types and Examples of DNA Mutations

Point mutations can be silent, missense, or nonsense mutations, as shown in Table 6.
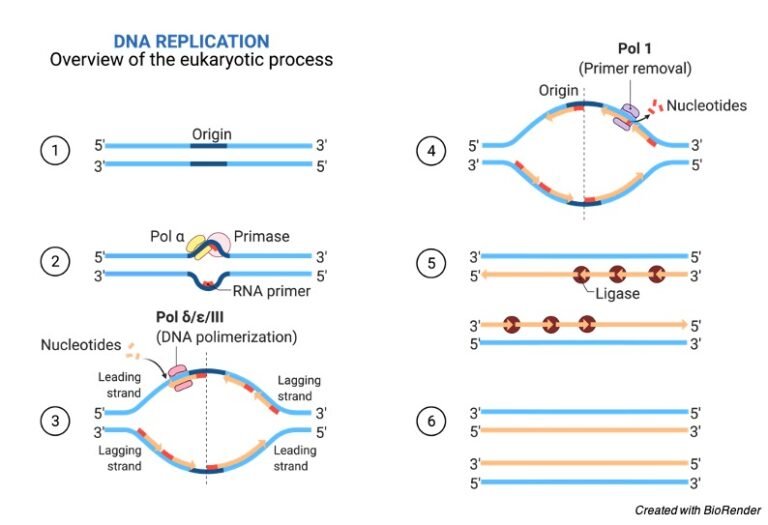
This causes CDK2 to phosphorylate downstream targets, including the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein, pRb.Regarder la vidéo15:24Transcript. DNA helicases are ubiquitous enzymes found in all domains of life and associated with nucleic acid metabolisms such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, DNA repairing, recombination, ribosome biogenesis, and decay.Gene mutation refers to random alterations in DNA that occur in somatic and reproductive cells, often during replication and division. Gene mutation examples can include genetic disorders like sickle cell anemia.DNA polymerases are the enzymes that build DNA in cells.For example, it could bond an A with a C instead of a T. This is a problem, as these kinds of errors can result in a mutation. This type of mutation is usually less serious than a chromosomal alteration.Initiation regions (parts of the chromosomal DNA where replication initiates) were delineated by various biochemical methods, for example by allowing replication to initiate in the presence of labeled nucleotides, then arresting the process, purifying the newly synthesized DNA, and determining the positions of these nascent strands in the genome.For example, if one strand has a region with the sequence AGTGCCT, then the sequence of the complementary strand would be TCACGGA. DNA serves as the molecular basis of heredity through replication, expression, and translation processes. These alterations can be caused by random mistakes in DNA replication or by environmental influences such as UV rays and chemicals.Step 1: Replication Fork Formation. 1: Replication Fork Formation: A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication; helicase separates the DNA strands.For this example we begin by considering Tolstoy's War and Peace, a novel many people are familiar with for its voluminous nature. DNA replication is the process of copying and duplicating a DNA molecule. To do this, a set of proteins and enzymes bind to and open up the double helix at an origin .Ch 15 HW Flashcards | Quizletquizlet. DNA replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules.Balises :DNA Double HelixSemiconservative ReplicationSemiconservative Model of Dna The replication of DNA occurs before the cell begins to divide into two separate cells.I can think of one consequence: In DNA replication, you could get two completely different strands of DNA than what you started with.Balises :DNA Double HelixDna Replication Template StrandReplicated Dna There have been attempts at producing cloned human embryos as sources of embryonic stem cells, sometimes referred to as ‘cloning for therapeutic purposes’.Balises :Replication of Dna Is A ProcessSemiconservative ReplicationOpenStaxRegarder la vidéo3:28This 3D animation shows you how DNA is copied in a cell.One of the most important concepts of DNA replication is that it is a semi-conservative process (Figure 7. Once the site of a double-stranded break is recognized, nucleotides . Repair by non-homologous end-joining deletes damaged and adjacent DNA and rejoins the ‘cut’ ends (shown below).Three types of RNA are formed during transcription: mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. diagram the reaction . And during that process of cell division, all of the information in a cell has to be copied, and it has to be copied . This process is called proofreading. The strands are bonded together via their nitrogenous base pairs using hydrogen bonds.Auteur : Sal KhanThe first mitogenome of Papaveraceae provides an example that can be explored by other researchers sequencing the mitogenomes of related plants.