Dna strand sequence example
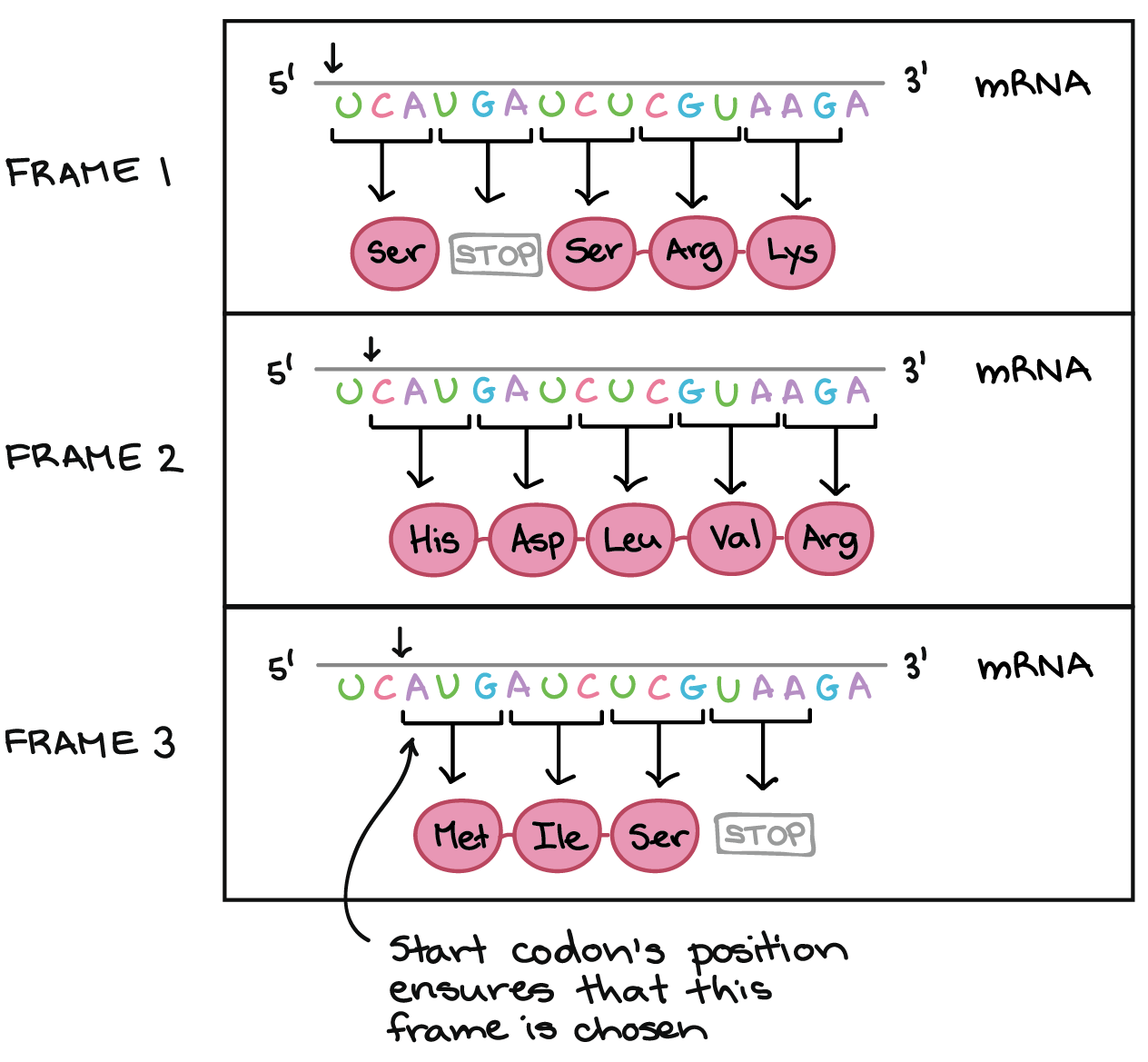
Translation: the process of using RNA to synthesize a sequence of amino acids to form a polypeptide (or protein) Figure 2. This classic paper proposes that the precise sequence of DNA nucleotides is the code which carries genetic information, and that each strand of the DNA double helix can serve as a template to create a new copy, thus allowing the .The DNA template is used by RNA polymerase to produce a strand of RNA with a nucleotide sequence that is the same as the coding strand for the . The segment of DNA you built is the origin of replication. Sanger sequencing, also known as chain-termination sequencing, refers to a method of DNA sequencing developed by Frederick Sanger in 1977. This animation describes the general structure of DNA: two strands of nucleotides that pair in a predictable way.To determine the overall anti-codon sequence that will match a strand of mRNA, simply retranscribe the RNA sequence; in other words, write out the complementary bases. The animation untwists the double helix to show DNA as two parallel strands.The genetic code is a sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA and RNA that code for the production of specific amino acids.This page titled 15. In their seminal 1953 paper, Watson and Crick . The most common type is the transition, where one pyrimidine may be substituted by the other, or one purine by the other. For example, let's say you have the following sequence: AAGGGGTGACTCTAGTTTAATATA.
DNA Is a Structure That Encodes Biological Information
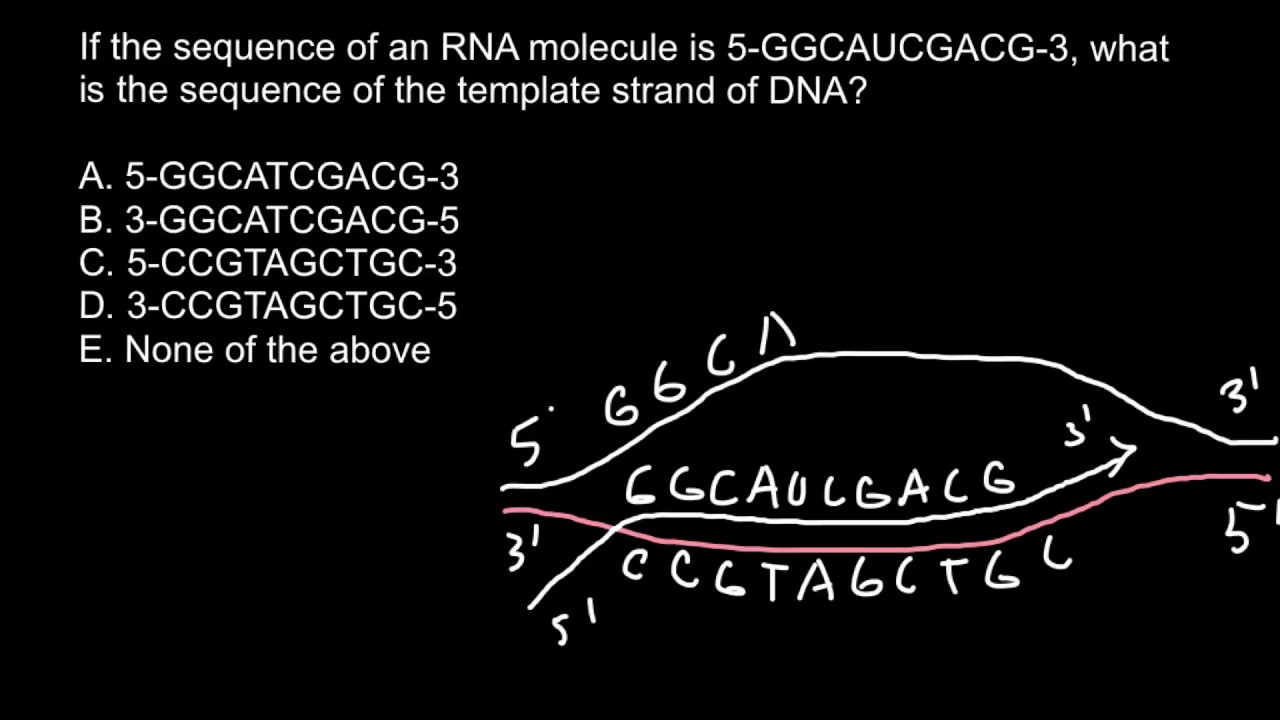
RNA sequencing came first, when Robert Holley sequenced a tRNA in 1965. For example, [ x 1 x n ]. Using the complementary base pairing rules, you can conclude that the complementary strand is: .For example, a strand of DNA with a nucleotide sequence of AGTCATGA will have a complementary strand with the sequence TCAGTACT ( Figure 9. 1: ddNTPs (Original-Deyholos-CC:AN) To sequence a DNA fragment, you need many copies of that fragment (Figure 11. RNA polymerase is the main transcription .DNA is made of four types of nucleotides, which are linked covalently into a polynucleotide chain (a DNA strand) with a sugar-phosphate backbone from which the bases (A, C, G, and T) extend.
DNA replicates by separating into two single strands, each of which serves as a template for a new strand.If researchers have a portion of the sequence of DNA for the gene of interest, they can design a DNA probe, a single-stranded DNA fragment that is complementary to part of .Reverse and/or complement DNA sequences.
DNA Strands
Each strand is made up of a sequence of four nucleotides, A, C, G, and T.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Nucleic acid sequence
Include all parts of the DNA molecule.Knowing this rule, you can figure out the complementary strand to a single DNA strand based only on the base pair sequence. If you do not reverse complement the selected sequence (from the upper strand / 5′-3′ strand), you will get another forward primer that starts from the end of your gene of interest (Fig 5).The rules of base pairing tell us that if we can read the sequence of nucleotides on one strand of DNA, we can immediately deduce the complementary sequence on the other strand. The RNA polymerase proceeds to read one strand moving in it's 3'→ 5' direction.
Reverse and/or complement DNA sequences
Each DNA fragment is then immobilized on a bead and amplified by PCR, using primers designed to anneal to the adapters, creating a bead containing many . [ 1 m ] is a gate that binds signals x 1 x n to . For example, the codon UAC (uracil, adenine, and cytosine) . Nature 1953;171:964–967. Break the tRNA sequence you found into . For example, let's say you know the sequence of one DNA strand that is as follows: AAGCTGGTTTTGACGAC. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, .The Steps of Transcription.When referring to DNA transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand [1] [2]) is the DNA strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the RNA .If DNA sequencing is applied to the study of many genes, or even a whole genome, it is considered an example of genomics.Base pairing, A with T and G with C, holds two strands together to form a double helical structure (Figure 1 (b)). DNA is well-known for its double helix structure. Presto-change-o! Since DNA is double-stranded, the strands hold together where the bases pair.In this example, wobble occurs because A has an extra hydrogen atom.3: Hydrogen-bonding between base pairs in the DNA double .
DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article)
Key points: Transcription is the process in which a gene's DNA sequence is copied (transcribed) to make an RNA molecule.Either DNA strand can be a template.
What Is the Complementary Base Pairing Rule?
DNA contains four bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).In this technique, the whole DNA is extracted from the atypical environmental samples followed by amplification of 16S/18S rRNA gene by PCR and separation of the . Google Classroom. This primer is hybridized to the denatured template DNA, and determines where on the template .For example, let’s say you know the sequence of one DNA strand that is as follows: DNA (coding strand): 5’-TTG ACG ACA AGC TGT TTC-3’ Using the complementary base pairing rules, you can conclude that the .biologydictionary. Watch this video to see how either strand of DNA can be used as a template for different genes on the .DNA Sequencing - Definition, Methods & Examples - Biology .During translation, which is the second major step in gene expression, the mRNA is read according to the genetic code, which relates the DNA sequence to the amino acid . It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called . The direct sequencing of tRNAs was possible because tRNAs are small, short nucleic acids, and because many of the bases in .DNA: 3′ AG C C G T A GAA T T 5′ Using this strand of DNA as a template, draw a picture of the complete DNA molecule.
The rules of base pairing explain the phenomenon that whatever the amount of adenine (A) in the DNA of an organism, the amount of thymine (T) is the same (called .
The Structure and Function of DNA
How to sequence DNA.8 The two strands of DNA are complementary, meaning the sequence of bases in one strand can be used to create the correct sequence of bases in the other strand.Build a single strand of DNA with the following structure: 5'-AGCCTG-3' Build the complementary DNA strand to the sequence above and pair it with the DNA molecule you made in step 2. Making proteins from DNA requires a two-step process: Transcription: the process of copying the gene’s DNA into RNA. Now draw a complete picture of the mRNA strand that will be made from this DNA. The specific sequence of a promoter is very important because it determines whether the corresponding gene is transcribed all of the time, some of the .
Manquant :
strand sequence The code is read in triplet sets of nucleotide bases, called codons, that designate specific amino acids.
Substitutions most often arise as errors during DNA replication or repair.Genes contain the instructions a cell needs to make proteins. Genetic implications of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid. Answer questions 1-6 in the Results & Questions section under DNA Replication.A DNA strand is a long, thin molecule. A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C.

netDNA Sequencing: Definition, Methods, Examples | Sciencingsciencing.
How to sequence DNA
The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA.The DNA strands have the opposite orientation: one strand is in the 5′ to 3′ direction with respect to the carbon .
Primer Designing
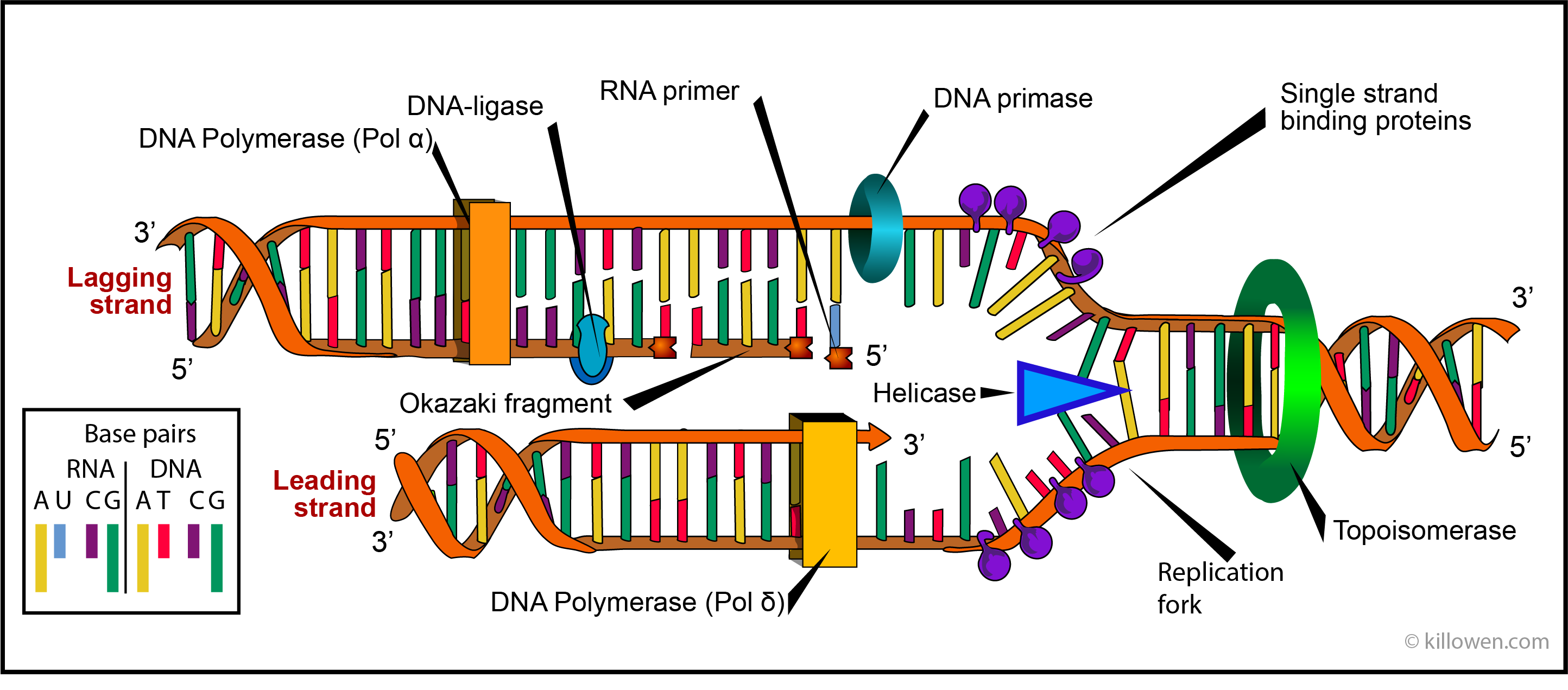
Some 50 different protein transcription factors bind to promoter sites, usually on the 5′ side of the gene to be transcribed. Reverse and/or complement DNA sequences.Learning Objectives.The two strands that compose a double-stranded piece of DNA are antiparallel, meaning they run in opposite directions. Dideoxy sequencing. Amino acids are linked together to form proteins.Let's say you have a DNA sequence of a specific gene on one strand of DNA.DNA strands are polymers or chains of deoxynucleoside monophosphates that are linked together by phosphodiester bonds (Figure 1 (a)).Course: MCAT > Unit 5.In 454 sequencing (pyrosequencing), for example, a DNA sample is fragmented into 400–600-bp single-strand fragments, modified with the addition of DNA adapters to both ends of each fragment. This method is based on amplification of the DNA fragment to be sequenced by DNA polymerase and incorporation of modified nucleotides – specifically, dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs).From these data, the sequence of the newly synthesized DNA strand is determined, as shown above the peaks.DNA sequencing techniques are used to determine the order of nucleotides (A,T,C,G) in a DNA molecule. Triplets are groups of three successive nucleotide bases in DNA. Depending on the promoter, either strand of DNA can be used as the template strand.DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA.The said DNA strand hybridized with its complementary strand i. Recall that DNA .Strand-seq is a single-cell sequencing technology that resolves the individual homologs within a cell by restricting sequence analysis to the DNA template . Unlike PCR, DNA sequencing does not amplify the target sequence and only one primer is used.The DNA sequence onto which the proteins and enzymes involved in transcription bind to initiate the process is called a promoter. A) DNA polymerase binds to a single-stranded DNA template (blue) and synthesizes a complementary strand of DNA (red). Lansdorp, DNA template strand sequencing of single . Using the previously noted mRNA sequence, the tRNA anti-codon sequence is A-A-T-C-G-C -U-U-A-C-G-A. You do not need to draw your molecule with atomic accuracy.That is, whenever an A base occurs in one strand, a T base occurs opposite it in the other strand; when a C base occurs in one, a G occurs in the other (Figure 28. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends of your mRNA . The promoter is the sequence of DNA that encodes the information about where to begin transcription for each gene. This image is linked to the following Scitable pages: DNA Sequencing Technologies Key to . The simplest type of mutation is a substitution of one base for another in the DNA sequence. This complementary base-pairing thus explains why A and T are always found in equal amounts, as are G and C.
The remarkable structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), from the nucleotide up to the chromosome, plays a crucial role in its biological function.

Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Fact Sheet
The new strands are copied by the same principle of hydrogen-bond pairing between bases that .
How to sequence DNA
DNA base substitutions.

Scientists call the two strands of your DNA the coding strand and . In the next round of cell division, the double strand with the C-A pairing would separate during replication, each strand .

DNA is the information molecule. In most cases, promoters exist upstream of the genes they regulate.; An enzyme, an RNA polymerase, binds to the complex of transcription factors.The replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis phase, or S phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis.For example, a strand of DNA with a nucleotide sequence of AGTCATGA will have a complementary strand with the sequence TCAGTACT .The actual coding of the mRNA transcript is very straightforward.Double-stranded DNA consists of two polynucleotides that are arranged such that the nitrogenous bases within one polynucleotide are attached to the nitrogenous bases .